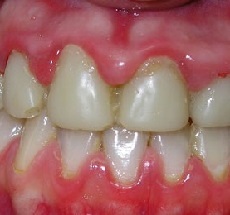
 Hypertrophic gingivitis is a chronic inflammatory process of the gum tissue, which proceeds without disorders of the dentogingival attachment and is accompanied by an increase in the volume of the gum tissue (proliferation). For hypertrophic gingivitis is characterized by the growth of the gingival papillae and the gums themselves, which cover the crowns of the teeth.
Hypertrophic gingivitis is a chronic inflammatory process of the gum tissue, which proceeds without disorders of the dentogingival attachment and is accompanied by an increase in the volume of the gum tissue (proliferation). For hypertrophic gingivitis is characterized by the growth of the gingival papillae and the gums themselves, which cover the crowns of the teeth.
Patients suffering from this form of gingivitis, complain of severe pain, constant bleeding gums and a significant increase in the volume of the gum, which can partially cover the crowns of the teeth from the outside (not from the side of the tongue).
At the same time, the patient's gum remains quite firm and underneath, on the teeth, dental stone is formed, which creates favorable conditions for the reproduction of microorganisms. With hypertrophic gingivitis, teeth can slightly shift.
Causes
Why does hypertrophic gingivitis develop, and what is it? The causes of this form of gingivitis are as follows:
- Endocrine disorders(hormonal changes). Isolate the independent form of gingivitis in young men - "youthful" gingivitis and hypertrophic gingivitis in pregnant women.
- Disturbances in the development of the dento-jaw system: pathology of the occlusion (especially deep incisal overlap), crowding of teeth in the frontal part of the lower jaw, or close arrangement of the teeth, anomalies of the position of the teeth in the arc, etc.
- Hypertrophic focal gingivitisdevelops under the influence of a mechanical trauma (the sharp edge of the destroyed tooth, overhanging edges of the seal, the clasp of the prosthesis, etc.).
Depending on the clinical picture, two forms of hypertrophic lesion of the gingival tissue are distinguished: fibrous and granulating. Each of the forms of the disease is characterized by its symptoms.
Classification
Consider two forms of this pathology:
- Fibrous formhypertrophic gingivitis is characterized by the growth of the gingival papillae, which have a pale pink hue. They have a dense structure and at the same time bleeding. As a rule, patients complain only of non-aesthetics.
- Hypertrophic gingivitis with edematous formis manifested by swelling of the gingival papillae, swelling and cyanosis. The surface of the gums is loose, dents remain when touched, and bleeding may occur when probing. Patients are concerned about pain when chewing and brushing their teeth.
The choice of the method of treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis depends on the form of the course of the disease, the prevailing symptoms, the general health of the patient.
Symptoms of hypertrophic gingivitis
In addition to visually increasing the volume of the gums in hypertrophic gingivitis, especially in its edematic form, there are a number of other symptoms:
- Bleeding and soreness of gums even with light touches, especially during brushing;
- Gums sore during eating, acute pain when eating cold, hot or sour food;
- Difficulties with chewing food because of overgrown gums.
Depending on the degree of irritation of the gums, three degrees of development of hypertrophic gingivitis are distinguished:
- 1 degree - light, gingival papillae cover 1/3 of the tooth;
- 2 degree - medium, the gingival papillae cover up to 1/2 tooth height;
- 3 degree - heavy, gingival papillae cover more than 1/2 of the tooth's height.
When the form is edematous, the gingivitis in a number of cases either partially or completely disappears after the elimination of etiological factors (after the end of the orthodontic treatment, after replacing substandard seals, with the normalization of the hormonal background, after the abolition or replacement of drugs, after childbirth).
In both forms, regular courses of professional hygienic treatment and anti-inflammatory therapy are combined with high-quality personal hygiene of the oral cavity.
Hypertrophic gingivitis: photos
As this ailment looks, we offer detailed photos to view.
Diagnostics
Instrumental examination reveals bleeding gums, mild plaque and the presence of supragingival tartar. Using a periodontal probe, the dental sulcus is examined: as a rule, the integrity of the dentogingival connection is not broken, dentogingival pocket is absent; symptom of bleeding is positive.
For qualitative diagnosis, indices are used:
- hygiene;
- periodontal;
- PMA;
- And:
- the Schiller-Pisarev test;
- biopsy of gum tissue;
- complex examination of gum tissue.
Clinical tests are also important, allowing to identify the signs of gingivitis before the presentation of the patient's complaints, in order to prevent the clinical manifestation of gingivitis. First of all, bleeding when probing the dentogingival sulcus refers to such tests. It should be noted that the morphological signs of inflammation are determined even in the clinically intact gum.
Treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis
To determine the appropriate treatment option, it is necessary to find out the root cause of hypertrophic gingivitis. After determining the etiological factor, the doctor proceeds to the next stage of therapy: conducts professional hygiene of the oral cavity and teeth.
For the treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating therapy is performed. Gum bleeding helps to take vitamin complexes and applications with Vikasol. Apply drugs that have capillary-strengthening properties, as well as drugs that accelerate the regeneration of the gingival tissue.
The granulating form of the disease is treated with cauterizing agents - piozidotherapy and diathermocoagulation. The use of Piotsida is effective for the treatment of gingivitis of the first and second severity. Destructive methods of therapy are not used to treat gingivitis fibrous form. Observations show that wound healing after surface pyocidotherapy lasts 7-10 days, after deep 12-15 days, and ends with the formation of hardly noticeable tender scars.
Unfortunately, hypertrophic gingivitis does not always give in to conservative methods of treatment. In most cases, the third stage remains indifferent to medications, and the specialist has nothing else to do but to remove the pathologically enlarged gingival papillae surgically.
Operative intervention is carried out under local anesthesia (in the absence of indications for general anesthesia) and is called "gingivectomy." The enlarged gingival papillae are excised, leaving only the part that should be in a healthy person.
Prevention
With hypertrophic gingivitis, prevention is reduced to the elimination of chronic mechanical gum injuries, professional hygiene of the oral cavity, proper hygienic care for teeth and gums, solving the patient's dental problems. Very important is the therapy of endocrine diseases, rational selection of medicines.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



