 Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a highly specific human infection from the Papovaviridea family, which has the ability to infect and transform epithelial cells.Identified more than a hundred types of HPV, from which 35 infect the urogenital tract of a person, causing damage to the integumentary epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a highly specific human infection from the Papovaviridea family, which has the ability to infect and transform epithelial cells.Identified more than a hundred types of HPV, from which 35 infect the urogenital tract of a person, causing damage to the integumentary epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs.
The carrier of papillomavirus is every sixth person - this is indicated in the WHO data. Infection caused by the papilloma virus, is a wart (condyloma) and belongs to the group of virus-infectious diseases, which are characterized by the appearance of papillomatous structures on the skin and mucous membrane. HPV is characterized by its chronic form with persistent relapses.
Causes
Why does the human papillomavirus develop, and what is it? Pathogen - a virus that affects the upper layer of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. Transmission of these viruses is possible only from person to person, infection occurs when it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes of a sick person.
Infection with the human papillomavirus can occur:
- During sexual intercourse. According to the International Medical Association, papillomavirus is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases, which is more than 60% of cases.
- At birth. Infection can be transmitted at birth from a mother to a newborn baby, which subsequently is fraught with infection with papillomavirus or a disease of laryngeal papillomatosis.
- With autoinoculation. Self-infection can occur if the elementary rules of hygiene are not observed: epilation or shaving.
- Household way. The human papillomavirus is characterized by increased survivability, and for a long time can be stored in a warm moist environment of public places, such as: toilets, baths, gyms, swimming pools. Infection occurs through various skin lesions directly on contact, using personal care items or in public places.
Different types of HPV cause or are involved in development:
- dysplasia of the cervix (62%);
- pre-invasive and invasive cervical cancer (38%);
- genital warts genital tract, urinary tract (51%);
- 10% of clinically healthy women are carriers of HPV;
- 85% of patients with typical genital warts of the vulva are examined additional foci of HPV infection of the vagina and cervix in a pronounced and malovyrazhennoy forms.
These data allow us to treat patients with papillomavirus infections of the genital tract as a group of high-risk intraepithelial carcinoma of the cervix.
Classification
The following classification applies:
- HPV, the manifestation of which are different types of warts (HPV 1-5):
- Plantar warts (appearance resembles callus), these are 1-4 types of HPV;
- Flat warts, these are 3, 10, 28, 49 types of HPV;
- Ordinary warts, this is the 27th type of HPV.
- HPV, affecting the vulva, vagina, genitalia, cervix and respiratory tract, these are 6, 11, 13, 16, 18, 31, 33, 35 types of HPV.
- HPV, a lesion in the form of rashes is associated with the condition of precancerous disease (HPV of high oncogenic risk), it is HPV 39 and other types.
Apparently, these benign neoplasms can form on any part of the body:
- neck;
- face;
- under the breast;
- in the armpits;
- on the genitals;
- on the mucous membranes of internal organs, oral and nasal cavity.
The need for treatment of human papillomavirus is due to the following fact. Strain is an intracellular parasite that is not capable of self-replicating. For this purpose, he uses the cells of the human body. Parasitize the virus can long enough by introducing its own DNA into the human chromosomes. Its noticeable activation is observed against a background of reduced immunity.
The incubation period
The incubation period is long: from half a month to several years. For papillomavirus infection is characterized by latent (latent) flow. A person can simultaneously become infected with several types of papillomaviruses. Under the influence of various factors, the activation of the virus, its increased reproduction, and the disease passes into the stage of clinical manifestations.
In most cases (up to 90%) within 6-12 months, self-healing occurs, in other cases there is a prolonged chronic recurrent course with possible malignancy of the process (depending on the type of virus).
Symptoms of the human papillomavirus
Human immunity is strong enough to overcome the virus at an early stage of its development. And in most cases, the disease does not develop. However, after some time, several months, years or even decades, people may have some symptoms of infection with the human papillomavirus.
There are several groups of diseases most often caused by HPV:
- Wartsare round, more rigid than the body of the growths from 2 mm to 1 cm in diameter. The boundaries of warts are very clearly delineated, there are warts of irregular shape. They are rough to the touch and can be of different colors. Most often they are formed in places where the skin is most severely damaged: on the hands, knees or elbows.
- Plantar Warts. Develop when infected with viruses 1, 2 types in those places where the shoes are rubbed or pressed on their feet. The skin in the place of the wart becomes thicker, there are no clear boundaries of the warts.
- Genital Warts- a kind of warts that appear, as a rule, on the mucous membranes and skin of the genital organs: the glans penis and skin of the foreskin in men, the skin of the labia in women. They can also appear in the bladder, urethra, on the cervix, in the vagina, on the skin around the anus, in the oral cavity. Outwardly, these genital warts are similar to small convex formations, their edges are uneven (looking like a cauliflower). This disease is caused by human papillomavirus 6 and 11 types.
- Bovenoid papulosis. Small flat plaques-warts (somewhat similar to flat warts) appear around the genitals. It often develops in men who constantly change their sexual partners. Called by types - 16, 18, 31, 33, 42, 48, 51, 54.
Any viral infection that is constantly in the human body (and HPV refers specifically to such), is activated only with a decrease in immunity.
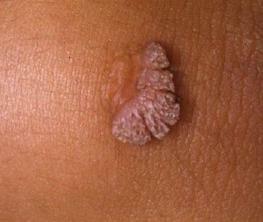
Human papillomavirus: photos
To find out what the human papilloma virus looks like in various manifestations, we have prepared a compilation with a photo.
Symptoms of human papillomavirus in women
Infection can take place in a latent form, and can cause the development of genital papillomas. Genital warts are observed mainly in women aged 15 to 30 years.
The main risk of developing the disease caused by types 16 and 18 is the development of cervical cancer. Cervical cancer reduces life expectancy by an average of 26 years. From the point of view of cancer development, only the virus that has been in the body for more than a year becomes dangerous.
Unfortunately, these diseases in women often occur asymptomatically up to the last stages, at which the effectiveness of treatment is significantly reduced.
Symptoms of human papillomavirus in men
For men, the human papillomavirus is less dangerous than for women. Most often they are passive carriers. The likelihood of developing cancer is much less.
HPV in men can cause the appearance of genital warts on the foreskin, glans penis or frenulum. Such formations must be urgently removed, because they prevent not only the observance of personal hygiene, but also the management of sexual life.
Prevention
We list the main areas of prevention of human papillomavirus infection:
- measures of personal hygiene in public places;
- a healthy lifestyle that supports immunity at a high level;
- correct mode of work and rest;
- moderate physical training;
- reception of vitamins, fruits, juices;
- only one sexual partner (ideally);
- use of a condom during sexual intercourse.
Currently, there are vaccinations against human papillomavirus: Gardasil and Cervarix. The vaccine Gardasil is effective against HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18 (it protects against cervical cancer and genital warts), and the Cervarix vaccine is effective against HPV 16 and 18 types (it protects against cervical cancer, but not from genital warts).
Treatment of human papillomavirus
Currently, there is no antiviral drug that would cause the disappearance of the human papillomavirus from the body.
Various interferons (reaferon, tsikloferon and others) and interferonogens (poludan, prodigiozan and others) can reduce already existing condylomas, but do not reduce the incidence of new ones. Therefore, the main way to treat the human papillomavirus virus remains the removal of condylomas by chemical or surgical methods.
Here are the main methods of removing papilloma tissues:
- Radiosurgical. The radio wave electrode cuts off the tumor, coagulates the vessels. Then an antiseptic dressing is required.
- Laser. Non-contact and bloodless method. On the site of the removed papilloma there is a crust under which healing takes place. Cons - the risk of recurrence, high cost, the need to grind the remaining scars.
- Electrocoagulation. By efficiency, result and prices, the method is similar to the two previous methods.
- Surgical. This is an operation under local anesthesia.
Before starting treatment, be sure to ask your doctor:
- What treatment methods are available in the clinic where you undergo treatment?
- How much does each treatment cost and what are the possible complications?
- Will the operation be painful?
It should be emphasized that removal of papillomas should not be considered a complete cure for papillomavirus infection, since in this case, a person does not cease to be a virus carrier, that is, within a few years papillary polyps may appear again. That is why, for the purpose of prevention, doctors are recommended to carry out recovery of the whole organism as a whole.
Cryocoagulation
Cryocoagulation (moxibustion with liquid nitrogen) is a quick and effective method of treating genital warts. The procedure may be slightly painful and unpleasant, however this rarely worries patients very much.
Cryocoagulation of the condyloma is carried out in several sessions for several weeks. Complete elimination of genital warts is observed in 75-80% of patients who underwent all procedures.
Advice to patients
Do not try to diagnose and treat the human papillomavirus itself.
- First, you need to choose the right method.
- Secondly, there is always a risk of confusing pointed condyloma with a malignant tumor.
Better not risk and trust your health professionals - this will ensure you a long and happy sex life. Sexual life during the treatment of papillomavirus is stopped until complete recovery. It is necessary to examine and, if necessary, treat a partner.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
