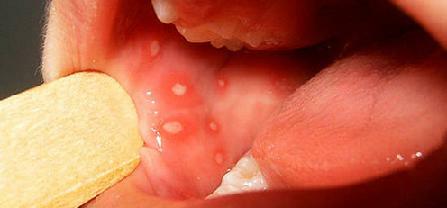
Cough with phlegm: what and how to treat if there is no temperature
If adults have a persistent dry or wet cough, this condition indicates a loss of airway, which causes this or that disease.
Such a symptom is a kind of self-defense of the body and is caused when foreign particles appear in the respiratory organs, for example, it can be green sputum when coughing.
Often with catarrhal diseases, there is a cough with sputum, which coughs up. Sputum is a viscous thick liquid that is produced by the mucous membrane.
Its basis is water with glycoproteins, lipids and immunoglobulins. Depending on the composition, the foamy consistency can have a different color, which varies from pale yellow to green and brown. From coughing with obvious phlegm, expectoration occurs, and microbes and accumulated toxins are removed from the respiratory tract.
In most cases, dry cough is transformed into a wet cough with phlegm, which is expectorated. The most common reason that provokes it is smoking.During smoking, a large amount of mucus accumulates in the airways, which leads to a strong cough with phlegm.
Also smoking paralyzes the thin hairs that are in the airways, because of which expectoration is greatly complicated.
Causes and types of phlegm on coughing
Cough without fever can cause a variety of diseases. One of the reasons for the appearance of symptoms is the development of asthma. At the initial stage of the disease, the patient feels slight hoarseness and a dry cough with hard-to-recover sputum. After a while the wheezing becomes strong and a strong cough with sputum appears. In this case, a thick foamy mucus may form in the form of precipitates.
In addition, it can be noted:
- Another cause may be chronic bronchitis. A similar disease with chronic blocking of the airways causes a dry cough that gradually passes into a cough without temperature. In this liquid consistency can contain salty purulent mucus brown.
- Cough with yellow sputum often occurs as a result of the appearance of a common cold. In this case, the color of sputum during a cough may change, as pus accumulates in it.
- Mucus in large quantities in the way of breathing accumulates if there is an inhalation of dust, smoke and other irritants that provoke a cough with phlegm.
Often, these symptoms are observed with an allergic reaction or chronic sinusitis. A green liquid consistency when coughing is observed if the disease has become chronic.
A severe cough and with phlegm can also report the presence of such a serious disease as lung cancer. Therefore, it is worthwhile to be alerted if bloody veins are found in the consistency. Also, mucus may contain purulent clusters.
If the dry cough has flowed smoothly into a cough with phlegm, this can be a signal of the development of pneumonia. Yellow or gray salted phlegm in turn changes color due to the activity of bacteria present in it.
Yellow sputum when coughing
The appearance of yellow sputum may indicate that the patient develops bronchitis, pneumonia or sinusitis. In the event that a cough with sheer yellow sputum appears unexpectedly and abruptly, you should immediately consult a doctor to begin treatment as soon as possible.Especially dangerous if the mucus contains purulent or blood clots. The yellow color appears, as a rule, when the main consistency is mixed with pus.
To accurately diagnose the disease and prescribe the right treatment, the doctor prescribes sputum analysis, which is collected in a special jar. The procedure is performed in the morning on an empty stomach, before that the oral cavity is rinsed with a weak antiseptic solution.
Also purulent sputum can be yellow with frequent smoking. With bronchitis, the color of the liquid consistency can reveal the cause of the disease and the presence of bacteria in the body.
Treatment is prescribed only after careful examination and clarification of the exact diagnosis.
White sputum
White sputum curd consistency indicates the presence of respiratory tract fungus infection or tuberculosis. Fungi can affect the bronchi as a result of prolonged antibiotic treatment with reduced immunity. This leads to the appearance of a pathogenic microflora on the mucosa. In the case of tuberculosis, mucus is usually released in small amounts.
If white spots are found in the white sputum, the doctor can diagnose a pulmonary complication due to damage during the coughing of the laryngeal vessels. A white, watery consistency may be caused by external stimuli, a viral infection or diseases of the respiratory organs.
Transparent sputum indicates that the inflammatory process is absent. A thick and transparent consistency can indicate that lung inflammation, bronchitis, allergies, asthma or colds develop.
With a constant increase in the amount of mucus and sputum, the patient is poisoned, so it is important to start treatment on time to prevent congestion in the bronchi.
Cough and blood
Bloody splotches in the sputum when coughing report a respiratory disease. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help in order to identify the causes and start the necessary treatment.
When the reasons lie in the development of lung cancer, the blood in the sputum is in the form of veins. Including a cough with blood can be caused by bronchitis, in this case you can find small scarlet veins in a small amount.
If the causes are the development of pneumonia, fresh cords of blood will appear from the cough with sputum. From what caused the painful symptoms, it will depend on what treatment the doctor will prescribe.
A protracted cough
Prolonged is a cough that lasts more than four to eight weeks, with a positive dynamics to recovery is not observed. This condition is a very disturbing symptom that reports a serious illness.Before the treatment begins, the doctor prescribes the X-ray of the lungs to exclude cancer. The reasons for this state of the patient can be reduced to the presence of inflammation, bronchial asthma, tuberculosis. A prolonged cough may also occur in heavy smokers with prolonged bronchitis. Such a disease is considered chronic and it is difficult to cure it.
A prolonged cough is observed in people who, in the nature of their activities, are associated with chemicals. In particular, with constant contact with asbestos, people often develop asbestosis disease.
To get rid of the disease, it is required to change the kind of activity, so as not to contract with the stimulus, there are no other ways to solve such a problem.
The appearance of cough in the morning
Quite often people cough in the morning, and there's nothing to worry about. Thus, they cough up phlegm, which accumulated overnight in the respiratory tract. However, it is important to understand that in healthy people mucus departs in small amounts. If a large amount of sputum is produced, there may be reasons for this.
Most often in the morning, heavy smokers and coughing up mucus inveterate smokers. As you know, a morning cough of a chronic nature signals about tobacco poisoning. If you do not start treatment on time, the symptoms will only increase.
Causes of severe cough in the morning can also be chronic lung disease, tuberculosis. The patient can cough intensely if mucus from the nasal sinuses is stuck in the throat.
Treatment of cough with phlegm
When cough and sputum is caused by acute respiratory viral infection or bronchitis, the accumulated consistency is difficult the physician prescribes treatment with the use of special mucolytics, which dilute sputum. Also, in the case of difficultly separated sputum, expectorants are prescribed.
Many people, worrying about their health, sometimes refuse to take medicine, giving preference to folk remedies. However, it must be borne in mind that such treatments may also have contraindications and cause side effects. Therefore, before starting treatment, you should consult your doctor.
It is also important to understand that mucolytic and antitussive drugs can not be taken at the same time, otherwise the patient's condition will only worsen.
Medicinal products that relieve cough are divided into three main groups:
- Expectorants are prescribed if it is required to treat symptoms of a cold with sparse phlegm.
- Anti-cough medicines are prescribed when it is necessary to treat an unproductive and dry cough.
- Mucolytic drugs are used when it is required to treat symptoms with thick, viscous and difficult to separate sputum.
Coughs of expectorant action
Quickly and effectively cure moist cough Althea's preparations, including Mukaltin, Alteika syrup and Althea's Root, will help. Medicinal expectorant is prescribed if it is necessary to treat acute and chronic pathologies of the respiratory system in the form of bronchitis, emphysema of the lungs, tracheobronchitis. The drug is used for viscous hard to separate sputum.The drug dilutes the consistency, relieves inflammation, stimulates the wave-like contractions of the walls of the bronchi, so that mucus is easily removed from the respiratory tract. However, to treat Althea with symptoms is contraindicated in case of individual sensitivity, ulcer of the duodenum and stomach. Diabetics should also be cautious during treatment.
Preparations based on thermopsis help to cure cold symptoms by irritating the center of breathing, which contributes to expectoration of sputum. This includes pills for coughing Termopsol, Kodelak bronchus with thyme. The medicine has an expectorant, anti-inflammatory and mucolytic effect due to the content in the active elements.
Quickly cure a wet cough is helped by breastfeeding, which includes such medicinal herbs as oregano, mother-and-stepmother, plantain, licorice, sage, anise, marshmallow, pine buds from cough, chamomile, violet, ledum, calendula.
Also, many prefer to treat the symptoms of cold with the help of the Bronchophyte elixir, it contains a rosemary, plantain, anise, licorice, sage, violet, thyme.
Mucolytic drugs for coughing
Mucolytic drugs are prescribed to drink when you need to treat bronchitis. Such preparations dilute sputum, improve its excretion and, thus, break favorable conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic organisms.
Drugs, the active ingredient of which is acetylcysteine, help get rid of severe symptoms in chronic bronchitis. They are also taken with laryngitis, otitis media, pneumonia. These drugs are contraindicated for pulmonary hemorrhage, bronchial asthma, adrenal pathology, hepatic and renal insufficiency.
Bromhexine and its preparations Solvin and Bronchosan are widely used in the conduct of inhalations. The effect of treatment can be seen after only 2 days. With increased viscosity, sputum is prescribed to drink drugs based on carbocisteine, among which medicines such as Fluidite, Fluviert, Bronhobos and Libexin Muno.
An interesting video in this article offers information on how to cure a cough.
stopgripp.ru
Cough with phlegm
Medical specialists apply to such a concept as cough with phlegm, the term "productive." This means that during the coughing episode, the production of bronchial tubes is allocated - mucus secretions, which are excreted with coughing movements outward.
It is believed that such discharge is a sign of purging the pulmonary system, and therefore one of the symptoms of an early recovery. Nevertheless, it should not be forgotten that the presence of mucous secretions may also indicate the development of serious diseases, for example, bronchial asthma, pneumonia, oncology of the respiratory system, ischemic disease heart.
Causes of cough with phlegm
Excretions during expectoration can appear exclusively in respiratory tract diseases, representing the result of increased production and secretion of bronchi (during bronchitis or asthma), the effusion of blood plasma from the vasculature into the pulmonary cavity (during pulmonary edema), the release of pus from the cavities (with abscess, tuberculous caverns, bronchiectasis).
The most common reasons are:
- upper respiratory tract infections (respiratory viral infections and pathologies);
- obstructive form of bronchial inflammation;
- pneumonia;
- allergic conditions, including bronchial asthma;
- rhinitis;
- abscess of the lungs;
- tuberculosis.
The exact reason for triggering a cough reflex can only be determined by a diagnostic method, while Of great importance is the characterization of bronchial secretions, as well as the presence of other associated symptoms.
Is sputum cough phlegm?
Is it contagious if it coughs productively? This question is often of interest to many patients, especially the mothers of small children who doubt about whether it is possible to lead a child into the kindergarten, if the seizures become productive and began to clear slime.
It is worth noting that cough syndrome is contagious regardless of whether it is wet or dry if it is caused by a viral infection. On average, the period of "infectiousness" (in medicine - contagiousness) of a viral disease varies from 5 to 10 days from the time of the onset of the first symptoms. However, some diseases can be dangerous for others for a longer period:
- diphtheria - up to 2 weeks;
- whooping cough - up to 18 days from the onset of the illness. As a rule, after 28 days, the patient who has recovered whooping cough will not be exactly dangerous, even if the coughing trouble continues to bother the patient.
Therefore, it is not entirely correct to believe that if a child has a temperature stabilized and a mucous secret has appeared, then the risk of infecting other children is canceled. The virus often continues to exist in the body and is released by the patient when exhaled and sneezed.
Symptoms of coughing with phlegm
As the symptoms of the disease progress with the accumulation of excretions of the bronchial tree, it becomes necessary to purify the respiratory tract from the accumulated secretion. In this case, a cough reflex works-a call for a sharp exhalation of the air, due to irritation of the bronchial walls with a mucous secretion.
When there is an abundance of mucus, it is important to distinguish the cleansing process from the transition of the inflammatory pathology to the chronic form.
Usually coughing movement originates from a sharp and deep breath, which lasts no more than 2 seconds. After that, the guttural musculature, covering the vocal chink, is also sharply reduced. Bronchial muscles immediately come to tone, the abdominal muscles contract - this action of the muscle fibers is aimed at overcoming the resistance of the closed glottis. At this time, the pressure within the chest cavity is about 100 mm Hg. Art. Then there is a sudden opening of the glottis and an exhaled exhalation. Basically, if the bronchi have accumulated secretions, the cough reflex is triggered involuntarily, but the patient himself is able to trigger it independently.
As a rule, the cough and cramping of the bronchi by itself are not a disease - they are just symptoms of another disease, which is important to detect and cure. Do not ignore other signs that indicate the presence of the disease:
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath;
- temperature increase;
- loss of appetite;
- pain inside the chest;
- wheezing when breathing;
- change in color and other properties of sputum.
Cough with expectoration during pregnancy
In pregnancy, any disease is perceived extremely negatively: still, it is not known how the disease will affect fetus, as well as pregnancy itself, and medications throughout this period should be taken very selectively. However, there is an indisputable fact that in pregnant women immunity is clearly weakened, so ARD with ARVI during gestation, unfortunately, is not uncommon.
Cough syndrome during pregnancy is also often found: it is not only possible to treat it, but it is also necessary. Illiterate or untimely treatment can pose a serious threat to pregnancy. First of all, coughing jerks can provoke an increased tone of the uterus, which can lead to painful spasms and even detachment. At the same time, arterial and intra-abdominal pressure increases, which can provoke miscarriage at early stages or premature birth at later stages of gestation.
When respiratory illnesses, it is necessary to see a doctor, and not only: it will be better if the woman remembers the doctor for any anxious or suspicious symptoms. It should be borne in mind that coughing attacks and mucus secretion from the bronchi can accompany not only a cold, but also diseases of the stomach, thyroid, heart. Do not start treatment yourself, let the medical specialist do it.
Types of phlegm on coughing
Bronchial mucous accumulations are pathological excretions that go out in the process of coughing tremors from the respiratory tract. In healthy people, too, mucus is produced inside the bronchi: this mucus performs a protective function, not allowing dust, chemicals and bacteria to penetrate to the lungs. If the amount of this mucus increases, pus with other impurities is added to it, then it is usually said about the appearance of moist discharge. Allocation is divided into several types, which depends on their number, color, odor, density, multilayeredness.
Let's talk about the types of mucous secretions for respiratory diseases.
- Green sputum when coughing is usually a companion of many inflammatory pathologies involving the bronchi and lungs. Such diseases can be provoked by a bacterial and viral infection, or have an allergic nature. To the listed diseases carry protracted bronchitis, croupous pneumonia, bronchial asthma, tuberculosis, oncology, etc. As a rule, green dense mucus is a sign of a stagnant purulent process in the lungs.
- Cough with hard-to-recover sputum appears most often as a consequence of ARVI or ARI, and can also be the result of stagnant phenomena in the lungs. If the slimy secret has too dense consistency and viscosity, then it is difficult for him to get out of the respiratory pathways, it accumulates inside the bronchi, provoking constant coughing, not bringing relief.
- Blood in sputum when coughing can appear as a result of a small and harmless bleeding from the capillary vessels of the bronchial tree, which could burst during a coughing attack, and due to serious disease. Therefore, the presence of blood should alert, especially if such a sign is present for several days, or if the discharge contains a large amount of blood. Do not forget that the admixture of blood can get to a secret from patients with tonsils, nasopharynx, bleeding gums.
- Yellow sputum when coughing - this is the result of the appearance of pus in the secretions. Most often this is a sign of an incomplete bronchitis, or its transition to a chronic form. If you continue to neglect treatment, then over time, such a secret can change the color from straw-yellow to rusty or green (an obvious sign of a purulent process).
- Cough with purulent sputum often indicates the development of stagnation inside the lungs, especially if the discharge becomes much thicker. Broncham becomes difficult to remove the purulent secret, which accumulates and can acquire an unpleasant smell and taste. As a rule, without therapy with antibiotics in this situation can not do.
- White sputum when coughing is potentially able to appear with inflammation of the lungs. If the white secret is secreted by lumps, or resembles cottage cheese, then this unambiguously means that the causative agent of pneumonia is a fungal infection. In this situation, antibiotics will not help: special anti-fungal therapy will be needed.
- Black sputum when coughing is in most cases a professional sign - such excretions are typical for miners, masons, excavators. To learn more about the presence or absence of the disease, you will have to pass the secret to the analysis.
- Gray sputum when coughing, as well as black, often accompanies respiratory illness in representatives Some professions, whose work is related to the presence in the air and inhalation of a large amount of dust with suspended particles. To the same category carry heavy smokers, inside the respiratory organs which are deposited nicotine gums, giving the secreted secretions a gray tint.
- Pink sputum when coughing is a sign of the presence of a small amount of blood inside the mucus. Most often this is the result of the bleeding of bursting capillaries, which can occur with too aggressive coughing attacks. However, for such pink discharge it is necessary to observe: if they last more than 3 days, or change color to intense red, then you should immediately contact a specialist.
- Red sputum when coughing indicates the appearance of blood in the discharge. This can be considered as hemoptysis in tuberculosis, actinomycosis, oncology of the respiratory system, with abscess, pulmonary infarction, heart failure or pulmonary edema. This condition is considered very dangerous and requires immediate medical attention. In rare cases, redness of the secretion may be caused by taking certain medications.
- Transparent sputum when coughing is the most innocuous kind of mucous secretions. Usually such a sign accompanies the onset of respiratory illnesses, when complications are still absent, and the disease can be cured without any negative consequences. Nevertheless, if the mucus is viscous, "vitreous this may be a sign of bronchial asthma.
- Frozen sputum when coughing occurs with anthrax or pulmonary edema. Both that, and other disease are considered very serious, that demands the immediate reference to the doctor.
- Dense sputum during coughing usually appears at the initial stages of the transition of the dry process to wet, or with stagnant phenomena. To the mucous secret was not thick, use thinning medications, chest massage. It is also recommended to use a large amount of alkaline warm liquid.
As you can see, the characteristic of the secretions has the most important diagnostic value. No less important role is played by the description of coughing attacks, so we will dwell further on this symptom.
Types of cough syndrome
Wet cough syndrome is considered a natural physiological phenomenon, through which the accumulation of accumulated mucus from the tracheobronchial tree occurs. However, many are concerned that such a symptom is not always the same. Can this prove anything? In some cases, it really can, because manifestations of cough reflex are a valuable informative moment in setting the right diagnosis.
- A painful cough with phlegm is able to indicate that the mucus is too viscous to go out without hindrance. Therefore, in order to push out a thick discharge, the respiratory tract needs to exert much more effort, which causes soreness or even heaviness in the course of the bronchi. To facilitate the release of mucus, use medications that dilute it.
- Cough with viscous sputum is often characteristic of croupous pneumonia, an inflammatory reaction in the respiratory system. With properly prescribed treatment, after a short time, such mucus becomes liquid, begins to expectorate well.
- Coughing spells with phlegm can be observed with a large accumulation of mucus in the bronchi. If there are many discharges, they gradually begin to irritate the bronchial walls, which provokes a coughing attack. Such an attack continues until all the discharges leave the airway. Then the accumulation occurs anew, and the process repeats. To ensure that mucus does not accumulate in large quantities, it is recommended to periodically move, walk around the room, do light gymnastics. Massage of the chest is useful.
- Cough after eating with phlegm is often not a sign of respiratory diseases. He has other causes associated with the pathology of the digestive system. This symptom is characteristic for peptic ulcer, gastroesophageal reflux, as well as other gastrointestinal diseases. To clarify the diagnosis, it is better to consult a gastroenterologist.
- Cough with phlegm without temperature is a characteristic symptom of ARI or viral infection in patients with weakened immunity. The absence of fever at this stage is not an excuse for ignoring the disease. Treatment is prescribed accordingly with other available symptoms.
- Cough with phlegm and a temperature of 37 ° C is considered one of the typical signs of ARI. This temperature is not dangerous, it does not require the appointment of antipyretic drugs. Moreover, the use of tablets and potions that "knock down" the temperature is highly discouraged in this situation. Temperature values of about 37-3, ° C mean that immunity works, and the body struggles with the disease on its own. In this case, you do not need to interfere.
- An allergic cough with sputum is less common than without it. Usually it is not accompanied by an increase in temperature, there may be a runny nose. If the bronchial secretion is excreted, then, as a rule, it does not contain an admixture of pus or blood - the clearing is transparent. Attacks occur more often at night or after contact with an allergen: animal hair, dust, pollen, etc. 8.
- Cough with phlegm and runny nose - a common occurrence in ARVI or with allergies. It is necessary to distinguish these two diseases: in ARVI often there is a fever, and with allergies it should not be.
- Dyspnoea and cough with phlegm in many cases mean the initial stage of bronchial asthma. This disease consists in worsening patency of the bronchi due to bronchospasm, inflammatory puffiness of mucous membranes, ingestion of bronchial mucus. All these factors have the complex name "obstruction of the bronchi". Shortness of breath with worsening of the condition occurs paroxysmally: in the intervals between attacks the patient usually feels quite satisfactory.
- Cough of the smoker with phlegm - heavy, with wheezing, occurs more in the morning. Slime from the bronchi can be light, sometimes with a gray tint, with an unpleasant smell of nicotine gums. The cough reflex works in response to irritation of the bronchial walls with cigarette smoke, the obstruction of bronchioles with tobacco resins, and the accumulation of a protective secret in the respiratory system. It is observed regularly, almost constantly, can be accompanied by inflammatory processes (chronic) of the trachea, bronchi, larynx.
- Cough with phlegm in the morning is observed with bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and smokers with experience. To establish the cause of morning bouts, it is often necessary to check not only the respiratory system, but also the organs digestion, since often the mucus inside the lungs is a secretion of the stomach, abandoned by night sleep inside the respiratory ways. This happens during diseases of the esophagus - reflux-esophagitis.
- Night cough with phlegm occurs in bronchial asthma, cardiac insufficiency, sinusitis, pertussis. When diagnosing this type of coughing, attention should also be paid to other symptoms: soreness inside the chest or heart, color of discharge, temperature, runny nose.
- Bark cough with sputum may be a sign of obstructive bronchitis, pertussis, false croup, which is often found in children of childhood. In adults, it can be a sign of pharyngitis, laryngitis, and inflammatory process in the bronchi and (or) in the trachea.
- Coughing up to vomiting with sputum in children is common, as the cough and vomiting center is almost there. Therefore, even a mild attack can provoke the appearance of vomiting, especially if the baby has recently eaten. In adult patients, such a reaction may be a sign of disturbances in the digestive system, namely, peptic ulcer.
- A persistent cough with sputum is a clear sign of chronic damage to the respiratory system. This condition can be observed in heavy smokers, in persons working inside dusty unventilated premises or in chemical industries, as well as in patients who did not receive acute treatment bronchitis. Chronic diseases of the respiratory system are more difficult to treat. If the disease is associated with a professional activity, a change of place of work may be mandatory.
- Paroxysmal cough with phlegm is a frequent satellite of allergy, for example, bronchial asthma. During seizures, the patient experiences shortness of breath may secrete a mucous transparent secret from the bronchi. In breaks between attacks of the patient, as a rule, nothing disturbs - he feels almost healthy.
As can be seen, a cough reflex with secretion can be observed with various lesions of the trachea, bronchi, lungs, larynx, heart or digestive system. Therefore, it is very, very difficult to determine the cause of the indisposition independently. Trust a good doctor: a comprehensive diagnosis will help determine the disease in time to begin treatment of respiratory problems.
Who to contact?
Pulmonologist General practitioner Family doctorDiagnosis of cough with phlegm
The collection of data on the history of the disease is of great importance for the diagnosis of respiratory pathologies. The doctor will start by receiving the following information:
- When did the disease begin?
- Did other diseases, such as viral infections, precede him?
- Is the seasonality of the pathology traced, are there any seizures of shortness of breath or shortness of breath?
- Are there additional symptoms, such as a runny nose, stuffy nose, heartburn, stomach pain, etc.?
- Is there a temperature increase?
- What is special about bronchial secretions? What color are they? Is there a smell?
- Are there chronic diseases, bad habits?
- What are the features of professional work?
- Is there a tendency to allergies?
- Did the patient take ACE inhibitor drugs (captopril, enalapril, prestarium, etc.)?
After finding out the anamnesis, the doctor proceeds to a number of additional studies.
- Physical examination (general examination). Includes the detection of signs of heart disease, examination of the mouth, throat. The doctor pays attention to the increase in lymph nodes, the presence of free nasal breathing, the purity of the surface of the tongue and tonsils. Conducts audition of the lungs for the presence of wheezing, whistles, crepitations, as well as the nature of the listed symptoms.
- Chest x-ray. It is performed to detect neoplasms and tuberculosis changes inside the lungs, and bronchiectasis and sarcoidosis can also be detected.
- Evaluation of the functionality of external respiration - allows to detect bronchial obstruction, interstitial lung diseases, bronchial asthma.
- Analysis of bronchial secretions with microscopy of the material. Smears are stained by Gram and Tsil-Nielsen, mucus sowing and cytological examination are carried out.
- Instrumental methods of research. Methods of bronchoscopy with cytology and histology are used (mainly if there is a suspicion of oncological disease), biopsy of suspicious tissues, transbronchial lung biopsy, CT scan.
The diagnosis is based on a set of studies, based on the results of a general examination, analyzes of the coughing material and instrumental assessment of the state of the respiratory system.
Treatment of cough with phlegm
Some believe that if bronchial mucus is released, the disease does not need treatment. This is a great misconception. Treatment at this stage is mandatory. It should be aimed at facilitating the diversion of excreta and the elimination of the underlying disease.
If the discharge is poorly expectorated and remains in the bronchial cavity for a long time, it can lead to bacterial complications. Therefore, the most used medicines in this situation are expectorant medications, mucolytics and combined agents. Some of them make slime more liquid, while others control its production in order to produce exactly the amount of excreta that the organism can take out most easily.
Dilution of sputum during coughing can occur with the use of expectorants:
- plant (based on plants) - are represented by pectusin, solutane, tussin, piles, syrup "Doctor Mom
- synthetic - are represented by bromhexine, lazolvanom, ambroksolom, ATSTS.
Herbal preparations may have fewer side effects, but they are more likely to cause allergies, especially in pediatric patients. All this must be taken into account when choosing the means of treatment.
Treatment for a cough with hard-to-recover sputum should be done only with expectorants and mucolytic medications. In no case can you use antitussive drugs - they block the cough reflex, and hard to remove mucus in general ceases to be excreted. As a result, we get the accumulation of mucus inside the bronchi and lungs, the attachment of bacterial infection and complications, sometimes in the form of pneumonia. Choose medication carefully, after consulting with a doctor. We remind you that such medications should dilute and facilitate the excretion of bronchial mucus, cleaning the respiratory tract from the inside. Simultaneously, the main disease is treated, symptomatic treatment, immunostimulating therapy is carried out.
Means for coughing sputum
If the mucus from the bronchi is difficult to separate and removed, doctors recommend drinking plenty of warm liquid, including herbal teas and compotes. Apply medications that eliminate inflammation, having an enveloping, expectorant and bronchodilator effect, reducing the sensitivity of bronchial walls, increasing the cough threshold. If not contraindicated, you can use steam inhalation with the addition of various drugs and herbs. Inhalations help moisturize the mucous membrane, calm pain, improve the composition of mucus, relax smooth bronchial muscles.
At the same time, medicines based on thermopsis or ipecacuan should not be used in early childhood, since they can stimulate increased irritation of the respiratory system and the appearance of vomiting.
Let's consider the most effective means in more detail.
Inhalations with a spit with sputum often involve the use of herbal remedies: leaves of eucalyptus, sage, calendula, chamomile, St. John's wort, as well as preparations of Salvin and Romazulona. With inhalations of steam, it is recommended to use phytoncides - all known onions or garlic, the proportion: 0. In the pharmacy you can buy onion tincture on alcohol - it is used for the amount of 25 cap / 100 ml of pure water. A good effect is expected from such simple means that use on, l of water:
- sea salt or baking soda (1 h. l.);
- essential oil 10 cap. (eucalyptus, mint, needles, anise, peach);
- balm "Asterisk" - on the tip of the spoon.
You can use oils for inhalation - from sea buckthorn, olives, rose hips, rosemary.
Cough medicines with sputum are divided into several categories:
- products based on bromhexine (Bromhexin, Ascoril, Solvin);
- funds based on ambroxol (Ambrobe, Ambrosal, Flavamed, etc.);
- drugs based on carbocisteine (Bronhobos, Fluviert);
- means based on acetylcysteine (ACTS, Fluimutsil);
- vegetable preparations based on althea, anise, elecampane, plantain, etc. (Mukaltin, Pectussin, Bronchikum, etc.). •
Tablets from cough with phlegm:
- Carbocysteine - stabilizes the consistency of mucus, contributes to its exit from the broncho-pulmonary system. Assign 2 capsules three times a day, with the improvement go to 1 capsule three times a day;
- Likorin - normalizes the secretion of the bronchial glands, relaxes the spasmodic smooth muscle structures of the bronchi. Take ½ or a whole tablet 3 to 4 times a day after eating;
- Likvitorit - a drug of licorice, eliminates inflammation, spasm, improves expectoration. Assign 1-2 tablets up to 4 times a day for half an hour before meals;
- Mukaltin - a preparation of an althaea, a soft expectorant. Apply orally 1-2 tablets up to 3 times a day before meals. •
Antibiotics for coughing with sputum are prescribed only in advanced cases of the disease, as well as with suspected complications. In most cases, the following antibiotics are considered effective:
- penicillin series is represented by amoxicillin (Flemoxin), augmentin, amoxiclav, ampicillin and others. The listed medicines perniciously act on the majority of bacteria which cause an inflammatory reaction in the respiratory organs. If one of these drugs does not show the expected effect, it is replaced by another belonging to another group of antibiotics;
- fluoroquinolone series is represented by levofloxacin, moxifloxacin (Avelox). Such drugs are usually prescribed if antibiotics from a number of penicillins are ineffective;
- the cephalosporin series is represented by cefuroxime (also Zinnat, Aksetin), cefixime (Suprax), etc. These antibiotics are often used to treat inflammatory processes in the bronchi, lungs, pleura, etc .;
- macrolide series is represented by azithromycin (Sumamed), which is often taken with atypical pneumonia, where the pathogens are mycoplasma or chlamydia. •
Cough syrup with phlegm is a very popular remedy, especially in children's practice. Many syrups are analogous to tablets, with a similar composition and action. Children are more willing to take syrups: it is easier for them to swallow a sweet aromatic liquid than to swallow a bitter pill. To choose a syrup it is desirable, being guided by recommendations of the doctor:
- Linkas is a herbal medicine, it eliminates the fever, spasms of the respiratory system, improves the production of mucus by the bronchi. It is prescribed for pharyngitis, tracheobronchitis;
- vegetable syrup Suprima-Broncho - can be prescribed with laryngitis, pharyngitis, pneumonia, whooping cough, tracheobronchitis. May cause an allergic reaction;
- Syrup Lazolvan - a remedy from the group ambroksola. A very common and effective drug. Used for inflammation of the bronchi, lungs, bronchial asthma, congestion, bronchiectasias;
- Herbion - syrup from plantain. Treats inflammation of the respiratory system, helps even with a cough syndrome smoker;
- Bromheksin-syrup - mucolytic, promotes expectoration, thinning viscous mucus. Improves and facilitates the secretion of secretions;
- Erespal when coughing with phlegm - a syrup based on Fenspiride, an anti-bronchoconstrictor. Relieves spasms, eliminates inflammation, reduces the secretion of mucus by the bronchi. Actively used for bronchial asthma, bronchospasm, chronic bronchitis, pertussis, pharyngitis. Can be used in children from the moment of birth, from 2 hours. l. up to 6 tbsp. l. a day before meals. At reception there can be a drowsiness, frustration GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. • \
Herbs from coughing with phlegm are the most acceptable treatment without medication. Pine kidneys, onion, garlic, marshmallow, mint, chamomile, plantain, mother-and-stepmother, St. John's wort, elephant, sage are used as components for the collections or therapeutic mixtures. Herbs can be used in the form of broths, infusions for inhalation, herbal teas for oral administration. A good effect is given by special breastfeeding, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. There are 4 types of such fees:
- No. 1 - althea rhizome, oregano, mother-stepmother leaf;
- №2 - mother-and-stepmother, plantain, rhizome of licorice;
- №3 - rhizome altea, anise, rhizome of licorice, pine buds, sage;
- №4 - chamomile color, Labrador tea, calendula, violet, rhizome of licorice, mint.
Vegetative components in these collections have complex mucolytic, expectorant, bronchodilating and anti-inflammatory effect. The secret begins to retire on time, the cough reflex is gradually docked.
Folk remedies for cough and phlegm
What other folk remedies are used in the treatment of respiratory diseases with expectoration of a secret:
- We put a whole lemon in water, boil for 10 minutes. Remove from heat, cool. Cut the lemon into 2 equal parts, squeeze the juice into which we add 2 tbsp. l. glycerin, top up to 200 ml with honey, mix. Accepted for 1 tbsp. l. received mass three times a day before meals and at bedtime.
- Mix the equal parts of freshly squeezed carrot juice, black radish and milk. We consume 6 times a day for 1 tbsp. l.
- Mix two chicken yolks, 2 tbsp. l. fresh butter, 2 h. l. natural honey, 1 hour. l. flour. We use the obtained mass for 1 hour. l. throughout the day, can be repeated.
- Take black radish (7 pcs.), Cut into slices, add a little sugar to each piece, leave it for 6 hours. The resulting juice is drained, then we take 1 tbsp. l. every 60 minutes.
- We prepare a kissel from a viburnum on honey, we drink during the day.
- We prepare the infusion of sage (1 tbsp. l. for 250 ml of hot water), we insist, filter, add equal amount of boiled milk. We drink 100 ml several times a day, with honey or sugar.
- Finely chopped, kg of onions, add 400 g of sugar and 40-60 g of honey, boil with 1 liter of water for 3 hours on low heat. Then cool it, drain the liquid. We consume 1 tbsp. l. about 5 times a day, it is possible during coughing seizures.
The use of folk remedies can be more effective if combined with inhalation by steam, using baking soda, medicinal herbs. A positive effect is observed when adding fir, cedar, eucalyptus oil to the fluid for inhalation. Such procedures are best done at night, before going to bed.
What if my cough does not go away with phlegm?
The appearance or intensification of the presence of pus in the mucous secretions, a significant increase in the amount of secretion, an increase in temperature indicators (preliminary signs of exacerbation) may be the reason for the earliest possible and soonest appointment antibiotic therapy. Begin such treatment with the use of ampicillin (1 g from 4 to 6 times a day), levomycetin (per, g four times per day), tetracycline, cefazolin, lincomycin.
To activate a protective immune mechanism, it is recommended to take vitamin drinks and multivitamin preparations. In order to stimulate the nonspecific resistance of the body, biogenic stimulants are used:
- an extract of aloe liquid injecting in / m or s / c of 1 ml per day for a month;
- biosedema IM injection 1 ml (2 ml) every day. For 20-30 days.
From herbal remedies it is recommended to add preparations from elderberry, nettle leaves, parsley root, willow bark.
If the condition steadily worsens, then there can be no question of independent treatment. Therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor - therapist, pulmonologist, otolaryngologist, phthisiatrist.
Help with cough with phlegm
During an attack, the main type of help can be the acceleration of the removal of mucous secretions from the respiratory tract. In the laryngeal or bronchial cavity pathogenic microorganisms can accumulate, and they can be removed only with good expectoration. How quickly it will be possible to clear the respiratory tract from the secretions, so quickly the body will feel relief and begin to recover.
Simultaneously with the use of medicines prescribed by the doctor, the patient should drink a large amount of warm liquid to facilitate mucus evacuation. This will greatly improve the excretion of excreta and purification of the respiratory system. As drinking it is useful to use herbal teas based on lime flowers, dog rose, raspberry, currant, other medicinal plants.
If there is a mucous secret in the bronchi, then drugs that block the cough reflex should not be used. Such preparations include, for example, codeine, as well as all agents based on it.
You can give some advice to those who can not cope with the disease:
- monitor the humidity in the room (normal humidity should vary from 40 to 60%);
- if you smoke, drop it. Moreover, avoid smoky places;
- Avoid overcooling and sudden overheating, do not leave the hot room in frosty air;
- Avoid inhaling vapors of various chemical sprays, detergent-cleaners;
- Do not suppress the desire to clear your throat - so you clear the bronchi, making your condition easier.
Preventing cough with phlegm
The operation of the cough reflex is in most cases a symptom of the disease of the respiratory system, so its can be prevented if time to think about the prevention of respiratory diseases, such as bronchitis, SARS, acute respiratory disease, laryngitis, etc.
For prevention, factors that can provoke such diseases should be avoided: hypothermia, drafts, weakening of immunity, physical overload, stress, beriberi.
Avoid situations that can lead to irritation of the lungs: walk away from smoky, smoky, dusty and chemically treated rooms. Working with chemicals, lacquer-coloring substances can provoke the development of chronic respiratory damage. If being in such premises is inevitable, use appropriate protective measures - gauze dressings, respirators, etc.
If you are addicted to allergies or bronchial asthma, try to avoid provoking factors (contact with potential allergens).
Needless to say, smoking is one of the main factors in the appearance of chronic cough syndrome - very harmful for health in general. If you smoke, give up this habit. The rest can be advised to avoid places where people smoke. Passive smoking irritates the respiratory tract no less than smoking active.
A good preventive effect is provided by tempering the body. It is best to begin the procedure in the summer, when the body can easily tolerate temperature changes, and immunity in summer is considered more robust. Suitable for dousing with cool water, contrast showers, swimming in open water, air and sunbathing, outdoor sports. Winter hardening is better to do under the supervision of a specialist, because illiterate excessive cooling of the body can produce the opposite effect.
Prognosis of cough with phlegm
The prognosis directly depends only on the underlying disease, which triggered the cough reflex. If this symptom accompanies an acute viral or microbial infection of the respiratory system, then it is safely eliminated after the underlying disease has been cured.
If the cause of an attack is an allergy or the use of certain medications, then eliminating the allergen with substitution of drugs for others will help eliminate an unpleasant symptom.
A healthy lifestyle, adequate nutrition, lack of bad habits, active pastime can be the key to a favorable prognosis of respiratory diseases.
If the cough with phlegm is chronic, then getting rid of it will be more difficult - it can require complex complex treatment, often with the use of potent drugs and antibiotic therapy.
ilive.com.ua
Obstructive bronchitis in adults
Obstructive bronchitis in adults - diffuse bronchial damage caused by prolonged irritation and inflammation, at which there is a narrowing of the bronchi, accompanied by difficulty in getting out the accumulated mucus, phlegm. With bronchospasm, which are inherent in this disease, there is difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, wheezing, not associated with the defeat of other systems and organs. Progressive inflammatory process leads to impaired ventilation of the lungs.
The causes of bronchial obstruction
Factors affecting the development of obstructive bronchitis:
Medical factors:
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system and violation of nasal breathing, foci of infection in the upper respiratory tract - bronchitis, pneumonia
- Recurrent viral infections and nasopharyngeal diseases
- Tumors of the trachea and bronchi
- Hyperreactivity of the respiratory tract
- Genetic predisposition
- Propensity to allergic reactions
- Injuries and burns
- Poisoning
Socio-economic factors:
- Smoking, second-hand smoke (see video from what do cigarettes)
- Alcohol abuse
- Unfavorable living conditions
- Elderly age
Environmental factors:
- Long-term effects on the bronchial mucosa of physical stimuli in the external environment are allergens, such as pollen of some plants, house dust, animal hair, etc.
- The presence of chemical stimuli in the air at work or at home - inorganic and organic dust, acid fumes, ozone, chlorine, ammonia, silicon, cadmium, sulfur dioxide, etc. (cm. influence of household chemicals on health).
Types of obstructive bronchitis
Acute obstructive bronchitis- An acute form of bronchial obstruction for adults is not typical, as most often acute obstructive bronchitis occurs in children under 4 years old. However, in adults primary obstructive bronchitis is observed - due to the addition of several risk factors described above, an inflammatory process develops. On the background of acute respiratory viral infection, influenza, pneumonia, with inadequate treatment and other provoking factors, the onset of obstruction may begin. In acute obstructive bronchitis, the main symptoms in patients are as follows:
- First observed catarrh of the upper respiratory tract
- Severe dry cough, with hard-to-recover sputum
- Coughing attacks especially worse at night
- Difficulty breathing, with exhaled breath
- The temperature is subfebrile, no higher than 3, this distinguishes acute obstructive bronchitis from simple acute bronchitis, which is usually a high temperature.
Acute bronchial obstruction is curable, but if it acquires a chronic form, it can become a progressive, irreversible disease.
Chronic obstructive bronchitisis a progressive obstruction of the bronchi in response to various stimuli. Violation of bronchial patency is conditionally divided into: reversible and irreversible. Symptoms with which patients usually consult a doctor:
- Strong cough, with a discharge in the morning of sparse phlegm mucus
- Shortness of breath, first appears only with physical exertion
- Wheezing, shortness of breath
- Sputum can become purulent in the period of addition of other infections and viruses and is regarded as a relapse of obstructive bronchitis.
Over time, with an irreversible chronic process, the disease progresses, and the intervals between relapses become shorter. In chronic course,
How to treat obstructive bronchitis
Treatment of obstructive bronchitis should be with the active participation of the patient in the treatment process. If possible, it is necessary to eliminate the negative factors provoking the progression of the disease - this is primarily a refusal to smoke, the desire to lead a maximally healthy lifestyle, if the main cause of the development of bronchial obstruction is industrial hazards - is desirable change of work.
Bronchodilating therapy.It consists of three groups of medicines:
- Anticholinergic drugs. The most effective and known of them Ipratropium bromide in metered aerosols is Atrovent. The effect of inhalation drugs is slow for about an hour and lasts 4-8 hours. Daily dosage 2-4 inhalations 3-4 times.
- Beta is a 2-agonist. These medications are recommended to be used 3-4 times a day. If the patient does not have a clear manifestation of the symptoms of the disease, then they can be used only as a prophylaxis immediately before physical exertion. The most famous drugs: Berotek, salbutamol.
- Methylxanthines. Widespread use of prolonged theophylline, they are used 1 -2 times a day. The most famous of these drugs is Teopek. A solution of euphyllin is administered only in hospitals according to indications. Caution is necessary when treating methylxanthines in patients with heart failure.
Mukoregulatory drugs.To improve sputum discharge, in cases of violation of its secretion, use Acetylcysteine, Ambroxol or Lazolvan (see. list of all expectorants for cough).
Antibacterial therapy.In cases of bacterial infection, in the presence of purulent sputum and signs of general intoxication, antibiotics are prescribed for bronchitis of a wide spectrum of action for 7-14 days. In inhalations, antibiotics are not used. If the patient has chronic obstructive bronchitis, antibiotic treatment prophylactically, in order to avoid exacerbations, do not.
Corticosteroids. Their use is limited, and systemic corticosteroids are prescribed only with severe respiratory failure. Perhaps the use of inhaled hormones, because the side effects in this application are significantly reduced.
Therapeutic breathing exercises.The training of the respiratory muscles is indicated to all patients with chronic obstructive bronchitis. This gymnastics exercises in Strelnikova, and breathing Buteyko, and the use of Frolov's breathing apparatus.
Indications for inpatient treatment
- Exacerbation of chronic obstructive bronchitis, which does not stop with outpatient treatment (persistent cough with purulent sputum, shortness of breath, signs of respiratory failure increase)
- Respiratory failure, which developed sharply.
- Attachment of pneumonia.
- Signs of heart failure with the development of the pulmonary heart.
- Need for bronchoscopy.
Advantages of nebulizers for the administration of medicines for COPD
Medicinal products for the treatment of obstructive bronchitis should be used in the form of inhalations. Most often in the home for this purpose use nebulizers. Their advantages are as follows.
- The drug is sprayed in the form of fine particles in the composition of the aerosol, due to which the depth of penetration of the substance in the respiratory tract increases.
- Ease of use in children and the elderly (do not coordinate inhalation with inhalation, which is difficult to teach a small child or elderly).
- The nebulizer allows you to inject high doses of the drug and can be used to stop attacks of suffocation.
zdravotvet.ru
Cough expectoration
Sputum for coughing
A sputum is a secretion from the respiratory organs that occurs during expectoration and coughing. It includes saliva, secretions of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and sinuses of the nose.The development of the pathology of the patient determines the nature of sputum produced. As the sputum goes away, the character of the disease itself changes, which can be judged by the nature of sputum discharge. For example, if coughing leaves sputum, which has a putrid smell, this may indicate that there is a serious damage to the bronchi and lungs.
It is allowed to collect sputum in patients for laboratory tests. For a day, up to one and a half liters of sputum in a patient can go away.
Do not forget that sputum, as a biologically active liquid, can be a danger to others. In the case of the development of certain forms of tuberculosis, sputum may contain a high concentration of pathogens. When the patient coughs, such a sputum can be a danger to others, so it should be collected and processed very carefully. To collect it special vessels with glass lids are used.
Sputum, which is formed in the respiratory system, interferes with the breathing process, so it should be eliminated. This is facilitated by expectoration of phlegm. The special drainage position given to the patient helps to speed up the process.
Types of phlegm on coughing
Cough sputum can have a liquid, viscous and thick consistency. The presence of viscous sputum is characteristic of a disease such as croupous pneumonia, there is such a sputum during inflammation in the airways, in this case it gradually turns into a liquid one. The presence of mucus in the sputum and its total amount determines the viscosity of phlegm. A large number of shaped elements, such as: leukocytes, a variety of epithelium, determines the density of sputum. In the event that a large number of sputum is plasma, the sputum becomes liquid. This occurs with pulmonary hemorrhage, edema of the lungs or various poisonings.
Severe sputum when coughing
Strong sputum during coughing is observed in the case of inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system, when significant amounts of purulent and serous secretions accumulate in the lungs and bronchi. Most often, this phenomenon is caused by viral diseases, which are at the stage of resolution, when a bacterial infection joins. Sputum becomes dense and abundant, and pus is often mixed with it. Perhaps the appearance of strong sputum when coughing a child after he suffered a cold or ARVI - in this case, you should carefully monitor its condition: did the temperature increase, did the overall state. Both in the presence of a strong and frequent coughing indicates the penetration of infection in the lungs and lower parts of the bronchi.
When you cough, phlegm with blood
Sputum production during coughing is typical for a variety of diseases of the respiratory system. However, in the absence of pathologies, the mucus that is released during coughing is clear. If phlegm with blood is excreted when coughing, this indicates serious enough diseases of the human body. These may include:
- Lungs' cancer.A very common symptom of this disease is precisely the expectoration of a coughing bloody sputum. Blood is present in the sputum in the form of veins of bright red color. It is necessary to immediately make an X-ray of the lungs in case of manifestation of such symptoms, but it is not worth it panic until the patient has a rapid loss of weight, sweating, a sense of lack air.
- Bronchitis.Sputum with blood often accompanies bronchitis. During this disease, the patient's condition can change at different times. About chronic bronchitis can be discussed if bloody sputum is observed for more than three months a year.
- Pneumonia.Often, bloody veins in expectorated sputum are observed in the case of pneumonia.
- Tuberculosis.Bloody sputum, secreted by coughing in the morning, is a characteristic sign of a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis. In addition to the blood veins in the expectorant mucus, it is possible to observe impurities of pus. The causes of this disease state can also be in diseases of the cardiovascular system or organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Abscess of the lung.When coughing, it is also possible to give sputum with blood, but with this disease the patient has a stench from his mouth, fever, weakness, lack of appetite and sweating.
Purulent sputum when coughing
Cough with purulent sputum is typical for a number of diseases and in itself is not sufficient reason for setting any definitive diagnosis. Everything is determined by an additional consideration of the side symptoms characteristic of a particular disease. In particular, purulent sputum during coughing takes place with chronic bronchitis. Such a cough can manifest itself in damp and cold weather and have a paroxysmal character. The mucous sputum emitted during cough with pus contaminants contains a diverse microbial flora. Sometimes purulent sputum appears only in the mornings, during the rest of the day the cough is convulsive and dry. In other cases, coughing attacks occur around the clock all the time, accompanied by shortness of breath with vomiting. The temperature keeps at a normal level, rising only during a period of exacerbation of the disease.
Against the background of chronic bronchitis is often the appearance of bronchiectasis - accumulating pus, pathological expansions of the lungs. In the event that a cough with purulent sputum is caused precisely by bronchoectatic disease, the course of it is more painful and prolonged, it is not always possible for a patient to clear his throat to the end.
A prolonged cough with the release of purulent sputum in the mornings is typical for smokers with a long history. Bronchi are exposed to the harmful effects of tar and nicotine contained in cigarette smoke, and the impact is many times superior to the harmfulness of the action of pathogenic bacteria, constantly found in the bronchi. Prolonged smoking decomposes bronchi, wears out the respiratory system and often causes lung cancer.
Thick sputum on coughing
Abundant accumulations of thick sputum may contribute to a significant difficulty in the respiratory process. Dense sputum during coughing is typical for diseases such as infectious respiratory tract infections, it can be caused by inhalation of contaminated air and smoking. In this case, the cough carries a purifying function, facilitating the withdrawal of clots of sputum from the respiratory system.
However, not only smoking can cause the appearance of thick sputum in the respiratory tract, which is necessary expectorate, the cause of its appearance can become many diseases, such as asthma, tuberculosis, chronic forms bronchitis. For example, asthma, developing from a dry cough and light hoarseness, reaches the form of a cough with a large amount of expectorated thick sputum, which has the form of dense mucous secretions. When a tuberculosis disease occurs, a person who is ill often coughs up phlegm, which has a dense consistency, often containing impurities of pus and blood. Moreover, thick sputum when coughing can take place and with an ordinary cold. Therefore, we can conclude that, in itself, expectorated during coughing, thick sputum is not a symptom of any one specific disease, but only indicates that the body has a problem that requires intervention and permission. The diagnosis should be carried out individually and, depending on it, treatment should be prescribed. In any case, the excretion of sputum is facilitated by the diluting agents that make the consistency of sputum secretory less dense, thereby facilitating its expectoration.
Salty phlegm on coughing
Salty sputum when coughing is typical for such a disease as allergic bronchial asthma. With this disease, brackish sputum often appears together with blood veins, there may be a rise in temperature to 37 degrees or higher, but normal temperatures can also be observed. Another symptom of allergic bronchial asthma is stuffiness in the chest - as if there is not enough air. Appetite thus does not suffer - its loss does not occur. In the treatment of the disease, the agents that dilate the bronchi, such as ventolin and berodual, are of great help.
Sputum color when coughing
The color of sputum when coughing can not be linked to any particular disease. However, you should definitely consult a doctor when you get sputum yellow, green, brown, and also rusty, especially if any sputum of the specified colors is observed for more than a week. Especially if it takes place against a background of fever, chills, dyspnea.
Green sputum when coughing
Green mucous sputum when coughing is typical for many inflammatory diseases, affecting the lungs and bronchi. The causative agents of such diseases are various allergens, infections and catarrhal conditions. It can be bronchitis of every possible etiology, croupous pneumonia, tuberculosis, bronchial asthma, cancer and the like.
In addition to cough, there may be other symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, fever. In order to accurately identify the causes of the disease, sputum examination in the laboratory, lung X-ray, magnetic and computer tomography is carried out. If it is a question of suspicion of an oncological disease, a thoracoscopy is performed - a certain amount of affected tissue is taken for histological examination.
If the green sputum has a viscous consistency and is characterized by an unpleasant smell - it can be a question of stagnant processes in the lungs. This is a rather dangerous sign, especially if it's a child. The treatment process consists in taking antibiotics and strong-acting drugs. Bronchitis can be treated with mucolytic drugs and means that enhance expectoration. With regard to tuberculosis, lung cancer and pulmonary hemorrhage, these diseases should be treated in a hospital hospital.
Yellow sputum when coughing
Yellow sputum when coughing is allocated with the following diseases: sinusitis, bronchitis, pneumonia.
The greatest danger is a cough that starts suddenly, in which the allocation of yellow sputum is accompanied by the presence of blood and pus, which gives prominent sputum characteristic color tone. The presence of blood enzymes in the yellow sputum indicates an urgent need to see a doctor, since it is very likely that there is a tubercle bacillus. According to the color shades of excreted sputum, you can determine the cause of the bronchitis that has begun. If the sputum released during coughing has a yellow tinge, it means that a bacterial infection was found in the lower parts of the respiratory tract.
In order to conduct a diagnosis of the disease, it is necessary to make an analysis of sputum cough. To conduct it, sputum is collected on an empty stomach in a glass jar, specially prepared and washed for this purpose. In this case, immediately before expectoration of the sputum, the patient is recommended to wash the mouth with an antiseptic solution, and zatey with ordinary boiled water.
However, not always yellow sputum when coughing indicates a serious illness, often it is a companion of smokers with a long history.
When coughing white sputum
The appearance of white sputum when coughing (as, indeed, and some other) indicates the accumulation of excess mucus in the respiratory tract, the development of which is caused by various diseases.
Coughing white, clear sputum, which has a thick consistency, indicates the presence of a cold in the body. The development of such mucus is provoked by the course of allergic reactions, bronchitis, asthma and inflammation of the lungs. Categorically it is not recommended to restrain cough or swallow sputum. Slime in this case accumulates, it stagnates, which can result in poisoning the body. These factors necessitate the use in the treatment of drugs that provide mucus liquefaction and facilitate expectoration.
Sputum, which has a gray tinge and is endowed with odor, characteristic of decay, indicates the development of advanced stages of oncological diseases of the respiratory system. At the initial stages of the development of cancer, sputum is transparent, white with impurities of blood veins. Slime can be gray as a result of subsidence in the respiratory tract of tobacco burning products and be characteristic of heavy smokers. In people suffering from cardiac asthma, sputum may also have a serous color and a liquid consistency.
Brown sputum when coughing
As already mentioned above, there is no such color of sputum, according to which it would be possible to determine with certainty the onset of the disease. This is why the patient is forced to undergo a long series of examinations and take numerous tests to accurately diagnose a medical diagnosis. However, if the sputum produced during coughing is brown, this may indicate a viral or bacterial infection that occurs with inflammation. It can be an ordinary cold, pneumonia or bronchitis. With the onset of internal bleeding, the appearance of expectorated sputum is also possible.
When brown sputum appears when coughing, self-medication should not be dealt with, since this can provoke the appearance of more serious diseases. In view of this, you should, without delaying, seek help from a doctor. In order to maximize the effectiveness of the treatment process, it is desirable to take as much fluid as possible. In this case, the likelihood that the sputum, having a brown tinge, is diluted and as soon as possible will be removed from the lungs. In no case should you take drugs that suppress cough, because when it is suppressed, there is no output of sputum from the body.
Pink sputum when coughing
The pink color of sputum when coughing indicates the presence of bleeding, not so, however, abundant, as in the case of red sputum. It is also possible to change the color of the mucus secreted and display blood in the form of spots and veins. If the process of blood coagulation has already begun, sputum may have a rusty shade, indicating that red blood cells have already disintegrated.
The presence of blood in the sputum may indicate such diseases as:
- pneumococcal pneumonia:sputum in this case has a red-rusty color;
- lungs' cancer:The color of phlegm varies from pink to red, turning into brown and black;
- tuberculosis:in this case there are bright red bands in the sputum;
- Embolism of the lungs:blood is bright red.
The presence of blood in the expectoration of a coughing sputum indicates a danger, so that you should immediately go to a doctor.
Treatment for cough with phlegm
In the treatment of cough with sputum, an abundant drink that includes phytopreparations is effective. It is appropriate to use plant components that have anti-inflammatory, expectorant, The bronchodilator and enveloping action, thus reducing the irritation of the mucosa bronchi.
In the absence of contraindications, inhalations with sodium chloride and benzoate, extracts of plants, soda, ammonium chloride are allowed. As a result of this procedure, the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract is moistened, decreases the excitability of the reflex cough center, sputum liquefaction and smooth muscle relaxation bronchi. In addition, all of the above medicines play the role of anesthetics and analgesics.
Cough sputum diffusion
Long-term medical practice was used to develop methods that promote a speedy recovery by diluting cough sputum. This can be folk recipes and proven facts.
- The maximum increase in liquids drunk during the day. Drinking normalizes the water balance of the exhausted organism, while the sputum produced acquires a liquefied consistency. With a hard cough, alkaline nutrition is acceptable. The chemical composition of mineral water contributes to an easier release of sputum and the subsequent disposal of it. It is also very important to include fruits and vegetables in the daily diet.
- Carrying out inhalations. These procedures, conducted with a solution of medicinal herbs also have a liquefaction effect. The composition is as follows: one tablespoon of sage, thyme, mother-and-stepmother and chamomile. Everything is poured with boiling water, after which it is infused for an hour, after which one tablespoon of soda and eucalyptus oil is added. Inhalation should be carried out twice a day
- Dissemination of sputum with medical preparations. Effective use of the following means: lazolvan, ambroksol, ATSTS. All of them are appointed by the attending physician and are indicated for tracheitis and bronchitis, when it is difficult to get the sputum out.
- Broth pigeon pigeon. This is an old folk remedy that greatly facilitates the process of liquefying sputum. Moisturizes the mucous membrane of the bronchi, makes it possible to simplify the withdrawal of phlegm by softening the dry cough.
- Figs. It is quite good when it comes to bored cough or stiff sputum. The fig should be cut into two halves and placed in a glass of milk. The appearance of the desired shade indicates that the composition is ready.
kashelb.com
All expectorants for cough with bronchitis
When ORVI, bronchitis with a damp cough with poorly separated sputum, the use of medicines is recommended, which either dilute sputum - mucolytic drugs, or facilitate its separation - expectorants from cough. These include both herbal remedies and synthetic preparations.
Many of us prefer to restrict the intake of medications not obtained from natural substances, however, it should always be remembered that any a medicinal plant, no matter what positive properties it possessed, as well as synthetic agents have side effects, and has a number contraindications.
Since the composition of all medicinal plants is very complex and saturated, in addition to useful and medicinal herbs, a lot of other, sometimes toxic, harmful substances are included in the herbs and preparations. Moreover, in our days, the majority of the population suffers from various types of allergies, and any drug, even the most expensive, effective and safe, can cause an inadequate body reaction.
Classification of funds that facilitate cough and promote rapid recovery
All means for cough relief are subdivided into antitussives, expectorants and mucolytic agents.
- Antitussives, as well as combination preparations - are indicated for dry, unproductive cough, disturbing sleep and appetite (see. article antitussives with dry cough).
- Expectorants - are indicated with a productive cough, when the sputum is not thick, not viscous.
- Mucolytic agents - are shown with a productive cough, but with a thick, hard to separate, viscous sputum.
Any cough medicine must be prescribed only by your doctor. Antitussive remedies can not be used to treat concomitantly with mucolytic drugs, but there are combination drugs that have a weak antitussive and expectorant effect.
Expectorants - means that stimulate expectoration are also divided into:
- Reflex action - these drugs have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa, and this in its turn excites the vomiting center, but vomiting does not occur, but the production of mucus in respiratory ways. The peristalsis of the smooth musculature of the bronchi and the activity of the epithelium, which removes phlegm from small to large bronchioles and into the trachea, is also intensified. The result of this irritation is the facilitation of expectoration of mucus and the removal of sputum from the bronchi. In general, these are herbal preparations - thermopsis, Ledum, mother and stepmother, althea, plantain, thyme, etc.
- Direct resorptive action - after digestion of these cough suppressants in the digestive tract, they cause irritation of the bronchial mucosa, thereby increasing the secretion of liquid sputum.
Mucolytic agents are preparations that dilute sputum:
- Mukoliticheskie means, affecting the elasticity and viscosity of bronchial mucus (ATSTS, etc.)
- Mucolytic agents that accelerate the excretion of sputum (bromhexine, ambroxol)
- Mucolytic drugs that reduce the formation of mucus (Libexin Muko, M-cholinoblockers, glucocorticoids).
Expectorants for cough reflex action
The use of infusions from the herb of thermopsis should be treated very carefully. At children at the slightest overdose there can be a vomiting. Moreover, the cytisine (alkaloid) entering into its composition in large doses can cause a short-term stimulation of respiration in children, which then gives way to respiratory depression.
Preparations of AltheaIndication: Chronic and acute diseases of the respiratory system - bronchitis, tracheobronchitis, obstructive bronchitis, emphysema. At which a difficultly separated sputum is formed, increased viscosity. Pharmacological action: When using expectorants from the herb althea medicinal, the effect is achieved by stimulation of peristalsis of bronchioles, it has an anti-inflammatory effect, dilutes bronchial secret. Contraindications: increased sensitivity to this drug, gastric and duodenal ulcer. For preparations in syrup, use with caution in diabetes mellitus and fructose intolerance. Children under 3 years, with pregnancy only according to the indications. Side effects: allergic manifestations, rarely nausea, vomiting Mukaltin, tablets (20 rubles). Method of use: Children mukultin as an expectorant for cough take, dissolving 1 a tablet in 1/3 of a glass of water, adults are recommended to 50-100 mg 3/4 p / day before meals, a course of therapy 1-2 weeks. |
|
The roots of the althea(60 rubles) raw materials crushed Dosage: Take in the form of infusion, which is prepared as follows - a tablespoon on a glass of cold water, in a water bath is boiled for 15 minutes, cooled, filtered, squeezed, brought to 200 ml. Admission is carried out 3-4 r / day after eating, before taking shake. Children 3-5 years, 1 dessert each. spoon, 6-14 years for 1-2 tablespoons, adults 1/2 cup for 1 reception. The course of treatment is 12-21 days. |
|
Alteika syrup(90 rub) syrup Althea (30-130 rub) Application: Inside after meals, children under 12 years old - 4 r / day for 1 hour. spoon, diluted in a quarter of a glass of water, adults for 1 tbsp. l. syrup, diluted in half a glass of water. The course of treatment is up to 2 weeks, according to the indications the duration of therapy can be continued. |
Preparations of thermopsisThermopsolpills for cough (30-50 rub) The herb of thermopsis has a pronounced expectorant property, this herbal preparation contains many alkaloids (cytisine, thermopsin, methyl cytisine, anagirine, pachycarpine, thermopsidin), which exert a stimulating effect on the respiratory center, and at high doses on the vomiting Centre. Sodium bicarbonate, which is a part of the tablets Termopsol also reduces the viscosity of phlegm, stimulating the secretion of bronchial glands. |
|
Kodelak Broncho(120-170 rubles)without codeinethe composition includes (thermopsis extract, ambroxol, sodium hydrogen carbonate and glycyrrhizinate) Kodelak Broncho with thyme100 ml. elixir (150 rub)without codeine,in the composition (thyme extract, ambroxol, sodium glycyrrhizinate) These are combined expectorants that have expressed and mucolytic, and expectorant action, in addition have a moderate anti-inflammatory activity. Included in Ambroxol reduces the viscosity of phlegm, and Sodium glycyrrhizinate has antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. Indications: Kodelak Broncho is used for difficulty in sputum discharge during pneumonia, COPD, bronchitis acute and chronic, with bronchoectatic disease. Contraindications: Pregnancy, children under 12 years, during lactation, with increased sensitivity to components of Kodelak Broncho. With caution in bronchial asthma, ulcerative gastrointestinal diseases, people with hepatic and renal insufficiency. Dosage: When eating 1 table. 3 r / day, can not be used for more than 4-5 days. Side effects: Headache, weakness, dry mouth, diarrhea, constipation, with high doses and prolonged reception - nausea, vomiting. Dryness of the mucosa of the respiratory tract, allergic reactions, dysuria, exanthema. |
Thoracal Nos. 1, 2, 3, 4The composition of which includes medicinal herbs:
More details about these collections of medicinal herbs from coughing can be read in our article - Breastfeeding, "from coughing - instructions for use. |
|
Expectorant collection- Ledum, chamomile, elecampane rhizomes, mother and stepmother, calendula, peppermint, licorice, plantain. Application: infusion take 4 r / day before meals in 1/4 cup or 50 ml, course 10-14 days. Infusion is prepared as follows - 1 tbsp. l. collection boil in a water bath for 15 minutes in 200 ml of water, then cool, bring to 200 ml. Side effect: Diarrhea, heartburn, nausea, allergic manifestations. Bronchophyte(elixir, manufacturer of Ukraine) composition: Ledum, plantain, anise, violet, licorice, sage, thyme. |
Leaf of plantain, mother and stepmother, ledum and other vegetable preparationsLeaf of plantain(30 rubles pack) Plantain contains many useful biologically active substances, mucus, vitamins, essential oil, oleic acid, bitter and tannins, resins, saponins, sterols, emulsions, alkaloids, chlorophyll, mannitol, sorbitol, phytoncides, flavonoids, macro- and microelements. It has bacteriostatic, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, expectorant, mild laxative effect. It also has a mucolytic effect, restoring the work of the ciliated epithelium. Herbion with plantain(180-230 rubles) For more details on the use of Herbion in dry cough and Herbionum with a damp cough, read in our article. |
|
Grasshopper herb grass(35 rubles)is part of the expectorant collection, Breastfeeding No 4 and Bronchophyta. Herbal means of expectorant action, essential oil components have a locally irritating effect on mucous membranes bronchi, ledum has both antimicrobial and moderate anti-inflammatory effect, has an exciting effect on myometrium and CNS. Dosage: Infusion of 3 r / day for 1/2 cup, for infusion it takes 2 tablespoons of herbs per 200 ml of boiling water. Side effects: Increased bronchospasm, increased irritability, excitability, dizziness. |
|
Mother and stepmother(40 rub) Application: due to the biologically active substances included in the composition it has antimicrobial, expectorant, diaphoretic, choleretic, wound-healing and antispasmodic properties. Dosage: every 3 hours for 15 ml infusion or 2-3 tablespoons 3 r / day for an hour before meals. Prepare the infusion as follows - 2 tbsp. Spoons are filled with a glass of water and for 15 minutes. boil in a water bath, then cool, filter, volume is adjusted to 200 ml. |
|
Plantain syrup and mother and stepmothers(200 rubles) Contraindications: children under 6 years of age, pregnancy, lactation, peptic ulcer. Use: the syrup is taken to children 6-10 years old to 15 years old for 2 hours. spoon, adult 1-2 tbsp. spoon 4 r / day course 14-21 day. The change in the duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician. Side effects: allergic reactions (see. all tablets from allergies) |
|
Stoppussin phyto syrup(130 rubles)composition: plantain, thyme, thyme. This is a phytopreparation with an anti-inflammatory and expectorant effect. Contraindicated: during pregnancy and feeding, children under 1 year. Patients with epilepsy (causes), kidney and liver diseases, brain injuries should be taken with caution. Application: after meals 1-5 years for 1 hour. spoon 3 r / day, 5-10 years for 1-2 hours. l. 10-15 years for 2-3 tsp, adults for 1 tbsp. l. 3-5 r / day. Usually the course of treatment is not more than 1 week, continue therapy is possible according to the indications. |
|
Coldrex bronchus (syrup 110-250 rub) Syrup Caldrex bronchus has the smell of anise and licorice, the main substance used is guaifenesin, and also includes dextrose, macrogol, sodium cyclamate and benzoate, tincture of red pepper, star anise seed oil, racemic camphor, levomenthol. Contraindicated: children under 3 years, with peptic ulcer, hypersensitivity. Usage: Children from 3-12 years of age are shown an example in a single dose of 5 ml every 3 hours, an adult 10 ml every 3 hours. Side effects: abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, urticaria, rash. |
Thyme (thyme extract)Thyme grass(40 rub) Thyme essential oil (90 rub) It is also an expectorant for coughs of plant origin, has analgesic and antimicrobial effect. |
These are liquid extracts of thyme, which are mucolytic and expectorant agents for coughing with bronchitis, pneumonia, with diseases with paroxysmal coughing, and with hardly detachable sputum.
After meals, children 6-12 months - on, h. spoons 2 r / day, 2-6 years - 1 hour. l. 2 r / day, 6-12 years - 1 tsp3 r / day, for adults 2 tsp. 3 r / day. Pastilles should be absorbed, children 6-12 years old - 1 paste. 3 r / day, for adults 1-2 pastes. 3 r / day.
Children 1-4 years - on, ch. 3 r / day, 5-12 years - 1 tsp each. 4 r / day, adults for 1 tsp. 6 r / day. Bronchicum should be taken throughout the day at regular intervals.
After meals, children 3-6 years old, ch. Lolki, 6-12 years old by 1-2 tsp, over 12 years old on a dessert spoon, adults on a tablespoon 3 r / day, course 10-14 days.
Children 1-5 years old take 2-3 r / day for 10-25 drops, which can be taken in diluted and undiluted form. Children older than 5 years of 20-50 drops, adults 40-60 drops of 4 r / day. Syrup should be taken after meals for children 1-5 years 3p / day for 1 tsp., Over 5 years 1-2 tsp, for adults 2-3 tsp. 4 r / day. |
GelomirtolGelomirtol (170-250 rub) It is an expectorant for coughing with chronic and acute bronchitis, of plant origin. |
Expectorants for cough of direct resorptive action
Such active ingredients as ammonium chloride, sodium hydrogen carbonate, potassium and sodium iodides increase secretion liquid sputum, the same effect is possessed by essential oils of fruits of anise, medicinal herbs - rosemary, oregano and etc.
AmtersallComposition: ammonium chloride, sodium benzoate, potassium bromide, licorice root extract and herbs of thermopsis.Contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation, children under 3 years, peptic ulcer, hypersensitivity. Application: After meals, children 3-6 years old - 1 / 2hl. 3 r / day, 6-12 years - 1 teaspoon, 12-18 years - 1 dessert each. spoon, adults for 1 tbsp. l 3 r / day, the course of treatment 10-14 days. |
Mucolytic agents for coughing with bronchitis
Mucolytic agents help to dilute viscous sputum, improving the process of its removal, eliminating the nutrient medium for pathogenic microorganisms.
Acetylcysteine
Mucolytic agent, reduces the severity of the inflammatory process, reduces the frequency of exacerbations in chronic bronchitis. It is indicated for laryngitis (treatment in a child), otitis media, obstructive, acute bronchitis, pneumonia. Application: Duration of therapy for acute catarrhal diseases should not exceed 7 days, with chronic bronchitis a longer reception is possible. Preparations of acetylcysteine is better taken after eating, it should be borne in mind that always additional fluid intakeincreases the expectorant effect. Children 2-5 years of 100 mg 2-3 r / day, from 6-14 years 3 r / day for 100 mg, an adult at 200 mg 3 r / day or 600 mg once a day. Side effects: tinnitus, headache, stomatitis, vomiting, heartburn, tachycardia, lowering of blood pressure, bronchospasm, development of pulmonary hemorrhage, urticaria, skin rash. |
Bromhexine
Mucolytic agent, has expectorant and weak antitussive effect. The effect occurs within 2-5 days after the initiation of therapy. Side effects: vomiting, nausea, allergic reactions, headache, dizziness. |
Combined preparations Dzhoset, Ascoril, KashnolThey are used only for strict indications.On the appointment of a doctor with obstructive syndrome.
Ingredients: Bromhexine, Guaifenesin, Salbutamol. |
Ambroxolanalogs - Lazolvan (Table. syrup, bottles 200-360), Ambrobe (tab. ampoules, capsules, syrup 120-200 rub), Ambrohexal (tab. syrup 70-100 rubles), Ambroxol (Table. syrup 20-40 rubles), Ambrosan (tab. 100 rubles), Flavamed (tab. the flask. 150-200 rubles), Haliksol (tab. 100 rubles).This mucolytic, expectorant drug, Lazolvan - is today considered one of the most effective mucolytic drugs. Contraindicated: in 1 trim-re pregnancy, in 2 and 3 trim-re with caution, patients with chronic diseases of the liver and kidneys. Application: Take the tablets after meals for 30 mg. 3 r / day for adults. Children are shown reception in the form of a syrup up to 2 years, ch. 2 r / day, 2-6 years ch. 3 r / day, 6-12 yearsfor 1 tsp. 3 r / day, adults for 2 tsp. 3 r / day, the course of therapy is usually no more than 5 days. The syrup should be taken with a large amount of liquid during meals. Side effects: heartburn, vomiting, diarrhea, allergic reactions, skin rash. |
Carbocysteine
expectorant mucolytic agent, increases the viscosity of sputum, improves the elasticity of bronchial secretions. Application: 15 ml or 1 measuring cup 3 r / day, separately from food intake. The course of treatment can not be conducted for more than 8 days Side effects: gastrointestinal bleeding, nausea, vomiting, urticaria, skin itching, weakness, dizziness. |
zdravotvet.ru