 Stomatitis in children is a concept that unites a group of diseases accompanied by inflammation of the oral mucosa.This is the most common diagnosis in pediatric dentistry, which occurs even in newborns and in children under 1 year old.
Stomatitis in children is a concept that unites a group of diseases accompanied by inflammation of the oral mucosa.This is the most common diagnosis in pediatric dentistry, which occurs even in newborns and in children under 1 year old.
The sores that appear in the mouth often cause unpleasant taste sensations, and as a result, children often refuse to eat. But with the development of stomatitis there are not only difficulties with eating, sometimes enlarging lymphatic nodes, the child may have fever or general lethargy and worsening of well-being.
The urgency of the problem in childhood is due to the high prevalence and contagiousness of the disease. As a result of imperfections in local and general immunity, the most vulnerable to stomatitis are infants, children of early and preschool age.
What is stomatitis?
Stomatitis is a common name for various inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane of the child's mouth. According to statistics, children suffer from stomatitis from one to five years. Children under one year are still well protected by antibodies derived from breast milk, and are rarely encountered with stomatitis, children over five already can boast of their own formed immunity.
Diseaseprovoked by two basic conditions:
- Low immune defense of the child's body.
- Features of the structure of the mucosa.
The mucous membrane in children is very thin and easily traumatized. The resulting cracks often become infected, since the saliva of the child, especially at the age of one year, does not yet have the bactericidal properties that the saliva of an adult. So, in the course of inflammation, stomatitis is formed.
Symptoms of stomatitis in children
When stomatitis in children, the main symptom of the disease becomes a lesion of the mucous membrane of the mouth in the form of a light gray plaque capable of passing into erosion and aphthae (sores).
Depending on the focus of the lesion and the degree of spread of the disease, several types of stomatitis are distinguished:
- Herpetic stomatitis- the most common type of disease that can occur in both children and adults. With this kind of ailment, active irritation of the mucosa in the mouth is observed, which gradually turns into small vesicles with liquid. The acute form is accompanied by a high temperature, which is difficult to bring down antipyretic agents, dizziness, nausea, chills and other symptoms of acute respiratory viral infection may occur.
- Fungal stomatitis. Called the Candida fungus. This type of stomatitis is caused mainly by children up to a year due to breast-feeding. Milk is a breeding ground for the reproduction of fungi. Therefore such stomatitis name still "thrush". It is characterized by the appearance of a persistent white coating in the mouth of the baby. Do not confuse it with normal touch after feeding.
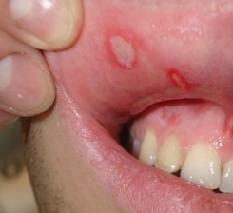
- Aphthous stomatitisin children it appears on the mucous membrane of the mouth in the form of aphthae from 5 to 10 mm in size on the inner sides of the lips and cheeks, the outer and inner sides of the tongue. Unlike herpes stomatitis, with aphthous in the mouth, only one sore is formed, in rare cases - two or three.
- Allergic stomatitismanifested in the form of redness of the gums, tongue. Subsequently, microbial flora can be attached and cause bacterial, fungal or viral stomatitis. The temperature may be normal, but may increase. If the pathogenic flora has not joined, then such a stomatitis is not contagious.
- Bacterial stomatitis. This type of disease is typical for children of different ages and is due to mechanical or thermal trauma oral cavity, as well as in violation of the rules of personal hygiene, during teething in children, etc.
How to treat stomatitis in children directly depends on the type of pathogen that caused inflammation. Most often, the disease develops against the background of a general decrease in the immunity of the child. Sometimes the cause of stomatitis in children, especially small children, is a common injury to the mouth, because kids are constantly pulling into their mouths different objects.
Stomatitis in children: photos
How does stomatitis in children in the mouth, in the photo, the initial and other stages.
Aphthous stomatitis
Clinically, ulcers resemble ulcers with herpetic stomatitis. But there are differences, aft - it is erosion of round or oval shape with smooth edges and a smooth bottom, the bottom of the aphtha is painted in bright red color. The main location of such ulcers on the mucous membrane of the lips and cheeks.
As the disease progresses, the aphtha changes and is covered with a cloudy film. After the film breaks, a secondary infection can join, which can complicate the course of the disease. The condition of the child at the same time changes, there is drowsiness, moods, lack of appetite, and often a refusal of food. Body temperature rises rarely, but it can stay within 38º.
Fungal stomatitis
This kind of stomatitis is provoked by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida, which enter the body of the child through household items, birth canals. Fungi multiply under favorable conditions (mucosal trauma, antibiotics) and cause disease.
Usually, candidal stomatitis in the first stage is not accompanied by obvious symptoms. The child experiences dryness in the mouth, slight itching and burning. Infants up to 12 months can be more often applied to the chest to compensate for the dry mouth, and older children, from 2-3 years, on the contrary, refuse to eat.
Children from 5-6 years complain of an unpleasant aftertaste and a smell from the mouth. With an external examination of the oral cavity, you can notice a grayish or yellowish coating on the mucosa. It has some similarities with droplets of sour milk or curd.
As the condition worsens, the mucosa quickly becomes covered with a white bloom, well, and if the form is started, then the mucous membrane is almost completely covered with such a coating, and also "jam" is formed in the corners of the mouth.
Herpetic stomatitis
Herpes stomatitis in children appears when the virus is infected with herpes simplex. The source of infection is both children and adults who have herpes on their lips and nose. On a vulnerable to any malaise the mucous membrane of the child's mouth, especially the newborn, the virus is transmitted immediately. The virus can be picked up not only by airborne droplets, but also through household items. The source of infection can be even an ordinary dummy.
The disease develops very quickly, the incubation period is up to five days and the disease is of mild, moderate and very severe form.
- Whenlight formsymptoms of intoxication are absent, at first there is an increase in temperature to 37.5º. The mucosa of the mouth becomes bright red, the formation of vesicles occurs, which is called the vesicle stage. Then they begin to burst, there is an erosion of the oral mucosa - this is the second stage of stomatitis. The rash becomes a marble color when the disease begins to go to a decline.
- Medium and heavy formthe disease manifests itself in the symptoms of intoxication of the child's body. Before the rash occurs, the general condition of the baby worsens, there are manifestations of weakness, drowsiness, the child does not want to eat. In the beginning, parents may think that this is an acute respiratory disease or a common cold. Lymph nodes increase, the temperature rises to the level of 38º. When the rash begins to appear, the temperature reaches 38 - 39º, possibly nausea and vomiting. It can spread not only the oral cavity, but also the surrounding tissues of the face. In addition, there is a sluggish saliva, gums are inflamed.
Every tenth child suffering from herpetic stomatitis, he can develop into a chronic stage and periodically there can be relapses. Most often occurs in children aged 1.5 to 3 years.
How to treat stomatitis in children
It is clear that the question of how to cure stomatitis in a child is very concerned about all parents. First of all, you should contact your dentist. He will make an accurate diagnosis, determining the nature of the onset of the disease, and then appropriate therapy is prescribed. The task of any parent is to follow clearly all the instructions of the specialist, because children, especially small ones, will not be treated themselves.
With any form of stomatitis it is important to adhere to a diet that excludes the ingestion of irritating food; after each ingestion rinse the oral cavity decoctions of herbs or antiseptics until the signs of the disease disappear (babies are irrigated with oral cavity from the can).
The principles of treatment of stomatitis in children can be reflected as follows:
- Anesthesia. This can be very convenient in the application of the drug "Lidochlor Gel", the effect of which begins almost immediately after application to the surface of the cheeks and gums, and the duration of its action - 15 minutes. Also, anesthesia emulsion is used for anesthesia with stomatitis.
- Treatment of not only affected areas, but also healthy tissues (to prevent damage) by a pharmacological preparation, affecting the main cause of the disease (antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, antiseptic).
Further, the treatment of inflammation of the oral mucosa depends on its type and origin.
Treatment of fungal stomatitis
To prevent the reproduction of the fungus in the mouth, it is necessary to create an alkaline environment in the oral cavity. For this, antiseptic solutions are used, which can be easily prepared at home. It:
- A solution of soda (2-3 h. l. for 250 ml).
- A solution of boric acid.
- Blue.
Processing the oral cavity needs 2-6 times a day. In this case, especially carefully the preparations are applied to the cheeks and gums, since it is there that accumulations of harmful microorganisms are located.
Another drug for the treatment of stomatitis is the Candide solution. Its active substance destroys the walls of the cells of the fungus. Course treatment is carried out within 10 days. At the appearance of the first signs of improvement, in no case should treatment be thrown, otherwise, as in the case of taking antibiotics, the resistance of the pathogen to the drug is formed.
In rare cases, you can use "Diflucan", it is prescribed for children during adolescence, the dosage is prescribed by a doctor.
Herpetic stomatitis: treatment
As with fungal stomatitis, acidic foods are excluded from the diet, especially citrus fruits, canned food, salty and spicy food. With herpes stomatitis in children, treatment includes both local procedures and the use of common therapeutic agents:
The main way to treat stomatitis in a child is taking special antiviral drugs (acyclovir, viferon in candles, viferon-ointment). At the heart of the disease is the herpes virus, which can not be disposed of forever, but it is possible, through a well-planned treatment, to suppress its activity. Immunostimulants are also recommended, because weakened immunity gives the disease progress.
For rinsing, it is optimal to use Miramistin solution. Rinse the oral cavity 3-4 times a day for 1 minute (by the way, a short time after rinsing you can immediately make an application of Viferon-gel, unless of course you use the gel, and not the candles). Miramistin in young children can be used as follows: moisten a gauze swab and treat them with the mouth cavity, or sprinkle the mouth cavity from the spray nozzle (included).
During illness the child needs a semi-postal regime. Refuse from walks and outdoor games. Remember that stomatitis is an infectious disease characterized by high contagiousness (it can be transmitted to others, especially weakened children and the elderly). Give the sick child a separate towel, his cutlery, try to reduce his contact with other family members.
It is very important to correctly distinguish herpetic stomatitis from aphthous, because they are treated with completely different medications. Therefore, it is advisable to treat stomatitis not independently, but by referring to a children's dentist!
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children
With aphthous stomatitis in a child, treatment is aimed at accelerating the healing of aft and anesthesia. Until now, widely used aqueous solution of methylene blue, or in common parlance - blue. The wound is treated with a cotton swab dipped in a solution, at least 3 times a day, better - 5-6 times.
Also, treatment should take into account the possible cause that caused the disease, because there are a lot of reasons and all of them require a different approach to treatment. Therefore, immediately after you find the aphthae in a child, you must immediately remove allergenic foods from your food (honey, strawberries, chocolate, nuts, citrus fruits ...), and also it is necessary to exclude from the diet spicy, spicy, rough food.
The selection of antiseptic, antimicrobial agents is often carried out by trial and error, since the course of any inflammatory process is individual, someone who is helped by the spray Lugol, spray Hexoral, or rinse with Iodinol, Miramistin, to whom Vinylin or methylene blue dye - Sinka - is very helpful. Rotocan, an antiseptic with a healing effect (for mouthwash), has proved to be very successful.
Treatment of bacterial stomatitis
Mucous one-year-old children are thin and easily injured, and in saliva there is still not enough enzymes to protect the body from external "enemies". Therefore, when stomatitis should often rinse the mouth with solutions of chamomile, chlorhexidine, furacilin, manganese, soda, strong tea or any other antiseptic.
The main treatment for bacterial stomatitis is chlorophyllipt (solution), oksolinovaya ointment. When the wounds begin to heal, they can be smeared with rosehip oil, propolis, aloe juice or calanchoe, vitamin A solution, solcoseryl.
Treatment of stomatitis in children: Dr. Komarovsky
Famous pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky will tell you how to treat a stomatitis in a child depending on its type, and what can be done at home.
Prevention
The main way to prevent stomatitis is to observe hygiene rules. We must ensure that young children do not lick dirty objects, hands.
It is noticed that children who are breastfed are less likely to get sick of all forms of stomatitis. The elders need to explain how important it is to wash their hands, brush their teeth and not take toys in the kindergarten.
Hardening, eating with a minimum of sugar and frequent outdoor activities will help to strengthen immunity, the child will not get sick, even if the infection gets into the mouth.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



