 Staphylococcus aureus is a very common and very dangerous conditionally pathogenic bacterium, which can affect any person regardless of sex and age. These microorganisms are widely distributed in the premises where there are many people.
Staphylococcus aureus is a very common and very dangerous conditionally pathogenic bacterium, which can affect any person regardless of sex and age. These microorganisms are widely distributed in the premises where there are many people.
The source of infection becomes an infected adult or child. Pathogenic microorganisms are activated in those who have a sharp decrease in immunity or worsening of the general condition.
One of the most difficult types of staphylococcus is golden. It is he who causes various diseases of the throat. And with its overly active reproduction, a person can get even a purulent sore throat.
Despite the fact that the microorganism itself has been sufficiently studied, the staphylococcal infection it causes remains one of the most serious diseases in terms of treatment. This interesting fact is due to the high variability of staphylococcus and its ability to quickly develop resistance to various antibiotics (especially when the patient does not comply with the dose, the frequency of medication and the duration of the course).
Staphylococcus aureus: what is it?
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that looks like a ball in appearance. The disease is very common. According to the data, 20% of the world's population is already a direct carrier of staphylococcus.
It is found everywhere: on the skin, in the nose, in the intestines, throat and even on the genitals. This prevalence also affects the number of diseases that can accompany and cause the bacterium.
Among the main causes contributing to the development of staphylococcal infection, identify:
- Presence of chronic diseases;
- Decreased immunity due to stress, beriberi, antibiotics, malnutrition and taking immunosuppressant medications;
- Interaction with a potential carrier of infection (eg, angina, which is transmitted by airborne droplets);
- Failure to comply with sanitary norms in the presence of cuts on the body, abrasions, open wounds. Infection of the wound with staphylococcus can lead to its suppuration and lead, ultimately, to infection of the blood;
- Use of unwashed fruits, vegetables and other bacterial products contaminated.
Often, the infection of Staphylococcus aureus affects children. Risk factors in this case are:
- Pathologically pregnant pregnancy;
- Prolonged anhydrous period in childbirth;
- Pregnancy during pregnancy;
- Hypotrophy of the newborn;
- The appearance of a premature baby;
- Non-observance of personal hygiene of the child.
The biggest problem in the fight against staphylococcus is that it has amazing viability. This microorganism can not be affected by cold, direct sunlight, or lack of moisture. Even a practically dried bacterium of staphylococcus retains its properties.
How is Staphylococcus aureus transmitted
In most cases, infection occurs in medical institutions. Staphylococcus aureus is transmitted both by airborne droplets and through food (contaminated meat, eggs, dairy products, cakes, cakes with cream) or household items.
Infection penetrate the baby's body also through microtraumas of the skin or mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. The maximum risk of infection is inflicted on premature infants and children with weakened immunity. During childbirth, through wounds or scratches, and also through breast milk, a mother can infect a child. If bacteria get into the mother's body through cracks in the nipples, it can lead to purulent mastitis in her.
Staphylococcus aureus in children and newborns
One of the toxins produced by the golden staphylococcus - exfoliatin has the property of greatly affecting newborns. The secreted poison penetrates into the pores of the skin and provokes the appearance of blisters, outwardly resembling burns, and because of this they have received the name of the syndrome of the "scalded baby".
This disease rarely affects newborns, as they are protected in 6 months by the immunity received from the mother's milk, In parallel with the contact of the baby with bacteria, additional immunity is produced, which continues to protect it. To prevent illness, the child should carefully monitor his hygiene and nutrition.
What is the danger of this bacterium?
With a weakening of the defenses of the body, the infection wakes up and causes various diseases, up to the infection of blood or sepsis. High pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus is associated with three factors.
- First, the microorganism has a high resistance to antiseptics and environmental factors (can withstand boiling for 10 minutes, drying, freezing, ethyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, except for "green").
- Secondly, Staphylococcus aureus produces enzymes penicillinase and lidase, which makes it protected from almost all antibiotics penicillin series and helps to melt the skin, including sweat glands, and penetrate deep into the body.
- And thirdly, the microbe produces endotoxin, which leads to both food poisoning and the syndrome of general intoxication of the body, up to the development of an infectious-toxic shock.
And, of course, it should be noted that there is no immunity to the disease, so an adult or child who has managed to cure Staphylococcus aureus can get infected again.
Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus
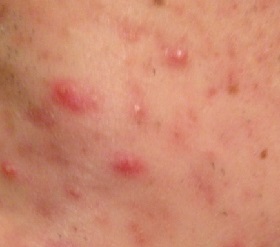 In children and adults, staphylococci cause various lesions - abscesses, sycosis, hydradenitis, dermatitis, carbuncles, eczema, periostitis, panaritium, osteomyelitis, blepharitis, folliculitis, furuncles, pyoderma, pneumonia, meningitis, peritonitis, cholecystitis, appendicitis.
In children and adults, staphylococci cause various lesions - abscesses, sycosis, hydradenitis, dermatitis, carbuncles, eczema, periostitis, panaritium, osteomyelitis, blepharitis, folliculitis, furuncles, pyoderma, pneumonia, meningitis, peritonitis, cholecystitis, appendicitis.
Consider the most common diseases that can cause Staphylococcus aureus.
- Gastrointestinal tract. Within several hours after the adoption of food, which was contaminated with staphylococci, the development of foodborne toxemia begins. Multiple vomiting begins, nausea and dryness in the mouth appear. Disturbances and pain in the abdomen are disturbing.
- Skin diseases. Depending on the area affected by staphylococcus, skin diseases are divided into phlegmon or abscesses, boils or carbuncles. The furuncle is characterized by a slight reddening, denseness and soreness of the skin, carbuncle is a more serious disease involving several hair follicles. May be accompanied by fever, weakness, loss of strength.
- Pneumonia: most common in children, especially in small children, is also diagnosed in weakened people; characterized by a short period initial fever with rapid development of respiratory failure, severe obstruction symptoms may occur.
- Mucous membranes. Often, the pathogen is found in the nasopharynx and throat. If an infection develops, inflammatory processes are observed in the ears, nose, throat. In severe forms otitis and sinusitis occur. Not always the pustular secret comes to the surface. Unfortunately, this makes diagnosis difficult.
- Bacterial endocarditisis one of the complications of staphylococcal bacteremia. The most frequently developed and individuals with weakened immune system, as well as drug addicts.
- Ritter's diseaseor the syndrome of "scalded skin" is another manifestation of staphylococcal infection, found mainly in newborns and young children. The manifestations of the disease may resemble scarlet fever (a similar rash) or erysipelatous inflammation (the focus of red inflamed skin with flat boundaries), occurring in streptococcal infections.
- Toxic shockis the most severe disease that causes Staphylococcus aureus. It begins suddenly and proceeds with fever, dizziness and headache, low blood pressure, palpitations and vomiting. Throughout the body or in some places there is a rash in the form of spots. After a week, skin flaking occurs.
As you can see, depending on the area of lesions of Staphylococcus aureus, the symptoms in children and adults have a cardinal difference. They are directly related to the place of introduction of the bacterium into the body, the state of the patient's immune system and the aggressiveness of the pathogen. Corresponding to how to treat Staphylococcus aureus will depend on the specific site of infection.
How to prevent infection
Adhere to certain preventive measures to avoid infection.
- Observe the hygienic rules, wash your hands well;
- Do not touch, do not comb the wounds, rashes on the skin;
- Do not use other people's hygiene items: razors, combs, towels, etc .;
- Follow all the rules for heat treatment and storage of food.
It should be noted that severe forms of staphylococcal infection are rare and, as a rule, in children with poor health, congenital diseases, malformations.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in adults
Staphylococcus is an unusually tenacious bacterium. As they say, it does not sink in the water, it does not burn in the fire. Highly resistant to environmental factors. Do not always die with various methods of disinfection: boiling, quartz, antiseptic, disinfection, autoclaving. This is the difficulty of treating Staphylococcus aureus. It is difficult to select antibacterial drugs that would affect staphylococcus aureus. Immunity to this bacterium is not produced, diseases can be repeated.
Cure Staphylococcus aureus is possible, but due to the fact that this microorganism is able to develop resistance to antibiotics, the process of treatment is sometimes complicated. The course of prescribed antibiotics must be fully completed, since if the patient does not complete the course, then not all the golden Staphylococcus aureus (in the intestine or other organ), and subsequently it will acquire resistance to this drug.
If the antibiotic therapy is ineffective or impossible, patients are prescribed a staphylococcal bacteriophage, which, in fact, is a bacterial virus. Its advantages are that it affects only certain pathogenic microorganisms without damaging the normal microflora, has no contraindications and side effects.
The most terrible enemies of staphylococcus are a solution of brilliant green (common green) and chlorophyllipt in the form of an oily or alcoholic solution. Zelenka is used to treat wounds on the skin. Chlorophyllipt is prescribed by a doctor for sanation of the nasopharynx and throat.
Staphylococcus aureus in the intestine: symptoms and treatment
In most cases, the incubation period after infection with the type of bacterium considered is no more than a day, so the first signs can appear only after 5-6 hours.
Staphylococcus aureus in the intestine has the following symptoms:
- a digestive disorder, expressed by a liquid stool, while urinating in the toilet is very frequent (up to 10 times a day), and the consistency of the outgoing masses is watery with impurities of mucus or even blood;
- cutting intense pains in the epigastric region and in the lower abdomen;
- nausea, severe vomiting;
- noticeable intertrigo;
- increase in body temperature to low values;
- weakened body, fatigue.
"Struggle" with staphylococcal infection is directed to:
- suppression of activity of the pathogen;
- improvement of immunity;
- stimulation of metabolic processes;
- treatment of chronic diseases that weaken the body.
The choice of the method of treatment is based on the results of the analysis of stool.
Staphylococcus aureus in the nose: symptoms and treatment
The favorite habitat of Staphylococcus aureus is the nasal cavity. And it can be found in completely healthy people. Many for a long time are simply carriers of a pathogenic bacterium.
Symptoms of staphylococcus in the nose include:
- reddening of the nasopharynx lining the mucous epithelium;
- atrophy of the mucosal epithelium of the nasopharynx;
- a cold that is insensitive to the treatment;
- increased body temperature;
- general intoxication;
- the appearance on the nasal mucosa of the pustular formations.
The presence of staphylococcal infection often leads to the development of sinusitis, chronic rhinitis, frontal sinusitis, as well as atrophy of the nasal mucosa. Treatment of staphylococcus in the nose is necessary in those cases when the disease leads to inflammatory processes and the occurrence of sinusitis, chronic or acute rhinitis. Its activity in the body is due to the weakened immunity.
Staphylococcus aureus in the throat: symptoms and treatment
The carrier of the infection, as a rule, is asymptomatic. With a weakening of the body's defenses, Staphylococcus aureus in the throat can cause symptoms of purulent sore throat:
- sudden rise in body temperature;
- Strong headache;
- weakness, worsening of appetite;
- an increase in tonsils, which can cause discomfort when swallowing food, hyperemia of the mucosa and the appearance
- purulent plaque;
- increased regional lymph nodes.
A distinctive feature of these diseases in the presence of Staphylococcus aureus is a purulent discharge in the throat. As a treatment for staphylococcus in the throat, antibiotics are usually prescribed by a specialist to cope as soon as possible with the infection and prevent the likelihood of relapse, at least for the near future.
Before treating staphylococcus in the throat, it is necessary to take into account the presence of individual intolerance components of the medicine, so for each patient should be selected a special set of treatment. Dosage is also established by the attending physician in dependence and it depends on the age and weight category.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



