 Lung tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by mycobacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis), characterized by the formation of specific foci of inflammation in the affected tissues and a pronounced reaction of the organism.
Lung tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by mycobacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis), characterized by the formation of specific foci of inflammation in the affected tissues and a pronounced reaction of the organism.
Recently, in most economically developed countries, the incidence of pulmonary tuberculosis and mortality from it decreased. But despite this, tuberculosis is still a widespread ailment, affecting, to a greater extent, teenagers, young children, adult women and the elderly of both sexes, and to a lesser extent adult men.
As a rule, the onset of the disease is associated with a decrease in the body's immune defenses. Getting into a weakened organism, mycobacteria begin to multiply and cause the development of inflammation in the lungs, consisting of the so-called tuberculosis granulomas.
It is generally accepted that tuberculosis is a disease of low-income people living in conditions of unsanitary people. In fact, no one is insured against this disease - people of absolutely any age and social status suffer from it. In this article, we will talk about the symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults, the first signs in the early stages, as well as the principles of treating this disease.
Causes
The causative agent of tuberculosis was discovered in 1882 by the scientist R. Koch, as a result of which the name of Koch's wand is still widespread. Infection can affect any organ, but most often the pathological process involves the lungs. In the 19th century, tuberculosis was one of the main causes of death.
This indicator was significantly reduced in the 20th century, thanks to improvements in overall sanitation, the emergence of antibiotics and vaccination. In recent years, repeated outbreaks of tuberculosis have been observed due to an increase in the number of HIV-infected people who have a frequent complication of this infection.
Infection occurs from a sick person by airborne droplets, less often through raw milk from a cow affected by tuberculosis. But the disease may not appear if the human body copes with the infection. The onset of the disease is facilitated by weakened immunity, poor nutrition, nervous or physical exhaustion of the body, unsatisfactory sanitary and hygienic living conditions.
The incubation period (from the inflow of infection into the body to the development of manifestations of the disease) can last dozens of years. At the risk of developing the disease are people with chronic pathology (diabetes, HIV, chronic heart disease, etc.), patients with mental illness, people without a fixed place of residence, drug addicts, persons who are in prison.
Tuberculosis of the lungs: open and closed form
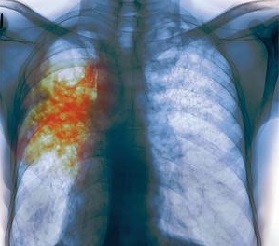 The term open tuberculosis means that the patient emits microbes of tuberculosis pathogens into the environment. This term is applied, mainly to pulmonary tuberculosis, in which the isolation of microbes occurs during coughing, expectoration of sputum.
The term open tuberculosis means that the patient emits microbes of tuberculosis pathogens into the environment. This term is applied, mainly to pulmonary tuberculosis, in which the isolation of microbes occurs during coughing, expectoration of sputum.
Open formalso called BK + (or TB +) - this means that when a microscopic examination of the sputum smear of the patient showed bacteria germs of tuberculosis (BK - bacillus Koch, TB - tubercular bacillus). In contrast to the BC + form, there is a form of BK- (or TB-), which means that the patient does not isolate microbes to the environment and is not contagious.
Termclosed tuberculosisis used rarely, its equivalents BK- (or TB-) are more often used. A patient with a closed form can not infect other people.
Primary and secondary
The most important clinical significance is the division of the disease into primary and secondary.Primary tuberculosisoccurs if the disease developed as a result of the first contact of a person with a microbacterium that causes tuberculosis. In this case, the organism of the patient with the infection is not yet familiar.
In the primary type, the inflammatory process ends with the formation of fossilized foci. In them, microbes can still "doze" for a long time. Under certain conditions, for example, if immunity decreases, the infection can become active again, then a new episode of the disease begins.
Cases of the occurrence of a repeated episode of the disease and it is customary to callsecondary tuberculosis, when the body with the infection is already familiar. It proceeds differently than it happens when a person falls ill for the first time.
Signs of pulmonary tuberculosis in the early stages
Tuberculosis of the lungs can last for a long time without symptoms or malosymptomatically and can be detected by chance during fluorography or chest x-ray.
The fact of seeding the body with tuberculosis mycobacteria and the formation of specific immunological hyperreactivity can also be detected when tuberculin samples are taken. In cases where the disease manifests itself clinically, usually the earliest signs of pulmonary tuberculosis in the early stages are:
- weakness;
- decreased efficiency;
- fast fatiguability;
- increased sweating;
- a prolonged increase in body temperature (as a rule, low figures are typical - up to 38 ° C, but may be higher);
- decreased body weight;
- decreased appetite;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- apathy, loss of mood, loss of interest in the world around them.
Often there is a generalized or limited by any group of lymph nodes lymphadenopathy - an increase in the size of the lymph nodes.
Symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults
As the development of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults, more or less obvious symptoms from the side of the affected organ are added. With this disease, it is coughing, sputum discharge, wheezing in the lungs, a runny nose, sometimes shortness of breath or pain in the chest (usually indicating the adherence of tuberculous pleurisy), hemoptysis.
Symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults are:
- constantly elevated temperature (not above 38 ° C);
- headache;
- weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- cough (both dry and with sputum, with blood in sputum);
- dyspnea;
- sweating at night.
There are mood swings, irritability, decreased efficiency. Only 1-2 symptoms can manifest, and not necessarily a cough. Therefore, if any of these symptoms appear, it is recommended not to be treated independently, but to consult to the doctor, in time to diagnose possible tuberculosis and begin its timely treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of this dangerous disease is made only by a doctor. An X-ray examination is necessary to determine the disease. Also, for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis, sputum is examined for the presence of microbacteria of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis in children may indicate positive Mantoux test. In some cases, for reliability, a blood test is taken.
Complications
The disease can lead to such consequences in adults:
- Pulmonary haemorrhage. Its massive nature and technical difficulties in stopping it - often cause death.
- Spontaneous pneumothorax. Penetration into the pleural cavity of air in a significant amount in cavernous forms can lead to a displacement of the mediastinum and a reflex stop of the heart.
- Tuberculous pleurisy. Exudative forms, with a gradual accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity, also lead to the progression of respiratory and subsequent cardiac failure.
- Process Generationby the hematogenous spread with the development of tuberculosis sepsis.
- Development of chronicpulmonary heartby increasing the pressure in a small circle of circulation with significant changes in the tissues of the lungs.
Prevention
To prevent tuberculosis, it is necessary to identify cases of the disease in a timely manner. For this you need to do fluorography regularly. It is necessary to limit contacts with people suffering from tuberculosis. For this, those suffering living in overcrowded apartments need to be isolated from the rest of the tenants. It is important to vaccinate the newborn in time.
One of the ways of infection is through food. It is very important to establish careful monitoring of milk and meat, as well as to regularly inspect workers working with cattle.
Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis
 Until the 20th century, tuberculosis was practically untreatable. Now there are many anti-tuberculosis drugs. And still the problem is quite acute.
Until the 20th century, tuberculosis was practically untreatable. Now there are many anti-tuberculosis drugs. And still the problem is quite acute.
Many patients do not know that they suffer from this disease, some do not want to go to the doctor and are treated independently. But this is dangerous, because with an incorrect treatment an easily curable form of tuberculosis can go into a drug-resistant form.
Cure tuberculosis in adult women and men is possible only as a result of the use of a whole complex of anti-tuberculosis drugs. How to treat tuberculosis: the appointment schedule, the doses used and the duration of therapy are determined only by the doctor.
One of the important moments in the treatment is the very mood of the patient for a speedy recovery. Since this process is rather lengthy, usually taken from 3 to 18 months, very often patients simply do not have the patience to bring the treatment to an end. Also, the accompanying pathologies, such as alcoholism and drug addiction, can interfere with the healing of the patient.
In conclusion: remember, the earlier you identify the symptoms of the disease, the more likely you will be to get better recovery and easier treatment. It is necessary to pay attention to one's own state of health and to undergo a medical examination in a timely manner.
Spa treatment
In the case of pulmonary tuberculosis, the most important stage on the way to recovery is sanatorium-and-spa treatment. It is recommended for all patients at the stage of convalescence (recovery), as well as for mild degrees of severity of the disease.
It is contraindicated in the open forms of the disease, bacterial release, miliary tuberculosis. The method of sanatorium-and-spa treatment of tuberculosis shows itself well in complex treatment in children. Positive influence is achieved due to the complex effects of climatic factors, therapeutic physical training, diet nutrition.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



