 Shingles are also called zoster herpes - a viral infection, which is accompanied by severe pain and skin rashes.
Shingles are also called zoster herpes - a viral infection, which is accompanied by severe pain and skin rashes.
The disease provokes the herpes virus (herpes zoster), it acts as the causative agent of chickenpox, which in medical circles is called "chicken pox".
Appearances of shingles occur, as a rule, in winter and autumn, and more often, in older people. This time and age are due to a simple fact - the state of immunity, which is lower in these seasons, and weakened in the elderly due to age.
Causes
What it is? So, shingles are essentially herpes. But that's not the one we usually call a cold. Everything is much more serious here. It's about Varicella zoster. He is familiar to many on an active childhood disease - chicken pox.
A person who has been ill with chicken pox becomes a carrier of a virus that has been inactive for a long time. Usually the virus is localized in the nerve tissues. According to doctors, the virus becomes active, most often due to weakening of immunity, frequent stress and nervous overstrain.
Provoke developmentshingles in adults can:
- Strong stress, debilitating work;
- taking drugs that lower the defenses of the body;
- various malignant tumors, lymphogranulomatosis and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas;
- the effect of radiation therapy;
- transplantation of bone marrow and organs;
- HIV infection in the stage of transition to AIDS.
Weakened immunity is the reason that this disease most often appears in older adults and those who have recently suffered hormonal, radiation or chemotherapy.
Classification
In most cases, shingles occur in a typical form that is classified as ganglionic, its symptoms will be described below. But in some cases, the disease can manifest itself in other clinical forms:
- Ear. The rash is localized on the auricle, in the external auditory canal.
- Eye. Eruptions are chosen as the site of localization of the trigeminal nerve branch and appear on the skin of the face, the mucous membrane of the nose, and the mucous membrane of the eyes.
- Gangrenous (necrotic). It develops in people with weakened immunity.
- Meningoencephalitic. It occurs quite rarely and differs in severe course.
- Abortive. It is considered the easiest form of the disease, characterized by the absence of a bubble rash and severe pain syndrome.
- Bubble. This form is accompanied by the appearance of large blisters filled with serous fluid.
- Hemorrhagic. This form is characterized by the appearance of bubbles filled with bloody contents.
Symptoms of shingles in adults
The total period of the course of herpes zoster in a person from the appearance of the first symptoms to the complete disappearance of scabs on the skin is usually 20-30 days. Sometimes the disease can completely end in 10-12 days.
It is very characteristic of herpes zoster that the rashes with it appear from any one side of the body. In the overwhelming majority of cases, all external manifestations of shingles are on the body - within the chest, abdomen and pelvis. In more rare cases, they can be localized on the hands, feet and head.
The initial period of the disease is similar to manifestations of a cold or ARVI. It is characterized by general malaise, neuralgic pain of varying intensity, it lasts an average of 2-4 days:
- Headache.
- Subfebrile body temperature, less often fever up to 39C.
- Chills, weakness.
- Dyspeptic disorders, gastrointestinal disturbances.
- Pain, itching, burning, tingling in the peripheral nerves in the area where there will be rashes.
- Most often, with an acute process, they become painful and regional lymph nodes increase.
- In severe cases, there may be a delay in urination and other disorders of certain systems and organs.
The next stage is characterized by the appearance of edematous pink spots, they are grouped into erythematous papules within 3-4 days, which quickly turn into vesicles. Approximately on the 6th-8th day, the vesicles begin to dry out, yellow-brown crusts appear in their place, which later fall off on their own, in their place may be retained an insignificant pigmentation.
Painful sensations, called even postherpetic neuralgia, can torment a person for several weeks, and even months after the disappearance of other symptoms depriving.
Atypical Current
The above-described clinic is typical for a typical form of the disease, but sometimes rashes may have a different character:
- Abortive form- after the formation of papules, the rash sharply regresses, bypassing the bubble stage.
- Bubble formdiffers by the development of larger bubbles, grouped; exudative elements can merge, forming bubbles - with uneven scalloped edges.
- Bullous form- the vesicles merge, forming large bubbles with hemorrhagic contents.
- Gangrenous formshingles - the most severe manifestation of the disease; ulcerative-necrotic changes develop on the site of the vesicles - with an outcome in cicatrization; while a severe general condition is observed (reflects pronounced immunosuppression).
- Generalized form- After the appearance of local rashes, new vesicles spread throughout the surface of the skin and mucous membranes (a similar form is often found in immunodeficiencies).
It is worth noting that, before the rash appears, the diagnosis of herpes zoster is practically impossible. The arising pains (depending on localization) can remind illnesses of heart, lungs, nervous system. After the development of a characteristic rash - with one-sided localization of exudative elements along the nerves (monomorphic elements - vesicles different sizes), as well as pronounced neurologic pains - the diagnosis of herpes zoster - does not cause difficulties.
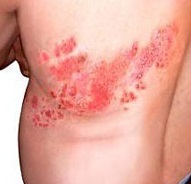
Shingles: photo
As the herpes zoster in an adult person, we offer a detailed photo of the rashes on the skin.
Complications
In severe clinical course and inadequate treatment, shingles can lead to serious complications:
- The most frequent (up to 70%) is postherpetic neuralgia. Pains along the nerve are left for months, and some last for years, and the older the patient, the more likely that this complication will develop;
- Paralysis, manifested by the defeat of the motor branches of the nerves;
- Paralysis of the facial nerve and skewing of the face on one side;
- Inflammation of the lungs, duodenum, bladder;
- Eye lesions of varying severity;
- Meningoencephalitis is an extremely rare, but the most dangerous complication. In the period from 2 to 20 days from the onset of the disease there is a severe headache, photophobia, vomiting, there may be hallucinations and loss of consciousness.
In connection with the risk of development of consequences, specialists urge patients to refuse self-treatment at home and on time to seek help from specialized institutions.
Treatment of shingles in humans
Uncomplicated cases are treated at home. Hospitalization is indicated to all people with suspected disseminated process, with damage to the eyes and brain.
In most cases, shingles in an adult can go away on their own in the absence of treatment. However, without the use of medication, the probability of serious complications of the disease is high, as well as the inability to tolerate severe pain in the acute and chronic phase. Methods of therapy are aimed at accelerating recovery, reducing pain and preventing the effects of herpes.
The scheme of treatment of herpes zoster in humans is based on the use of the following drugs:
- Antiviral drugs. For treatment of herpes zoster, acyclovir, valaciclovir and famciclovir are used. At the start of therapy within 72 hours of the appearance of the first rash, they are able to reduce the severity of pain, reduce the duration of the disease and the likelihood of postherpetic neuralgia. Famciclovir and valaciclovir have a more convenient mode of administration than acyclovir, but they are less studied and several times more expensive.
- Anesthetics. Anesthesia is one of the key moments in the treatment of herpes zoster. Adequate anesthesia makes it possible to breathe normally, to move and to reduce psychological discomfort. Of the common analgesics use: Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Dexketoprofen, etc.
- Anticonvulsants. Anticonvulsants are commonly used for epilepsy, but they also have the ability to reduce neuropathic pain. With Herpes zoster, some of them may be used, for example gabapentin and pregabalin.
- Antidepressants. The positive role of antidepressants in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia is shown.
- Corticosteroids. Reduce inflammation and itching. Some studies have shown their ability in combination with antiviral agents to reduce the symptoms of mild and moderate-severe forms of the disease. However, these drugs are not currently recommended for use in this disease.
The purpose of drug therapy is primarily for those people who have a high risk of complications, as well as in the prolonged course of the disease. Drug therapy is indicated for persons with immunodeficiencies and patients whose age has exceeded the 50-year-old barrier. The effectiveness of antiviral therapy in young and healthy people is not proven.
When shingles, it is important not to panic. In most cases, timely initiated antiviral treatment gives a quick result and helps to avoid complications. However, to neglect a visit to a specialist, especially if a facial or trigeminal nerve is involved, is also not worth it.
To which doctor to apply
When there are bubbles on the skin or mucous membranes, you need to contact a dermatologist. In some cases, an additional examination of the neurologist is required. With prolonged, severe, recurrent course, it is necessary to consult an immunologist and infectious disease specialist.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



