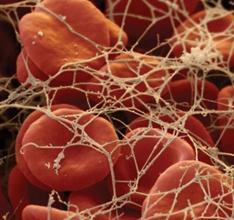
 Protein fibrinogen - a soluble and transparent component of blood serum, the basis of blood clots, is formed by the liver, is updated every 3-5 days.
Protein fibrinogen - a soluble and transparent component of blood serum, the basis of blood clots, is formed by the liver, is updated every 3-5 days.
When the plasma system of blood coagulation is activated by thrombin, it turns into monomers, which then drop out in the form of insoluble filaments. This is already a fibrin-polymer, of which the thrombus consists.
In the transcripts of blood tests, elevated fibrinogen indicates inflammatory processes. As the concentration of fibrinogen increases, the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation (ESR, sometimes ROE) increases. Marker of inflammation and tissue necrosis. Similarly, an increase in the concentration of FA indicates an increased risk of complications of cardiovascular diseases.
Especially it is necessary to note, that at pregnancy there is an increase in the maintenance of the specified fiber in a blood plasma and it is normal
Fibrinogen - what is it?
Fibrinogen is the first factor of the plasma clotting system, its level is determined before operations, childbirth, with liver disease, propensity to thrombosis or bleeding, cardiovascular pathology.
Main functions, performed by fibrinogen:
- direct participation in the formation of a fibrin clot;
- direct influence on wound healing speed;
- regulation of fibrinolysis;
- participation in angiogenesis (synthesis of new vessels) and in cellular interaction;
- has an effect on blood and on the wall of the arteries in inflammatory processes in the body.
Necessity of blood donation to fibrinogenoccurs at the following indications:
- with suspicion of hemophilia;
- in preparation for operations, as well as in the postoperative period;
- with diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- with pathology of the liver;
- during pregnancy (Pregnant women need to take a similar analysis every trimester to
- avoid possible complications.);
- in inflammatory processes, the etiology of which is unclear.
The critical rate of fibrinogen in the blood is 2 mg / l, if lower than this index, any intervention will be fatal. A value higher than 4 indicates a risk of thrombotic complications.
The norm of fibrinogen in the blood of women, men
The norms of mass fractions of fibrinogen, adopted by modern clinical studies in different people:
- adults (men and women): 2-4 g / l;
- pregnant women (maximum values for the third term): 6-7 g / l;
- in newborns: 1.25-3 g / l.
To determine the level of fibrinogen for analysis, venous blood is taken. It is necessary to give an analysis on an empty stomach (not earlier than twelve hours after eating). It is necessary to exclude physical activity within two hours before the delivery of this analysis. And forty minutes before the delivery of venous blood it is important to exclude smoking.
Fibrinogen in pregnancy
The first trimester of pregnancy in normal fibrinogen should be approximately 2.98 g / l. This is slightly below the norm, but the state of toxicosis of a pregnant woman is always taken into account. The second trimester - fibrinogen begins to rise, and, as a rule, is 3.1 g / l. And the third trimester is characterized by a significant increase in this protein - from 4.95 to 6 g / l.
High levels of fibrinogenand activation of the coagulation system lead to:
- Infertility;
- Premature detachments of the normally located placenta;
- Thrombosis of the umbilical cord;
- Gestozam;
- Spontaneous abortions in the early stages;
- Non-developing pregnancies;
- Premature birth;
- Thrombosis and thrombophlebitis in the mother.
To timely implement appropriate therapy, doctors prescribe the delivery of a coagulogram several times during the entire gestation period. The first analysis, conducted at the initial time, gives an idea of the baseline level of fibrinogen, and performed before childbirth shows: whether there is a danger of thrombosis and whether the body is ready for delivery.
Fibrinogen is above normal - what does it mean?
Fibrinogen above the norm means that the hemostasis system is activated and there is a danger of excessive formation thrombi or in the body the acute phase of the inflammatory process, as a rule, is severe.
Thus, a high level of this factor is observed in severe pathological conditions affecting vital organs and the whole organism as a whole:
- rheumatism;
- myocardial infarction;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- infectious diseases;
- diabetes;
- pneumonia;
- mild forms of hepatitis;
- the first stage of DIC syndrome;
- tuberculosis;
- oncology;
- any acute conditions of the body, such as a variety of injuries, burns.
Also, the increase in the formation of fibrinogen occurs during pregnancy, this is due to natural physiological processes. Its maximum concentration of fibrinogen reaches the third trimester - up to 7 g / l. Elevated indicators are observed with oral contraception and estrogen administration, as well as with age.
Fibrinogen is below normal - what does it mean?
If the fibrinogen content in the blood is below normal, its coagulability also deteriorates, which in turn can cause prolonged bleeding. The cause of this condition can be both congenital, and act as a result of a number of diseases. Because of what can decrease fibrinogen?
The main causes of low fibrinogen:
- DIC-syndrome - a severe violation of hemostasis, in which a large number of microthrombi is formed in small vessels;
- severe liver disease (cirrhosis);
- toxicosis during pregnancy (early and late);
- hypovitaminosis C and B12;
- congenital pathologies (afibrinogenemia and hypofibrinogenemia);
- poisoning with poisons (bites of poisonous snakes);
- reception of anticoagulants (streptokinase, urokinase);
- embolism with amniotic fluid (in a newborn);
- polycythemia (increased blood cells);
- reception of anabolics, androgens;
- reception of fish oil.
The lowered level of fibrinogen is also noted
- from vegetarians,
- when taking antioxidants (vitamin E),
- with the dosed use of alcohol.
The amount of fibrinogen, less than 0.5-1 g / l, threatens the risk of bleeding of the vessels of internal organs.
What to do?
It must be remembered that a decrease or increase in the level of fibrinogen is a laboratory symptom. A blood test for fibrinogen will detect abnormalities. In the case of a change in this indicator, a comprehensive supplementary examination is needed to find out the diseases that led to this.
Lack of adequate treatment can lead to severe internal and external bleeding when it decreases, or to increased thrombosis at high concentrations.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



