 Tuberculosis of the skin - this is a very extensive and diverse in its manifestations of a group of dermatoses, the emergence and the development of which is due to the penetration of tuberculous mycobacteria into the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
Tuberculosis of the skin - this is a very extensive and diverse in its manifestations of a group of dermatoses, the emergence and the development of which is due to the penetration of tuberculous mycobacteria into the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
There are focal (vulgar lupus, scrofuloderma, warty and ulcerative tuberculosis) and disseminated (papulonecrotic tuberculosis and erythema inducible) forms of skin tuberculosis.
Causes
In almost all cases, tuberculous skin lesions are secondary and endogenous. The causative agent usually enters the skin and subcutaneous tissue with lymphohematogenous path from the foci of tuberculosis in other organs, sometimes the infection penetrates in the skin along the length - from the affected neighboring organs; Exogenous infection of the skin is very rare - through its damage.
Significantly reduce the protective functions of the body can certain factors that can increase the risk of contracting tuberculosis of the skin. Such factors include:
- pathology of the nervous system;
- hormonal dysfunction;
- disorder of mineral and water metabolism;
- vitamin imbalance;
- certain vascular disorders;
- unsatisfactory climatic and living conditions;
- presence of various infectious diseases;
- To provoke sharp decrease in immunity can and a HIV.
Social factors also play an important role: living conditions, environmental factors and nutrition. No less important are the climatic conditions - the absence of sunlight and dampness can become provoking factors in the development of the disease.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis of the Skin
 Tuberculous skin lesions have numerous symptoms, which vary in the form of infection, the course of the disease and the way skin tuberculosis looks.
Tuberculous skin lesions have numerous symptoms, which vary in the form of infection, the course of the disease and the way skin tuberculosis looks.
The whole group of diseases is divided into localized (focal) and disseminated (spread) skin tuberculosis.
The focal forms of the disease include:
- Scrofuloderma. In the submandibular region, on the neck, chest, limbs, there are single or multiple bluish-red nodes with subsequent central softening and the formation of deep, soft, almost painless ulcers with overhanging edges, connected together in depth by fistulous movements. The course of the process is chronic with a tendency to spontaneous cure. After healing of ulcers, irregular "bridge-like" scars remain. It is observed mainly in children and adolescents suffering from tuberculosis of the subcutaneous lymph nodes, from which the process passes to the subcutaneous fatty tissue.
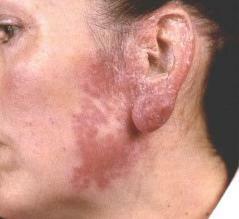
- Vulgar (vulgar) lupus- the most common form of the disease. A characteristic feature is a chronic course with slow progression. In most cases, lesions are localized on the face: nose, cheeks, lips. The first signs of lupoid skin tuberculosis are small rashes of brownish-red color. To the touch they are soft and smooth and only later they begin to peel off. Lupomas are most often localized in groups at a distance from each other and only with the course of the disease can merge. In the case of pressing the group with a lump of them to bleed, and the empty holes have a yellowish tinge. Often there are cases when the disease began in childhood and lasted a lifetime.
- Warty tuberculosis of the skin. It is localized point-by-point, in the places of penetration of tuberculosis infection. This type of disease can be attributed to the shortcomings of such professions, as a veterinarian, a pathologist, a butcher, which implies physical contact with the pathogen. As a rule, warty tuberculosis of the skin develops on the hands and feet.
- Ulcerative tuberculosis. Most often occurs in people with an open form of tuberculosis of the lungs, kidneys or intestines. It manifests itself in the form of bleeding ulcers. The ranks have an uneven surface and are covered with knots of yellow hue.
Among the disseminated forms distinguish:
- Papulonecratic skin tuberculosis. Appears at a young age in the form of small cyanotic-red nodules with a necrotic scab in the center, on the fall of which remain "stamped scars." Eruptions are symmetrical, mainly on the limbs and buttocks. Subjective sensations are absent. The course of the process is recurrent.
- Lichenoid skin tuberculosis(he deprive me of scrofula). Characteristic is the appearance of nodules the size of a pinhead to millet grains, a pinkish-brownish color, a softish consistency. Nodules are often associated with the skin follicles, on their surface are small scales. Eruptions are located on the body symmetrically, more often on the lateral surfaces of the chest. It develops in weakened children against active tuberculosis of the lungs, lymph nodes or osteoarticular tuberculosis.
The diagnosis of skin tuberculosis is based on anamnesis, clinical features, the presence of damage to other organs, positive tuberculin tests, isolation of tuberculous mycobacteria from ulcerative foci. In difficult cases, a pathohistological examination of the skin, inoculation with experimental animals and trial treatment is performed.
Skin Tuberculosis: Photo
What the disease looks like, we offer to view some photos.
Treatment of skin tuberculosis
With tuberculosis of the skin, treatment should be comprehensive taking into account the age of the patient and the concomitant pathology:
- impact on the infection;
- influence on the sick organism as a whole (immune status) and on the pathological
- processes (pathogenetic treatment);
- decrease in the level and elimination of symptoms of the disease;
- local treatment.
The tuberculosis process is difficult to treat. The patient needs a lot of patience and self-discipline. The disease affects not only the affected organ, but the whole body as a whole. Treatment is conducted in anti-tuberculosis facilities.
The most effective remedies include rifampicin, isoniazid. In the second stage, after 3 -4 months, pyrazinamide, streptomycin, ethambutol are prescribed. In ulcerative lesions, topical agents based on PASC or isoniazid are topically applied.
The basic course of treatment lasts about a year, but even in case of recovery the patient is in the focus of the attention of the phytotrans. Over the next three years, medical procedures are conducted twice a year to prevent recurrence of the disease.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the form of the skin tuberculosis, the severity of the symptoms and the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Tuberculosis of Lupus- a long-term disease. In some cases, the lesion focus may not show a tendency to progress for many years even without treatment, in others - the process slowly spreads, covering all new areas of the skin. This is facilitated by intercurrent diseases, unfavorable living conditions and other factors that weaken the body's defenses and reduce its reactivity.
- Scrofuloderma. The disease is chronic, lasting for months and years with remissions. Mild cases are successfully cured by modern methods. In cases of far-reaching ulcerative prognosis, the prognosis is less favorable.
- Warty tuberculosis of the skin. The prognosis is more often favorable, although the course of the disease is prolonged, chronic.
- Ulcerative skin tuberculosis. The prognosis depends on the course of tuberculosis of internal organs. Currently, in connection with the progress in the therapy of general tuberculosis, the prognosis of ulcerative tuberculosis of the skin and mucous membranes has improved, and the frequency of this disease has sharply decreased.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



