How to choose a cough medicine?
What are the cough tablets?
 Effective drugs for cough therapy in adults, adolescents and children is an actual topic to date and this is related to common cases of self-medication and a huge choice of drugs in the form of syrups, tablets, potions, drops, suspensions, sprays, inhalers, infusions and tinctures. In this case, patients often consult a pharmacist and pharmacist who can not assess the nature of the cough, determine the diagnosis and severity disease, the possibility of a complicated course of nosological form, which can be determined only by a qualified specialist - therapist, pediatrician or family doctor. If necessary, additional instrumental methods of examination are prescribed.
Effective drugs for cough therapy in adults, adolescents and children is an actual topic to date and this is related to common cases of self-medication and a huge choice of drugs in the form of syrups, tablets, potions, drops, suspensions, sprays, inhalers, infusions and tinctures. In this case, patients often consult a pharmacist and pharmacist who can not assess the nature of the cough, determine the diagnosis and severity disease, the possibility of a complicated course of nosological form, which can be determined only by a qualified specialist - therapist, pediatrician or family doctor. If necessary, additional instrumental methods of examination are prescribed.The correct treatment of a cough is not to suppress the cough reflex, which is a protective reaction of the body to irritation of the respiratory tract due to the development in them inflammatory process and with sputum production (wet cough) or with minimal mucus presence (dry unproductive cough), and also in case of inhalation of any irritant factor:
- small particles of dust;
- foreign objects;
- various infectious agents - pathogenic microorganisms, viruses, fungi;
- allergens.
In some cases, cough, especially in childhood, can occur in diseases that are not associated with pathological processes directly in the respiratory system, but has a central (neurogenic) nature - with neuroses, the syndrome of hyperactivity, psychopathy. Also cough is an additional symptom in diseases of other organs or systems: allergic diseases, heart and vascular diseases, digestive organs.
Therefore, in each specific case, a diagnosis and careful selection of strictly defined and maximized effective cough tablets for complex therapy of the underlying disease with elimination or relief of a specific type of cough.
Pathogenesis of cough
Mucous membranes of the trachea, bronchi and alveoli normally produce mucus.
But with inflammatory processes that occur during seasonal infections, colds, cough is one of the symptoms, acutely occurring pathological processes that accompanied by an increase in temperature, lethargy, weakness, runny nose and general malaise, in connection with the development of the inflammatory process in the epithelial cells of the larynx, trachea, pharynx, bronchi or alveoli. At the same time, hyperemia with persistent edema and production of mucous exudate develops, aimed at evacuating viruses and pathogenic microorganisms from the upper and lower respiratory tract.
Another cause of coughing is bronchospasm.
Inflammation of the alveoli, pleura, or lung tissue with pneumonia and pleurisy is accompanied by frequent dry, and irritating cough, but the diagnosis of these diseases is carried out only in the conditions of a medical institution.
Types of cough and treatment tactics
Cough, depending on the amount of sputum in the respiratory tract is divided into wet and dry.
In this case, treatment of each type of cough has its own characteristics and determines the choice of cough medicine.
Tablets from dry cough, in most cases suppress the cough reflex (blocking the cough center or the receptors of the tracheobronchial tree), so their
It is unacceptable to use for the treatment of a damp cough, as a result of which evacuation of sputum and bronchial clearance are completely blocked by a constantly developing secret.
Also, do not use tablets from wet cough, dilute sputum and promote both its formation, and an easier expectoration in the occurrence of dry cough, which is associated with irritation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract by a catarrhal inflammatory process or irritation with chemical or physical agents. If they are not effective, they can stimulate the secretion when the cells are not ready for it, so there is aggravation of edema and inflammation of the bronchi and trachea.
It is important to remember that cough is only a symptom of the disease and the main point of therapy is the definition and elimination of the cause of the pathological process.
Causes of cough in children and adults
To date, the main causes of coughing are:
1. Diseases of the respiratory system
- Catarrhal and infectious diseases of the bronchopulmonary system of viral and bacterial etiology (considered the largest and most important group of pathologies that are accompanied by a cough):
- diseases of the upper respiratory tract (nasopharyngitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, laryngotracheitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis);
- pathological processes in the lower respiratory tract (tracheitis, tracheobronchitis, bronchiolitis, bronchitis, bronchopneumonia and pneumonia, pleurisy, alveolitis, lung abscess);
- Specific infectious and inflammatory processes (tuberculosis and mycosis of the lungs, chlamydial pneumonia), 3) Diseases of infectious-allergic and allergic genesis (bronchial asthma, angioedema larynx);
- Congenital pathology of bronchi and lungs (bronchial hypoplasia, congenital bronchiectasis);
- Children's infectious diseases (whooping cough, measles, scarlet fever);
- Benign and malignant neoplasms of the respiratory tract (lung sarcoma, bronchogenic carcinoma, pleural tumors);
- Irritation of mucous respiratory tract by aggressive chemical substances (poisoning with petrol vapors, acetone, carbon monoxide);
- Foreign bodies in the respiratory tract;
- Interstitial lung diseases.
2. Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
- heart defects (congenital and acquired);
- angina pectoris;
- heart failure;
- inflammatory diseases of the heart (myocarditis, pericarditis).
3. Diseases of the digestive tract
- gastroesophageal reflux;
4. Diseases of the nervous system
- neurogenic dysfunction of the pharynx musculature;
- neuroses;
- Parkinson's disease;
- organic pathology of the brain (post-stroke complications, brain tumors).
5. Other reasons
- a smoker's cough;
- cough, as a side effect when taking certain medicines (inhibitors of renin-angiotensin).
Effective elimination of the cause of the occurrence of cough, is the basis for the therapy of cough, directed at the etiologic factor.
Classification of drugs that eliminate and relieve cough
 The modern classification of medical devices that affect cough is extensive, but to date the drugs are positively affecting the occurrence of cough reflex, its productivity and intensity in pharmacology and medicine are divided into three main groups:
The modern classification of medical devices that affect cough is extensive, but to date the drugs are positively affecting the occurrence of cough reflex, its productivity and intensity in pharmacology and medicine are divided into three main groups: - drugs that directly exert a retarding effect on the cough center of the central nervous system (in the brain) and on the nerve endings of cough receptors with complete or partial suppression of cough;
- drugs affecting smooth muscle and bronchial mucosa;
- drugs affecting the state of bronchial secretions.
Dry cough pills
Dry cough occurs as a complex reflex protective reaction of the body, which occurs with constant irritation of the respiratory tract by any infectious or other foreign agents with simultaneous presence of catarrhal inflammation and edema of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract with minimal production of sputum, mainly in the development of viral or bacterial infections.
Dry cough is irritating and unproductive, and most often occurs with catarrhal inflammation of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract - larynx, nasopharynx and / or the initial part of the trachea, as well as their combined lesions - laryngopharyngitis, laryngotracheitis and pharyngotracheitis. Also, a frequent dry and irritating cough can occur in children with infectious diseases - measles, paracut, parotitis, whooping cough and scarlet fever.
Dry cough can be a symptom of pleurisy, bronchoadenitis, the presence of a foreign body of bronchial tubes, as well as a symptom of diseases of other systems: psychogenic cough with neuroses or irritating cough with endocrinopathies and diseases of the digestive system (gastroesophageal reflux).
In this type of cough, in a number of cases, antitussive drugs that depress the cough reflex are prescribed. It is important to remember that this type of medication is used only for the purpose of the doctor at any age, but in young children (up to a year), premature and weakened babies, in the presence of perinatal pathology of the central nervous system, these drugs can oppress not only the cough reflex, but also respiratory center. Therefore, in pediatric practice, these drugs are prescribed only under the constant supervision of a specialist in the case of severe dry cough, significantly disturbing the well-being and sleep of the child, causing regurgitation and vomiting - in whooping cough, parakoklishe and in the complex therapy of obstructive bronchitis and bronchopneumonia.
These drugs are divided:
- preparations of central action;
- peripheral action;
- combined medicines.
Counter-cough medicines of central action
A group of drugs affecting the center-center cough center is used to eliminate coughing and is used to treat diseases with no sputum. It includes mainly medicines for the treatment of dry cough:
1. With narcotic effect (Morphine chloride, Codeine, Demorphan, Hydrocodone, Codipron, and Ethylmorphine hydrochloride).
2. Without a narcotic effect (Tusuprex, Glavent, Sedotussin, Sinekod, Pakseladin, Butamirat).
Narcotic antitussive medicines
These drugs are released in the pharmacy network only when presenting a prescription.
With caution the drugs of this group are prescribed for acute pain in the abdomen of an unknown genesis, convulsions (in the anamnesis), arrhythmia, alcoholism, bouts of asthma, suicidal tendencies, neuroses and emotional lability. And also with intracranial hypertension and brain injuries of prostatic hyperplasia, renal and / or hepatic insufficiency, hypothyroidism, severe inflammatory bowel disease, and with urethral strictures channel. Very rarely drugs of this group are assigned to weakened patients, in any period of pregnancy and during lactation, and also elderly patients and children due to a large number of adverse reactions, the possibility of overdose and poisoning.
It should be noted that the use of other antitussive and expectorants simultaneously with narcotic antitussives is prohibited.
The most common drugs in this group are Codeine and codeine-containing drugs and Ethylmorphine.
Codeine
 Codeine is an alkaloid of opium and is formed synthetically by methylation of morphine. Its therapeutic effect is based on suppressing the redistribution of the cough center of the brain.
Codeine is an alkaloid of opium and is formed synthetically by methylation of morphine. Its therapeutic effect is based on suppressing the redistribution of the cough center of the brain.Codeine is part of the combination of medications that are used as symptomatic agents for the treatment of an obsessive, painful and debilitating cough:
1) in combination with expectorant drugs and terpinhydrate
- Terpinkod;
- Codterpine;
- Kodarin;
2) with sodium hydrocarbonate, a herb of thermopsis and a root of licorice
- Codesan;
- Kodelak;
3) in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, naproxen, metamizole, paracetamol and analgin, and) with the inclusion of some preparations of phenobarbital with its soothing action
- Sedalgin;
- Pentalgin;
- Solpadein;
- Nurofen Plus.
Ethylmorphine
 Ethylmorphine is a central antitussive drug that promotes stimulation of opioid receptors neurons of the brain and a decrease in the excitability of the cough center and providing analgesic and soothing act. It is available in the form of tablets.
Ethylmorphine is a central antitussive drug that promotes stimulation of opioid receptors neurons of the brain and a decrease in the excitability of the cough center and providing analgesic and soothing act. It is available in the form of tablets.Indication for use Ethylmorphine is an unproductive, painful cough that is accompanied by a pain syndrome with pulmonary tuberculosis, pleurisy, neoplasms of the bronchopulmonary system.
Contraindication to the use of this drug is respiratory depression against the background of various infectious and inflammatory processes of the lungs (bronchopneumonia, bronchiectasis, pulmonary emphysema and other COPD), especially in the elderly, as well as increased sensitivity to drug. The most frequent adverse reactions are persistent headaches, insomnia, permanent constipation (especially in the elderly and senile age, in weakened patients) and the development of drug dependencies.
Non-narcotic antitussive medications
To date, the pharmacy network has a very large selection of non-narcotic antitussive drugs, which can be considered true cough tablets. Typical representatives of this group are Libexin, Paxeladin, Glaucin, Sedotussin, Tusuprex, Sinekod and other preparations.
The mechanism of action of these drugs:
- oppressive effect on the nerve endings of cough receptors with complete or partial suppression of cough and mediated inhibition of the cough center;
- interruption or weakening of signals going to the brain (medulla oblongata) from the affected mucosa of the trachea and bronchi.
Some of these substances are part of a combination of drugs, mainly Glaucin, which is an antitussive component many medicines containing also other soothing, expectorant or anti-inflammatory components (Stoptussin, Broncholitin).
Medicinal preparations of non-narcotic effect for today by patients and in some cases also by doctors are widely used, but, to Unfortunately, it is often unreasonable and wrong, because the indication for their purpose is the need to suppress frequent, irritating cough. In pediatrics, such cases are rare - mainly with whooping cough or in cases of intense productive cough with intense production sputum with the formation of abundant and liquid bronchial secretion (bronchorrhea), when there is a real threat of aspiration of bronchial contents.
In patients in the older age group (children over 12 years, adolescents, adults), these drugs are prescribed in cases of cough, combined with moderate bronchospasm. At the same time they are used both independently and as an addition to bronchodilator drugs, suppressing catarrhal or allergic inflammation.
The most commonly prescribed drugs in this group are Butamyrate, Libexin, Bithiodine, Paxeladine.
Butamate
 This antitussive drug effectively inhibits the excitability of the cough center, while providing moderate anti-inflammatory, expectorant action and a weak bronchodilator effect, reducing irritation of the trachea and bronchi and potentiating antitussive action without depressing influence on the respiratory center.
This antitussive drug effectively inhibits the excitability of the cough center, while providing moderate anti-inflammatory, expectorant action and a weak bronchodilator effect, reducing irritation of the trachea and bronchi and potentiating antitussive action without depressing influence on the respiratory center.Butamirate tablets are used for symptomatic treatment of inflammatory diseases of the bronchopulmonary system in adults and children and over 12 years of age who are accompanied by a frequent unproductive and severe irritating cough that has an obsessive character. Butamirate is the main component of medicines Sinekod, Kodelak-Neo, Omnitus.
Bithiodine
Antitussive drug, the therapeutic effect of which is due to active influence on the receptors of the mucous membrane of the bronchopulmonary system and to a lesser extent on the cough center of the central nervous system. Its active ingredient is Tipedidine, which is close to codeine by force of action, but does not cause drug dependence even with prolonged use.
Paxeladin
 This drug refers to antitussive drugs that do not have a chemical affinity for either opioids or their derivatives, or antihistamines. Its active ingredient is oxeladine citrate, which acts selectively at the level of the cough nerve centers. Pakseladin is released in prolonged-action capsules and in syrup. Like all non-narcotic antitussives, it is prescribed for the symptomatic treatment of frequent dry cough in most cases spastic or reflex. It is not used to treat productive cough - it is difficult to get rid of phlegm and aggravation of inflammatory processes, conditions are created for the development of complications (bronchopneumonia, pleurisy). Also, do not apply Paxeladin simultaneously with expectorant and mucolytic drugs - in this case, activates viscous products sputum, which provokes the development of bronchospasm, peristalsis of small and medium bronchi and obliteration of the lumen of the bronchi, which aggravates cough.
This drug refers to antitussive drugs that do not have a chemical affinity for either opioids or their derivatives, or antihistamines. Its active ingredient is oxeladine citrate, which acts selectively at the level of the cough nerve centers. Pakseladin is released in prolonged-action capsules and in syrup. Like all non-narcotic antitussives, it is prescribed for the symptomatic treatment of frequent dry cough in most cases spastic or reflex. It is not used to treat productive cough - it is difficult to get rid of phlegm and aggravation of inflammatory processes, conditions are created for the development of complications (bronchopneumonia, pleurisy). Also, do not apply Paxeladin simultaneously with expectorant and mucolytic drugs - in this case, activates viscous products sputum, which provokes the development of bronchospasm, peristalsis of small and medium bronchi and obliteration of the lumen of the bronchi, which aggravates cough.It is not recommended to use capsules before the age of 15 years.
Indications and features of non-narcotic antitussive drugs
A group of non-narcotic antitussive medicines of central action is shown mainly with a cough that is associated with marked irritation of mucous epiglotti (upper) respiratory tracts arising from infectious and / or catarrhal inflammation. In this case, the positive result is usually enhanced when they are used together with preparations of peripheral antitussive action with enveloping effect. An example of such a combined action is Broncholitin. But the effectiveness of its use is justified only in the absence of pronounced inflammatory changes in the mucosa in the lower parts of the bronchopulmonary system, in connection with the fact that the ephedrine entering into it "dries" the bronchial mucosa, increasing the viscosity of the bronchial secretion, increasing the inefficiency of coughing in bronchitis and pneumonia. Ephedrine also has an exciting effect on the central nervous system, so the use of this drug in children unjustified and dangerous - it can disrupt the child's sleep, contributing to increased dyspnoea and unproductive cough.
It is important to remember that the use of this group of drugs as self-medication can do more harm than good, cause complications in the form of bronchial obstruction, increasing the viscosity of bronchial secretions and promote the progression of inflammatory processes, edema and lowering of the pathological process in lower departments.
Group of peripheral drugs
The peripheral group includes pharmacological preparations from dry cough acting on nerve receptors and endings that are located in the tracheobronchial tree - Libexin, Levopront and Helicidin.
Libexin
Libexin is considered an effective antitussive drug, which additionally has a local anesthetic, bronchodilator and spasmolytic effects and has a moderate expectorant and anti-inflammatory effect with minimal decrease in respiratory activity center. The basic form of Libexin is round flat tablets of almost white color with a dividing stripe into four equal parts on one side and engraving "LIBEXIN" on the other, containing 100 mg of active ingredient - prenoxdiazin hydrochloride.
This drug is currently considered a drug of choice in the treatment of laryngitis, tracheitis, pharyngitis and less frequent bronchitis, which are accompanied by a dry, unproductive cough. Also as one of the components in the complex therapy of pleurisy and pneumonia, which are accompanied by pain and obstructive syndromes, and with congenital diseases of bronchopulmonary system, cystic fibrosis and other chronic lung diseases: tuberculosis, pneumoconiosis, emphysema in children and adults as a symptomatic remedy with compulsive irritating coughing.
With caution this drug is prescribed for ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as in the presence of a history of gastric bleeding, liver or kidney failure, glomerulonephritis, cystitis, allergic form of bronchial asthma with a tendency to stand bronchial obstruction.
Libexin is contraindicated for individual intolerance, pregnancy (especially in the first trimester), lactation and in early childhood.

Levoprint
This drug is prescribed for frequent dry cough to children and adults. It is released as a syrup and drops for oral administration.
Absolute contraindications to its reception are:
- pregnancy in any period;
- lactation period;
- liver failure;
- decreased mucociliary function of the bronchi;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Levoproton can cause side effects in the form of increased fatigue, diarrhea, drowsiness, dizziness, tachycardia, heartburn, nausea, vomiting and allergic reactions. With long-term use of this drug, mental disorders, the development of sopor and coma, possible, especially with overdoses in childhood and the elderly.
Group of antitussive drugs combined action
These drugs have simultaneously reducing the cough reflex effect and expectorant, moderate anti-inflammatory and mild bronchodilator actions in connection with their constituent several components - Stopptussin, Butamirate, Libexin-Muko, Tussin plus, Bronholitin, Protiazin, Hexapneumine.
All drugs of this group are widely used for the treatment of dry and unproductive cough, but it is important to remember that
They are contraindicated in the presence of productive wet cough or other conditions that are accompanied by abundant sputum discharge, as well as with the likelihood of developing pulmonary hemorrhages.
Therefore, the choice of an antitussive drug should be performed by a physician on the basis of an anamnesis, clinical examination of the patient and, if necessary, additional methods (laboratory or instrumental).
Indications and features of antitussive drugs
A group of "true" antitussive drugs of central and peripheral action is shown mainly with a cough that is associated with marked irritation of mucous epiglotti (upper) respiratory tracts arising from infectious and / or catarrhal inflammation. In this case, a positive result is usually enhanced when they are used together with drugs that have anti-inflammatory and enveloping effects in addition. An example of such a combined action is Broncholitin. But the effectiveness of its use is justified only in the absence of pronounced inflammatory changes in the mucosa in the lower parts of the bronchopulmonary system, in connection with the fact that the ephedrine entering into it "dries" the bronchial mucosa, increasing the viscosity of the bronchial secretion, increasing the inefficiency of coughing in bronchitis and pneumonia. Ephedrine also has an exciting effect on the central nervous system, so the use of this drug in children unjustified and dangerous - it can disrupt the child's sleep, contributing to increased dyspnoea and unproductive cough.
It is important to remember that the use of this group of drugs as self-medication can do more harm than good, cause complications in the form of bronchial obstruction, increase the viscosity of the bronchial secretion and promote the progression of inflammatory processes, edema and lowering of the pathological process in the lower parts of the bronchopulmonary system.
Cough preparations of local action
This group of antitussive drugs includes drugs that depress the cough reflex as a result of anesthesia of the mucous membranes respiratory tract, in connection with which the irritating effect of various agents, both infectious and non-infectious (chemical and physical factors). These drugs also reduce the viscosity of phlegm and relax the bronchi.
To local anesthetics include tablets Libexin, Tusuprex and resorption tablets Falimint.
Tusuprex
Tablets Tusuprex is often used for symptomatic cough therapy in children from the year, adolescents and adults patients, but in pediatric practice they are used only according to the doctor's prescription (due to the complexity of dosing in young children age). Also, this drug should not be used against the background of the development of bronchospasm (with obstructive bronchitis and bronchial asthma), in the presence of confirmed bronchiectasis and for any disease that is accompanied by a difficult separation phlegm.
Falimint
 Tablets for resorption of the Falimint are indicated in the presence of an unproductive irritant cough that is caused by pronounced catarrh of the upper respiratory tract (pharynx, larynx and upper parts trachea). This drug has in its composition a local anesthetic component and therefore reduces the intensity of dry cough.
Tablets for resorption of the Falimint are indicated in the presence of an unproductive irritant cough that is caused by pronounced catarrh of the upper respiratory tract (pharynx, larynx and upper parts trachea). This drug has in its composition a local anesthetic component and therefore reduces the intensity of dry cough.Falimint does not apply:
- in children under 4 years;
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- with intolerance to fructose.
Drugs affecting the state of bronchial secretions
Separately, a group of drugs with mucolytic and / or expectorant action is distinguished. These tablets and syrups, which are used in wet productive cough and are divided into the following subspecies of drugs:
1. Expectorants:
a) having predominantly reflex action:
- Terpinhydrate, Thermopsis, Sodium benzoate, Lycorin;
- the roots of Licorice, Devyasil, Istad and Althea;
- essential oils.
b) stimulating gastropulmonary and / or vomiting reflex:
- Gwaiphenazine, Ipecacuan, Sodium Citrate, Ammonium Chloride.
c) resorptive action with increased bronchial secretion:
- Sodium iodide, Sodium bicarbonate, Ammonium chloride, Potassium iodide.
2. Mucolytic agents:
a) direct action, which quickly destroy the polymer bonds of bronchial mucus:
- Mukaltin;
- The mukonist;
- Mukobene;
- Exomuk;
- Acetylcysteine, Fluimutsil, Carbocysteine group (Mukopron, Bronkatar, Mukodin, Fluvik, Mistabron, Mucosol;
- preparations with infusions of leaves of plantain, mother-and-stepmother, licorice;
- enzymatic preparations that reduce the viscosity of sputum - Chymotrypsin, DNAase, Trypsin, Ribonuclease, Streptokinase, DNAase, Pulmozyme;
b) Indirect action (mucoregulators):
- Ambroxol (Ambrobene, Ambrosan, Ambroghexal, Khalixol, Medovent, Lazolvan, Ambrollanazolvan);
- Bromhexine (Fulpen, Flegamine, Broxin, Bisolvon);
- Carboxymethylcysteine, Sobregorod, Sodium Ethanesulfate, Letostein, Sodium bicarbonate;
- changing the productivity of bronchial glands - anticholinergic and antihistamines.
3. Anti-inflammatory drugs with bronchodilator and / or expectorant effect:
- Suprima-bronho, Sinupret, Pulmotin, Glytsiram, Ascoril, Gelomirtol, Gedelix, Evkabal and Prospan.
Features of the use of expectorant drugs
At the basis of the mechanism of action of expectorants are - increased secretion of sputum by bronchial glands, dilution of secretion by reflex by way of and as a result of this easier departure of mucous or mucopurulent sputum from the lower parts of the bronchopulmonary system to its higher departments. These drugs actively irritate the receptors of the mucous membranes of the stomach and, inducing vomiting center, which is localized in the medulla oblongata and, in connection with this, significantly increase sputum excretion bronchi.
Expectorants are prescribed for diseases that are accompanied by a decrease in sputum production or vice versa, an abundance of thick, viscous, difficult-to-separate mucus that accumulates in the bronchi (with bronchitis and bronchial asthma), larynx (with laryngitis), in the trachea (with tracheitis), in the alveoli and small bronchioles (with bronchopneumonia and cystic fibrosis).
The use of expectorants for the treatment of respiratory diseases can not be combined with antitussive drugs of central and peripheral action that oppress the cough center or inhibit cough reflex. In this case, a large number of sputum accumulates in the lower respiratory tract, which often leads to their obliteration and development of severe infectious and inflammatory diseases (obstructive bronchitis, bronchopneumonia, pleurisy).
There are two groups of expectorant drugs that differ in the mechanism of their therapeutic action:
- means of reflex action;
- medicines with direct effect.
And
- preparations of vegetable origin;
- synthetic drugs.
Popular expectorants of plant origin
 Basically, almost all expectorants with a reflex action mechanism are represented medicinal plants and their extracts, which intensify and accelerate the excretion of sputum from the organs bronchopulmonary system. This group of medicines is extensive and in most cases they are represented by herbal medicines.
Basically, almost all expectorants with a reflex action mechanism are represented medicinal plants and their extracts, which intensify and accelerate the excretion of sputum from the organs bronchopulmonary system. This group of medicines is extensive and in most cases they are represented by herbal medicines.Expectorants have medicinal plants:
- licorice;
- thermopsis;
- anise;
- marshmallows;
- plantain;
- elecampane;
- ledum;
- oregano;
- thyme;
- mother and stepmother;
- ipecacuanha;
- thyme;
- violet;
- pine buds, etc.
Herbal extracts of these herbs are included in various breast pills, tablets, powders and syrups for the treatment of moist productive cough in children and adults.
Pills for cough with thermopsis
In most cases (and this is actually so), this drug is considered to be the best drug for treating wet cough.
Tablets from cough with thermopsis and sodium bicarbonate are very popular earlier and effective at the present time. Their balanced composition is a herb of thermopsis, which enhances sputum secretion while simultaneously reducing its viscosity and sodium bicarbonate, an emollient and gently tearing bonds in sputum molecules - effectively dilute sputum, promoting its rapid evacuation from the upper and lower divisions of the respiratory tract.
In these tablets there are no artificial additives, synthetic components, and in comparison with expensive medicinal preparations in efficiency they do not concede.
But for the purpose of this drug there are absolute contraindications:
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug;
- erosive and ulcerative pathological processes of the stomach and other parts of the digestive system;
- pregnancy.
Thermopsis is today considered to be an excellent remedy for treating wet cough in children. But it is important to remember that it is not used for infants for the therapy of bronchitis or bronchopneumonia with a large amount of sputum, while the child can not effectively cough, and thermopsis additionally activates the increase in mucus secretion by bronchial glands, which quickly leads to the development of respiratory insufficiency. Also, the herb of thermopsis has an emetic effect and the babies show frequent regurgitation and vomiting, which leads to dysfunctions of the digestive system, the development of lethargy, reduced weight gain and overall weakening of the body the kid.
Also, if the dose of Thermopsis is exceeded, its emetic effect is manifested, which can cause nausea at the beginning of treatment at any age (especially in children).
Mukaltin
Another effective herbal preparation for the treatment of wet cough is Muciltin tablets against cough, which are created on the basis of the extract of the althea medicinal. It has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and expectorant effect, which is due to reflex stimulation ciliary epithelium of the respiratory tract and an increase in peristalsis of the bronchi and bronchioles with activation of secretion bronchial glands.
Muciltine tablets also contain sodium bicarbonate.
Currently, this drug is recognized as one of the most effective expectorant drugs that are used to treat productive wet cough in children and adults.

Doctor Mom
Dr. Mom is a complex herbal preparation that is used in the treatment of diseases accompanied by a damp productive or cough with viscous sputum. It consists of active plant substances that have expectorant, softening, secretory, anti-inflammatory, moderate bronchodilator and mucolytic effects.
At the heart of pastilles and syrup are dry extracts from leaves, roots, seeds, bark, flowers of medicinal plants: aloe, elecampane, basil, ginger, licorice, turmeric, pepper cubebe, terminalee beleriki and nightshade Indian.
Additional positive characteristics of this drug is its good tolerability, even with prolonged use.
With caution, this medicine should be taken by pregnant women and with lactation and only with the appointment of a doctor and with constant monitoring.
Also, Dr. Mom is not assigned simultaneously with medications that suppress the cough reflex. A good effect is the use of this plant expectorant in combination with mucolytic drugs (Ambroxol, Lazolvan and Bromhexin).
At the beginning of treatment or with prolonged or uncontrolled use of the drug, nausea may occur before vomiting or frequent regurgitation in young children, which is due to the presence in the formulation of an extract of licorice, which has a weak emetic effect.
Expectorants of artificial origin
At the basis of the mechanism of action of expectorant antitussive drugs of direct action is the enhancement elimination of bronchial secretion as a result of exposure to sputum and stimulation of bronchial peristalsis. This group of medicines is represented by artificial medicinal preparations - iodized salts of potassium and sodium, Benzoate sodium, sodium hydrochloride, terpinhydrate, ammonium chloride, potassium bromide and essential oils - eucalyptus fir, aniseed. They are quite effective and are mainly used for inhalations.
In the pharmacy network, you can buy a combination of drugs for the treatment of wet cough, which have in their composition as plant substances, and artificial components - Moist-anise drops and Pertussin, which contains the extract of thyme and bromide potassium.
Mucolytic drugs
The action of mucolytic drugs is aimed at diluting the thick and viscous secretion bronchial glands without increasing sputum secretion to facilitate their evacuation from the lower and upper respiratory tract.
Mucolytic tablets today are considered one of the main components in the therapy of wet cough. They also restore the mucous membranes of the bronchi and the elasticity of the lungs.
To this group of drugs are - Ambroxol, ATSTS, Bromheksin, Carboccithin. When combined with various plant expectorants with mucolytics, the effectiveness of both increases sharply. Also mucolytics potentiate the action of antibacterial drugs, increasing their effectiveness, Therefore, they are widely used in complex therapy of pneumonia, bronchiolitis, obstructive bronchitis and pleurisy.
Ambroxol and Bromhexin activate the formation of pulmonary surfactant, which ensures the normal functioning of the alveoli of the lungs, preventing their collapse and adhesion, therefore they are widely used in pediatric practice for the treatment of bronchopulmonary pathology in young children, premature babies and toddlers with intrauterine hypotrophy.
Their negative side is the ability to cause bronchospasm, which is considered a contraindication to the use of these drugs during periods of exacerbation of bronchial asthma.
The main groups of mucolytic drugs
In medicine and pharmacology mucolytics are divided into several groups:
1) drugs that are developed based on proteolytic enzymes - chymotrypsin, trypsin and mesna. But this group of medicines is used only in extreme cases, always in a hospital and under the supervision of the attending physician;
2) drugs based on acetylcysteine - ATSTS, Mukobene, Fluimutsil, Exemuk, Mukomist and others.
The mechanism of action of these drugs is based on dilution of thick and viscous sputum as a result of rupture of large molecules of mucus to small in connection with this facilitates the process of coughing and evacuation of sputum from the respiratory tract. Also, acetylcysteine drugs have a protective effect on the inflamed cells of the bronchopulmonary system.
Preparations of this group can not be taken simultaneously with antitussive drugs, which leads to stagnation of sputum in the bronchi and alveoli, oppression of the cough and the development of complications (bronchopneumonia, respiratory failure, and with the layering of aggressive microflora - abscesses of the lungs and purulent pleurisy).
3) drugs based on carbocisteine (mucoregulators) - Bronkatar, Carbocysteine, Drill, Mukodin, Fluvik, Mukoprint.
They normalize not only the qualitative composition of the sputum (liquefying it and easing the cough), but also increase the activity of cells that produce bronchial secretion and the work of cilia of bronchial epithelium and bronchioles. And also have an anti-inflammatory effect and stimulate local immunity in connection with the increase in the production of protective immune complexes (group A immunoglobulins).
The most modern preparations of this group are Fluviert, its distinctive feature is a longer lasting effect.
4) mucolytics with expectorant effect - derivatives of Ambroxol and Bromhexine
The mechanism of action of these drugs is based on stimulation of secretion by alveoli of liquid sputum and liquefaction and already accumulated mucus, stimulate the formation of immunoglobulin and lysozyme in a bronchial secretion and have an expectorant effect.
But the pronounced effect of these drugs does not come immediately, but only on the fourth - the sixth day from the beginning of treatment.
Bromhexine preparations include - Flexin, Bronchosan, Flegamin, Bromoxin, Fulpen, Solvin.
Drugs of this group also can not be used simultaneously with antitussive drugs in connection with possible accumulation of excess sputum as a result of cough suppression and the absence of evacuation of the accumulated secretion from the bronchi and alveoli. In addition, when this group of drugs is prescribed, the use of a vibratory (drainage) massage and postural drainage (the patient's acceptance of certain body positions that improve the outflow phlegm).
Ambroxol preparations are active metabolites of Bromhexine with an improved chemical structure, so these medicinal means have a complex effect on the respiratory tract - mucolytic, anti-inflammatory and expectorant. Since 2012 Ambroxol is on the list of the most important and vital medicines. But Ambroxol preparations also can not be taken simultaneously with antitussive drugs.
The main drugs are Ambrobene, Lazolvan, Ambrohexal, Khaliksol, Bronhoverne, Dephlegmine, Ambrolan.
Good tablets against coughing
Definitions of "good pills for cough" from both medical and pharmaceutical point of view does not exist. Cough is only a symptom, the complete elimination of which or even its reduction can do more harm than good. With the development of bronchopulmonary pathology in both children and adults, treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathological process - cupping bronchospasm, the elimination of inflammation, the removal of a foreign body from the trachea and bronchi or the treatment of other systems and organs - neuroses, psychopathies (with neurotic character of coughing).
Therefore, the choice of the drug for cough treatment is individual and is made after a patient's examination, careful collection of anamnesis and diagnosis.
Tablets for children cough
The right choice of medicines for cough therapy in children is determined by the main factors - the cause of cough, the mechanism of action of antitussive drugs, features of a cough reflex in a child, and the full spectrum of all these factors can be assessed only by a specialist who will assign the baby the correct one in each case treatment.
Inhibition of cough reflex in a child, the use of several antitussive drugs from different groups simultaneously, increasing dosages, multiplicities and the duration of taking the drug can lead to many negative consequences, the development and progression of hazardous to health and even life complications.
Tablets for coughing during pregnancy
Pregnancy in most cases is an absolute contraindication to taking many antitussive medicines, especially narcotic antitussives, many complex medicines, in connection with their pronounced negative impact on the embryo, followed by the development of fetopathies and other violations of the correct laying of organs and systems of the future child.
Relatively contraindicated medicinal products for treating cough are:
- insufficiently studied drugs, in which application the risk of a dangerous effect on the baby's body is possible;
- medicines, with the possible risk of development in the future mother of side effects.
Also on any period of pregnancy, some medicinal plants and medicinal funds that have them in its composition - juniper, nettle, oregano, mother-and-stepmother, St. John's Wort and others. The negative effect of medicinal herbs on the fetus is sometimes many times more active than synthetic drugs - they have a fetopathological and teratogenic effect on the fetus, change the hormonal background of the pregnant, can stimulate the contraction of the myometrium and cause miscarriages, especially in the early terms.
Therefore, even at the planning stage, and even more so in the early stages of pregnancy, it is necessary to take with caution any medicinal and / or homeopathic medicines and herbs.
kashelb.com
When pills for cough with thermopsis help
Tablets from cough with thermopsis are helpful in the treatment of dry cough. They cause a wet cough after the first intake, when the bronchi begin to be actively cleared from the pathogens of the disease.The action of the drug passes several days after the administration of the last herb-containing thermopsis tablet.

The drug is classified as a group of expectorants of vegetable origin. The tablets contain powdered grass of thermopsis of lanceolate 067 g and baking soda 50 g. Potato starch and talc are added from the auxiliaries required for hardening the tablet form.
Doctors prescribe pills for coughing with grass thermopsis with fever, flu, pneumonia, tracheitis and bronchitis.
Powder of the herb of thermopsis, sold in pharmacies, can be prescribed for headaches and intestinal atony.
How do pills with a stool
 Thermopsis lanceolate is a medicinal herb, which has a second name - a mushroom. It contains six alkaloids, which can induce vomiting, if the medicinal raw material is taken inwards in large doses. Alkaloid anagarin makes this herb similar in effect to curare. Also in its composition there are esters, tannins and saponins that have a multifaceted effect on the human body.
Thermopsis lanceolate is a medicinal herb, which has a second name - a mushroom. It contains six alkaloids, which can induce vomiting, if the medicinal raw material is taken inwards in large doses. Alkaloid anagarin makes this herb similar in effect to curare. Also in its composition there are esters, tannins and saponins that have a multifaceted effect on the human body.Drugs containing mushroom grass, increase blood pressure and excite appetite. Medicines in which there is a herb of thermopsis, actively increase the tone of the uterus and are able to trigger the mechanism of spontaneous delivery.
At small amounts, the alkaloids in the plant excite the respiratory center and activate the expectorant effect. The herb of thermopsis has a moderate irritant effect on the receptors of the gastric mucosa, reflexively increasing the secretion of the bronchial glands. This helps the pill with the thermopsis to make a productive dry cough.
The active substances of the grass of the mice strengthen the reflex secretion of the secretion in the bronchi and cause the ciliated epithelium to activate, the task of which is to bring the phlegm out. Simultaneously, they irritate the walls of the stomach, activating the receptors of its mucous membranes. This can cause an exacerbation in people suffering from ulcerative gastritis.
 Tablets of thermopsis, actively exciting the center of breathing, contribute to the removal of sputum from the bronchi. To sputum go, it needs to dilute something. This function is performed by baking soda, which became the second component of this drug. Sodium bicarbonate has a medicinal property to dilute sputum in the bronchi and promote its active rejection.
Tablets of thermopsis, actively exciting the center of breathing, contribute to the removal of sputum from the bronchi. To sputum go, it needs to dilute something. This function is performed by baking soda, which became the second component of this drug. Sodium bicarbonate has a medicinal property to dilute sputum in the bronchi and promote its active rejection.So the minimum amount of poisonous grass thermopsis of lanceolate and baking soda effectively and quickly cope with an unproductive cough that can torment the patient for a long time.
Tablets with thermopsis can be used with a dry cough of unknown etiology for no more than five days. For the treatment to be productive, it is required to give the patient an abundant warm drink. This contributes to the improvement of sputum liquefaction and its further separation.
Side effects of the mouser
 Tablets with grass thermopsis are not as harmless as it seems at first glance:
Tablets with grass thermopsis are not as harmless as it seems at first glance:- The Mouse excites not only the respiratory, but also the vomiting center, which is in the immediate vicinity of the brain. In order not to provoke the appearance of nausea and vomiting, the tablets should be consumed no more than three times a day for 1 piece.
- Treatment with them may not last long. Usually it takes no more than five days to transfer the dry cough to wet. After treatment, the doctor recommends switching to drugs that help stop wet cough.
- The drug can be given from 12 years. To small children these tablets will not be of use, because the child does not have an expectorant mechanism. Bronchi will produce phlegm, and it will accumulate in the lungs, worsening the situation.
- Pregnant women should not use preparations containing a mushroom, because alkaloids actively stimulate the muscles of the uterus, responsible for its reduction. Stimulation of labor can lead to premature birth.
- The period of breastfeeding is also not suitable for treatment with this drug.
- In some people, the drug may cause an allergic reaction. In case of individual intolerance, the medicine is canceled and transferred to another remedy intended for the treatment of dry cough.
Inexpensive cough tablets have long been used to excrete sputum from bronchial tubes for colds. Their use helped to avoid complications after ARI. Over time, they were replaced by new, more expensive syrups and vegetable powders that have a directed effect.
But tablets with thermopsis and now help sick people get cured of persistent forms of unproductive cough. Sometimes a person who suffers a cough of unknown origin for a long time passes a few days after the application of simple tablets from a cough, in the composition of which is this herb.
respiratoria.ru
Antitussive, expectorant for dry cough
Coughing is a protective, reflex reaction of the body, which removes the pathological altered bronchial secretion from the respiratory tract. Sometimes it occurs when there are foreign substances in the trachea or bronchi.
Coughing is not a disease, it is a symptom, therefore it should be treated as a manifestation of the underlying disease. The choice of medications that affect cough, depends on the individual characteristics of the person, the type and clinical manifestations of the disease.
The effectiveness of the basic treatment of any disease accompanied by a cough, significantly increases with the rational use of antitussive, mucolytic and expectorants. We will consider the causes of dry cough and drugs used to soften it and transfer it into productive, into humid.
What is the best medicine for dry cough?
The choice of medication depends primarily on the nature of the cough and must be agreed with the physician:
- Cough is dry, painful, painful, unproductive, frequent, leading to a loss of appetite and sleep, choice -antitussives or combination drugs.
- A productive cough, but with a hard to separate, thick, viscous sputum, a choice -mucolytic drugs.
- The cough is productive, with phlegm, and it is not viscous, and not thick - the choice of expectorating cough medicines.
- Mucolytic agents can not be used simultaneously with antitussive drugs.
Dry cough - causes:
Most often, dry cough occurs at the onset of a cold, flu, acute bronchitis, pneumonia, as well as inhaling various substances that irritate the mucous membrane. In the case of a severe attack of dry cough, inspiration is accompanied by a wheezing noise between coughing jerks. This is due to the narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi, larynx or trachea and leads to shortness of breath. Before the attack of dry cough can feel pain with a deep breath.
Causes of dry cough:
Read also on the topic:- Dry cough without fever in adults-causes
- Barking cough in a child - treatment
- Chest Cough - Instruction
- Treatment of dry cough in children and adults
- Why dry cough does not go away, causes of dry cough
- Herbion from dry and wet cough - instruction
- Sinecode - instructions for use
- Causes of dry cough without fever
- Inhalation with bronchitis and laryngitis
- Allergic cough - symptoms
- Antibiotics for bronchitis
- Laryngitis in a child - treatment
- Viral, infectious diseases - ARVI, influenza, parainfluenza, pneumonia, bronchitis, etc.
- Allergy-allergic rhinitis, allergy to dust, chemicals, may be the initial sign of asthma.
- Bronchospasm - spasm in the bronchial tubes
- Medicines that reduce high blood pressure - enalapril maleate, caproptil, lisinopril.
- Reflex response to smoke, cold air, sharp odor
Strong dry cough - what to treat?
The better to cure a dry cough? The use of antitussives is considered advisable only at conditions when the cough is strong and often dry (exhausting) and only as prescribed by the doctor.
If the cough is dry, unproductive, it should first be transferred to the moist one, and then use mucolytic or expectorant drugs. And also with an unproductive cough, combined drugs that have both antitussive and expectorant effect are effective:
Sinekod
Sinekod - instructions for use
Dosage Form: Tablets for children in syrup and in drops for oral administration.

Pharmacological action: Sinekod - antitussive drug, has a direct effect on the cough center. Has an expectorant property, has a moderate anti-inflammatory, bronchodilating effect, improves spirometry. It is indicated for acute dry cough of various origin.
Contraindications: Do not use in pregnant and lactating women. Children under 2 months are contraindicated, children under 3 years can not use syrup, only drops, tablets are contraindicated for children under 12 years.
Side effects: Nausea, dizziness, diarrhea, allergic reactions.
Price: syrup 220 rubles, a drop of 320 rubles. AnalogOmnitussyrup 150 rubles, tab. 190 rubles.
Herbion
Herbion - plantain syrup
Dosage form: syrup

Pharmacological action: Herbion - a combined medicine of plant origin, has antitussive, expectorant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory effect. In the composition extracts of flowers mallow and grass plantain lanceolate. The drug softens and relieves dry cough.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to herbal preparations, intolerance to fructose. Take precautions with diabetes.
Side effects: Allergic reactions.
Price: the average price for pharmacies is 220 rubles.
Kodelak Phyto
Dosage form: elixir, syrup
Pharmacological properties: Kodelak Phyto-combined antitussive. Contains codeine and extracts of thermopsis, thyme and licorice. Has an expectorant effect.
Contraindications: bronchial asthma, children under 2years old, pregnant and lactating women, with respiratory failure and hypersensitivity to plant components preparation.
Side effects: allergic reactions, nausea, vomiting, headache, drowsiness, constipation. With prolonged use, drug dependence develops to codeine.
Price: 130-140 rub.
Stopoutsin
Dosage form: tablets, drops for internal administration

Pharmacological action: Stopoutsin - combined antitussive and secretolitic action. The composition includes butamirate citrate, which has a local anesthetic, bronchodilator and antitussive action, and Guaifenesin reduces the viscosity of sputum, improving its departure. Effective with dry cough in children and adults.
Contraindications: Children under 1 year of age and pregnancy during 1 trimester should not be used.
Side effects: Allergic reactions, rarely - vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, headache.
Price: drops 70-80 rubles., Tablets 130-140 rubles.
Bronhicum
Dosage form: syrup, elixir, lozenges
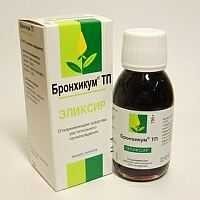
Pharmacological action: Combined drug with anti-inflammatory, expectorant, bronchodilator effect. The syrup and tablets contain the extract of thyme herb, and the elixir also contains the root extract of the primrose. Bronchicum is universal, it is an effective expectorant for dry cough and damp. At the stage of the disease, when a dry cough Bronchicum helps to cope with severe attacks, transferring a dry cough to wet. Then, with a damp cough, he facilitates expectoration of the sputum, contributing to its excretion from the lungs.
Contraindications: Syrup is contraindicated for children under 6 months, and children under 6 years of age should not take troches, patients with significant violations of liver and kidney function, with individual intolerance, during pregnancy and feeding the chest.
Side effects: irritation of the gastric mucosa, allergic reactions.
Price: 270 rubles.
Broncholitin
Dosage form: syrup

Pharmacological action: Broncholitin is a combined preparation of antitussive, bronchodilating and bronchoseptic action. The composition includes Glaucina hydrobromide, which has a depressing effect on the cough center, a mild anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect. Basil oil has a minor sedative, antimicrobial, antispasmodic property. Ephedrine stimulates breathing, dilates the bronchi, has a vasoconstrictive effect, thereby eliminating the edema of the bronchial mucosa.
Contraindications: heart failure, children under 3 years of age, pregnant and lactating women should not be used.
Side effects: tachycardia, tremor, insomnia, drowsiness, visual impairment, nausea, vomiting, difficulty urinating, rash, increased sweating.
Price: 60 rubles.
Libexin
Dosage form: tablets

Pharmacological action: Libexin is an antitussive remedy of peripheral action. It has a local anesthetic, bronchodilator effect, its antitussive effect is approximately comparable to codeine. Unlike codeine, Libexin does not cause dependence, does not affect the central nervous system. With chronic bronchitis has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Contraindications: diseases, with the release of abundant bronchial secretion, with caution used in childhood, in pregnancy is not recommended.
Side effects: dry mouth, temporary numbness in the oral mucosa, mild sedative effect, skin rash.
Price: 260-280 rub.
Linkas
When the cough is not so dry, you can use this herbal preparation.

Dosage form: Brown syrup, the composition includes extracts of 10 medicinal plants - flowers of althaea, onmsma, hyssop, violet, alpinia, fruits of pepper, licorice root, leaves adhatodes and others.
Pharmacological action: Linkas - a combined preparation of plant origin, reduces intensity of cough, increases its productivity, has mucolytic, expectorant, and anti-inflammatory effect.
Contraindications: Children under 6 months of use is not recommended, with hypersensitivity to herbal remedies, use with caution in diabetes mellitus.
Side effects: allergic reactions.
Price: 130-140 rub.
To prescribe and determine the duration of administration of the listed medicinal, expectorant drugs with a dry cough should be the attending physician. There are cases when, with a painful, debilitating, non-productive cough, medications do not help, and simple methods of traditional medicine, such as mustard, cans, steam inhalations, warming ointments and creams bring significant relief and quickly transfer dry cough to wet.
zdravotvet.ru
What herbs can be used to cure children

A child's cough can occur for a variety of reasons. But his treatment must be carried out immediately, otherwise, apart from complications, this symptom can provoke a transition to a chronic form. For the treatment of children's cough, many drugs have been developed, but the medicinal herbs remain the most safe and effective.
The child has a wet cough and a temperature of 38 degrees, what to do about it, you can find out by reading the article.
List of herbs for the treatment of dry cough

When a child has an unproductive cough, it leads to damage to the mucous membrane. After a certain period of time, he becomes stronger, and his treatment will take much longer. For education in the airways of mucus, doctors recommend the use of herbs to their small patients, and what herbs can be given to a child from cough, which herb helps, you can find out below from the article.
- clover;

- Linden blossom;
- althea root;
- leaves of mother-and-stepmother;
- flowers mullein.

These vegetable components are characterized by the presence of an enveloping and softening effect. They should be consumed in the form of tea. Only this way it will be possible to eliminate the attacks of dry cough and improve the condition of the crumbs.
How does a cough with thyroid disease look like, read the article.
When it is necessary to eliminate cough caused by whooping cough, then the following plants have great efficiency:
- ledum;

- thyme;
- oregano;
- rhizome is elecampane.

To overcome painful sensations in the field of a breast it is impossible without aira, a St. John's wort, a cumin. These herbs should be used in the form of a decoction, but combining them with other antitussive medicinal plants.
Than to treat a cough during pregnancy 3 trimester, you can find out by reading this article.
The corona willow and pine buds can exert a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. They should be involved in the therapeutic process during the cough treatment caused by bronchitis, influenza and pneumonia.
Frequent attacks of coughing with time becomes very intense, that the baby often wakes up at night.It is necessary to use herbs with a soothing effect. This is valerian, chamomile, motherwort. Their reception should be conducted not only at night, when tormenting a strong cough, but also before going to bed.In this way, you will be able to prevent a new fit of coughing. In addition, it will not be superfluous if in the prepared medicine you add the root of aira, lemon balm, chamomile and dill fruits.
For what reason there is a cough after eating and how to treat it, you can find out by reading the article.
Treatment for wet cough
If coughing attacks in a child are accompanied by sputum, this indicates a productive cough reflex. In such a course of the disease, it is very important to use medicinal herbs, the action of which is aimed at diluting sputum, increasing its quantity and speedy operation. The accumulated mucus must necessarily be removed from the bronchi, as it irritates and contains a large number of viruses and bacteria that pose a danger to the child's body.
How to treat dry cough at home is indicated in this article.
All herbs that can be used in the allocation of purulent-mucous sputum, should have an anti-inflammatory effect. When preparing a medicine, it is necessary to include in the process plants such as:
- inflorescence of elder, lungwort, linden;

- leaves of sage, mint, mother-and-stepmother;

- fruits of dill, cumin, fennel.

To make a drink, take a spoonful of each herb, add a glass of boiling water, soak the infusion in a water bath for 20 minutes. Wait until the tea cools down, drain it and take it. If there is abundant sputum, then in order to reduce it, you must use the grass of elecampane, St. John's wort, sage.
What are the symptoms of a smoker's cough, you can read in this article.
Therapy for ARVI
If a child has cough for a year or more as a manifestation of ARVI, then it is worthwhile to involve in the therapy plants that have an expectorant effect. For these purposes apply:
- mother-and-stepmother;

- ledum;
- elecampane;
- fruits of anise and thyme;
- marshmallows;
- licorice;
- plantain.

Alkaloids and saponins are present in all the components presented.These are the elements that make it possible to make sputum less often, increase its quantity and quickly remove it from the bronchi.
Which pills from the sore throat and cough are the most effective, you can learn from the article.
However, the effect obtained from such treatment does not last long. It is necessary to administer in small quantities. In addition, the result of such treatment is the withdrawal of sputum in large quantities, and for such a small child, it is sometimes very difficult to puncture it independently. This is what leads to a disruption of the drainage function of the bronchi.
Features of therapy in the growth from 2-3 years
To treat cough in these patients have their own fees, which can eliminate the annoying cough and ease the condition of the baby. The following options are considered to be the most effective:
- Take such herbs as the mother-and-stepmother's oregano, the root of the althea in the proportion 2. On 2 more spoons of raw material there is a glass of hot water. Pour a mixture of herbs and wait an hour.When the broth cools down, it must be filtered and taken every 3 hours in the amount of 3 tablespoons.
- To prepare the next broth should take in a similar proportion of such herbs: medinitsa, chamomile and oregano. The cooking and receiving process is the same as the previous recipe.
- In equal proportions take the leaves of plantain, chamomile, violet tricolor. For 3 tablespoons of raw material, take a scan of boiling water. Pour the collection and put on fire for 3 minutes. After an infusion of another hour, drain. The reception is conducted in the amount of 3 spoonfuls 5 times throughout the day.
- Take plantain, licorice root and mother-and-stepmother in the ratio 2. On 2 tablespoons of collection is a glass of boiling water. Infuse the medicine in a water bath for half an hour. Strain the broth and consume 2 spoons every 3 hours.
- In the same amount take the root of the althaea, licorice and elecampane. Pour everything with a glass of boiling water, put on a stove and keep there for 10 minutes. Cool the filtered beverage, use ¼ cup after 3 hours.
What is the treatment for perspiration in the throat and dry cough, you can learn from this article.
In the video - the use of herbs from cough for children:
What causes prolonged dry cough, you can learn from this article.
The presented fees are complex, but they also have an effect that is fast and powerful. If for some reason you do not have a certain component, then you can limit the available ones. In addition, in the treatment of infant cough can be used decoctions and infusions from a single medicinal component. The cooking process is carried out according to the standard scheme.
For children over 4 years
For such patients, their compositions based on medicinal herbs are also developed. The following fees are very active in the therapeutic process:
-
Mother-stepmother, plantain- effective remedy for cough relief in a child over 4 years old. These two components must be taken in equal proportions. Brew herbs better in a thermos, which is filled with l boiled water. To prepare the broth, you must wait 2 hours. After this drink must be filtered and give the patient to ¼ cup 3 times throughout the day 30 minutes before eating.

- Althaeus, licorice and elecampane- this herbs, which have a powerful effect on the cough treatment. If you use these plants together in one decoction, then you can already forget about this unpleasant symptom in a few days. To prepare the medicine, it is necessary to combine all herbs in equal quantities and pour two glasses of hot water. Wait 8 hours, then strain the drink to take ½ cup 3 times throughout the day.
Than to treat a dry cough and what preparations, it is possible to learn or find out having read through clause or article.

Coughing in a child can occur for the same reasons as an adult. But the treatment is markedly different, because when preparing therapy, it is necessary to take into account not only the degree of ailment, but also the age of the patient. Medicinal herbs, which effectively cough with children, can be used only after the doctor's approval. Parents should closely monitor the condition of their child. If there are any side changes, you must first stop taking the medication and immediately inform the treating doctor.
ProLor.ru
Thermopsys - instruction
 Dosage Forms of Thermopsis:Tinctures, extracts, powders, tablets. The most popular and common form of release in tablets (by 0.05 g)
Dosage Forms of Thermopsis:Tinctures, extracts, powders, tablets. The most popular and common form of release in tablets (by 0.05 g)
Composition:The main component of the drug is a perennial plant family of legumes Lancet-like thermopsis [termopsis lantsetnyiy] (other names are "drunk grass "mushchatnik"), growing in Siberia and Kazakhstan. In the manufacture of medicines, grass is used.
The herb of thermopsis includes essential oil, resins, saponins, alkaloids and ascorbic acid. In the manufacture of tablets, in addition to thermopsis, the licorice root [Glycyrrhizae radix], Codeine [Codeine] and sodium hydrogen carbonate [Sodium hydrocarbonate] are used as auxiliary substances.
Thermopsis application
It is mainly used to suppress cough of various origin in adults and children (up to two years of age), being also an excellent expectorant for all age groups. Also, medicinal preparations based on this herb are used for a variety of diseases of the respiratory tract (upper and lower divisions): chronic tracheitis, bronchopneumonia, bronchitis. With excellent effectiveness in the case of treatment of the above diseases, tablets "Thermopsis" have minimal side effects effects, regardless of the duration of administration (of course, with proper application and no violations in dosages).
Preparations based on the herb of thermopsis are also prescribed in complex treatment as a component of herbal or therapeutic tea.
When catarrhal phenomena occur in the upper respiratory tract, often accompanied by a difficult-to-separate inflammatory attack on the mucous membranes shells in the oral cavity, the pills of thermopsis are used as an effective expectorant cleansing the respiratory tract from the negative impact.
Thermopsis action
Antitussive tablets with thermopsis are not only effective, but also a very popular remedy, and he who already used this drug, is unlikely to seek an analog treatment, giving preference to the already tried method.
How do the tablets with thermopsis work? The main effect of thermopsis is its expectorant effect; When using the drug, bronchus begins to produce more mucus. In addition, thermopsis is rich in alkaloids containing nitrogen, which have a combined effect on respiratory organs. Although initially preparations with the content of thermopsis are intended as means for expectoration, an overdose can cause an emetic effect.
 The tablet, resorbed, enters the bloodstream, from there the drug enters the mucous environment of the bronchi and trachea, that, being an irritant, causes a cough and increased breathing, which leads to the removal of phlegm by expectoration.
The tablet, resorbed, enters the bloodstream, from there the drug enters the mucous environment of the bronchi and trachea, that, being an irritant, causes a cough and increased breathing, which leads to the removal of phlegm by expectoration.Sodium hydrogen carbonate, contained in tablets, reduces the degree of sputum density; licorice root produces both expectorant and anti-inflammatory effect, as well as antispasmodic act. Glycyrrhizin, contained in the preparation, is a stimulant for the ciliary epithelium of the bronchi, causing the expectorant properties of the tablets. Codeine as part of the drug also produces an antitussive effect.
Do not lose sight of the fact that with irritation of the bronchial cough can be by nature, both dry and wet, so Before using tablets with thermopsis, the effect of which may be unpredictable, you should consult a doctor doctor.
Contraindications
Tablets "Termopsis" due to natural ingredients in the composition is suitable for almost all age groups, excluding children under the age of two. However, given the complexity of the composition, the approach to taking the drug should be followed with caution. Possessing the effect of enhancing breathing, the drug is not recommended for those who suffer from asthma, also from its intake should refrain lactating and pregnant women (especially in the 1st and 3rd trimester), since there is a threat miscarriage.
Side effects
Despite the minimal side effects, long-term use of the drug may exert a certain dependency, given the presence of codeine in the formulation. You should also be careful with the appointment of the drug to people prone to allergic reactions: there may be skin itching, hives, nausea.
Overdose of the drug is fraught with headaches; there may be an emetic effect and the appearance of drowsiness. Also, with an overdose, coordination of movements is disturbed and breathing becomes difficult. Possible constipation.
If the renal function is impaired, the daily dose of the drug should not exceed 2 tablets, while a sufficient interval between doses should be observed.
Given the possible sedative effect, the tablet "Thermopsis" is strictly prohibited for use in driving, as well as in cases requiring increased attention.
In case of an overdose and the manifestation of the above symptoms, it is necessary to apply gastric lavage, use activated charcoal, and also to cancel the reception of "Thermopsis".
Dosages and Administration Thermopsis
In the absence of contraindications, tablets "Thermopsis" are administered orally 1 unit 2 or 3 times a day.
Interaction with other drugs
Given the content of codeine in the preparation, caution should be applied to "Thermopsis" when using drugs that depress the central nervous system.
Drugs that have astringent and enveloping properties, as well as absorbent substances, can weaken the absorption of the drug by the gastrointestinal tract.
Synthetic antibiotic chloramphenicol weakens the metabolism of codeine in the liver, thereby enhancing its effect when applying "Thermopsis".
Medicinal forms containing the herb of Thermopsis
Dosage and methods of administration
Unlike tablets that have an age limit for children under the age of two, infusion of thermopsis can be prescribed outside the age category.
The powder of thermopsis is prescribed: adult patients from 2 to 3 times a day (from 1 to 5 grams). Infusion (calculation when cooking, -1 gram for 180-200 ml of liquid) is taken 1 tablespoon 3-4 times a day.
Babies up to two years are prescribed infusion from, to 1 teaspoon at the rate of 2 grams per 100 ml; children of the eldest groups take an infusion in the amount of 1 dessert spoon from 3 to 5 times a day at a rate of 100 grams ml.
For adults, the highest dose of receiving the herb of thermopsis is no more than one gram per day, not more than, gram per day.
For children up to 6 months the highest dose of the herb of thermopsis: up to, 05 grams one time, not more, 15 grams per day. For children from 6 months to one year, the dosage is: up to, 1 gram once, not more, 3 grams per day. Children of the age group 3-4 years old take the herb of thermopsis: up to 15 grams a day, no more, 45 grams per day. Children of the age group 5-6 years: up to, 2 grams a day, not more, 6 grams per day. Children of the age group of 7-9 years: up to, 25 grams a day, not more, 75 grams per day. Children of the age group of 10-14 years: up to, 3 grams one-time, not more, grams per knock.
For medical purposes, a dry extract of the herb of thermopsis [Latin name Extractum Thermopsidis siccum], which is a powder of light brown color, is also used the composition of which is a mixture of milk sugar and a dry standard extract, in a ratio of 1 gram of the drug = 1 gram of Termopsis lantsetnyiy (the alkaloid content is 1%).
kashelb.com



