 Inflammation of the walls of deep, under the layer of muscles, veins on the legs with the simultaneous formation of thrombi in them is called thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the lower limbs. This pathology is a complication of varicose veins.
Inflammation of the walls of deep, under the layer of muscles, veins on the legs with the simultaneous formation of thrombi in them is called thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the lower limbs. This pathology is a complication of varicose veins.
Statistics say that most often thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities occurs in women. This fact physicians associate with wearing uncomfortable shoes, using hormonal contraceptives. Provoke the occurrence of thrombophlebitis and pregnancy.
Depending on the nature of the flow, acute, subacute and chronic forms of thrombophlebitis are isolated.
Causes
Why does thrombophlebitis occur, and what is it? Thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the lower limbs is an inflammatory process, a complication of varicose veins (its next stage in neglect of self). This area is inflamed due to the formation of a thrombus. Quite often this disease is one-sided: only one shin or thigh is affected.
Predisposing factors to the disease:
- hereditary predisposition;
- long standing in a standing or sitting position;
- strict bed rest for a long time;
- presence of an anamnesis of varicose veins;
- tendency to increased blood coagulability;
- oncological diseases;
- period of pregnancy;
- overweight;
- elderly and senile age.
Thrombophlebitis can also beclassify according to current form:
- Acute thrombophlebitis develops very quickly, in just a few hours;
- Chronic thrombophlebitis develops imperceptibly and gradually, and periods of exacerbation are rare;
- Migrating thrombophlebitis affects several vessels at once. New foci of inflammation appear regularly, but completely disappear with time, leaving no traces.
It must be remembered that this ailment is extremely dangerous, since two bad things can happen to the patient things: clogging of the blood vessel and separation of the thrombus with subsequent transfer to the bloodstream. The consequences of such phenomena can be fatal for a person.
Symptoms
With thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the lower limbs, symptoms and treatment are interrelated. In most cases, the patient has such symptoms:
- Pain in the leg where thrombophlebitis develops. Often the temperature of the diseased limb is lower than that of the healthy one.
- The body temperature rises a lot, sometimes the temperature gradient can reach 40 degrees.
- Swelling of the lower extremity occurs.
- The skin is pale, the skin becomes strained, tense.
The localization of thrombosis can also be different - the shin, ankle, thigh. Occasionally, the ailment develops without visible symptoms - this leads to a sharp complication, and in the future - to an unexpected lethal outcome.
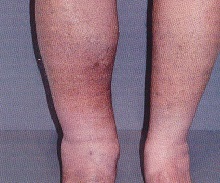
Thrombophlebitis: photos
What does thrombophlebitis of deep veins of lower extremities look like? We offer detailed photos of clinical manifestations.
Diagnostics
Before treating thrombophlebitis of deep veins of the lower extremities, it is necessary to conduct competent diagnostics. The doctor will ask you to undress and examine the inside and outside of each leg from foot to groin. In this case, such signs of the disease can be revealed:
- swollen superficial veins;
- swelling of the foot and lower leg;
- cyanosis of the skin in certain areas;
- a painful patch along the veins;
- hyperthermia (fever) of individual skin areas.
Sometimes the clinical picture of DVT does not allow you to establish a diagnosis by simply identifying the symptoms and signs of the disease. In such cases, more complex diagnostic methods are used:
- UltrasonographyIs a method that allows to detect thrombi in the lumen of the deep veins of the legs. Most often, duplex Doppler is used, with which you can both detect thrombi and assess the speed and direction of blood flow in the vessels.
- D-dimer- a substance released into the blood during the degradation (resorption) of the thrombus. At its normal level, it is possible to assume with great probability that there is no thrombosis in the patient's body and further examination (ultrasound of veins) is not necessary. It should be borne in mind that an elevated D-dimer in the blood does not always reliably indicate DVT, as its level may increase after surgery, trauma or during pregnancy. To confirm the diagnosis, an additional examination is carried out.
- CT scan- The method used to diagnose DVT is rare. To detect blood clots in the vessels, intravenously injected contrast, and then make a series of X-ray photographs, which are processed by the computer to obtain a detailed image.
- Venography- a method of visualizing blood vessels by injecting a contrast medium into the veins of the foot. The contrast with the blood flow falls into the deep veins and rises along the leg, it can be detected by X-ray examination. This method allows to detect thrombi in the vessels, when the blood test for D-dimer and ultrasound could not confirm or disprove DVT.
Complications of DVT
The most dangerous complication of DVT is PE. If the severed embolus is small and blocks an artery of small diameter, it most often does not cause any symptoms.
If a thrombus overlaps a sufficiently large vessel in the lungs, the following can develop:
- Shortness of breath and rapid breathing.
- Pain or discomfort in the chest.
- Cough with discharge of blood.
- Accelerated or irregular heartbeat.
- Reduced blood pressure, fainting, confusion.
- Increased anxiety or nervousness.
If these symptoms are found, seek medical help immediately.
Treatment of deep vein thrombophlebitis
When symptoms of deep vein thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities appear, the treatment can be either conservative or surgical, taking into account the individual characteristics of the organism and the course of the disease.
The principles of conservative therapy are the following:
- Creation of rest for a sick leg.
- Elevated limb position.
- Mandatory appoint in the treatment of thrombophlebitis anticoagulant, which dissolve the thrombus and prevent the formation of new clots. These include warfarin in tablets and heparin or fractiparin in injections. When using them, the parameters of hemostasis are necessarily controlled.
- Improvement of microcirculation (for this purpose pentoxifylline is prescribed).
- Also used are painkillers, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial drugs, solutions that improve the rheological (flowing) properties of blood (rheopolyglucin), vitamins and antioxidants.
- Ointments, gels can reduce inflammation, relieve pain, reduce blood clotting. But with thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the lower limbs, they are ineffective, so additionally prescribed medication in tablets, injections.
- The next point of treatment of a patient with a diagnosis of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities is the use of compression knitwear and active movements. With the use of elastic bandage, the symptoms of deep thrombosis decrease significantly: swelling and pain. Usually, stockings with compression from 23 to 32 mm Hg are used, and the length is adjusted depending on the topic of thrombosis. Thus, a patient with thrombophlebitis of femoral veins and pelvic vessels requires stockings up to inguinal folds, with permanent wearing, regardless of the location of the cause of the disease, stockings are recommended to the knees.
Combination therapy of these methods in combination with active movements brings great results. Significantly decreases the intensity of pain and swelling. Progression of the process of thrombosis is promoted by hypo- and adynamia. Therefore, the patient is advised to walk until the pain in his legs, if there is no contraindication.
Physiotherapy
It is possible to distinguish several methods of physiotherapeutic treatment used at the DVT of the legs.
- UHF- under the influence of high-frequency electric fields in affected areas, the outflow of lymph, blood circulation, regeneration processes in general is stimulated.
- Electrophoresis- drugs are injected through the skin with the aid of an electric current.
- Magnetotherapy- under the influence of the magnetic field, the characteristics of the blood composition are improved.
- Paraffin Wraps- useful in the threat of the formation of trophic ulcers. The procedure is not used for acute thrombophlebitis.
Also, with acute thrombophlebitis of the deep veins of the lower extremities, hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches) can be used.
Operation
Surgical treatment of deep vein thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities is performed with ineffectiveness of drug therapy, high risk of embolic complications and ascending thrombosis. To do this, you can use open surgery and endovascular.
- Cava filtersset in the vein with flotation thrombus. Implantation of the cava filter is indicated by the patient for contraindications to the use of anticoagulants. The lower hollow vein is the main trunk vessel, through which blood moves from the lower extremities, the internal organs of the pelvic cavity and the abdominal cavity, to the heart and lungs. Therefore, in case of inefficiency of drug treatment of thrombosis, you may be recommended to implant the filter in lower vena cava to prevent the development of thromboembolism (migration of the thrombus pieces through the inferior vena cava system). A filter in the lower vena cava is usually inserted through the femoral vein, but can also be inserted through the system of the superior vena cava (vein of the neck and upper limbs).
- Stitching of the inferior vena cavaPerform if there is no possibility to implant the filter. And also with multiple thrombi or relapse of the disease. In this case, a "clip" (special clamp) is applied to the affected area of the vessel and stitched. This allows you to partially close the channel, leaving a certain clearance for blood flow. The disadvantage is a worsening of the outflow of blood from the veins of the lower limb.
After the surgery (any of these), you should wear a compression bandage or stockings. In this case, the first three days are not allowed, in general, to remove them, since there is a high probability of formation of new phlebolites.
Nutrition and Diet
Nutrition with thrombophlebitis does not impose strict prohibitions. But you have to follow some rules. The menu should contain products that strengthen the wall of blood vessels and prevent blood clotting:
- onion and garlic;
- a variety of vegetables: tomatoes, carrots, beets;
- Nuts and dried fruits: figs, dried apricots, raisins;
- Fish and seafood;
- sea kale;
- dairy products: cottage cheese, kefir, yoghurt;
- Cereals: any cereals and sprouted grains;
- berries: cranberries, cranberries, grapes, sea-buckthorn;
- melons: water melons, melons;
- vegetable oils: linseed, olive;
- spices: ginger, cinnamon, red capsicum.
Limit the consumption of foods that damage the blood vessels or increase blood coagulability:
- animal fats: fat, butter;
- strong coffee;
- meat, especially in fried and smoked form (meat dishes can be eaten 2-3 times a week);
- strong meat broths;
- pickled dishes;
- beans: beans, peas;
- bananas, dogrose and black currant;
- baking, baking, confectionery;
- alcoholic beverages.
Avoid products containing vitamin K, which takes part in blood clotting, this is:
- spinach;
- broccoli;
- pork and beef liver;
- green leafy cabbage;
- watercress.
How to treat thrombophlebitis in the home?
Treatment at home is possible if the disease has not gone beyond the shin, and there is no danger of a blood clot in the deep venous system. Only a doctor can determine this, so consult an expert before starting an independent treatment.
If the disease has begun acutely, then observe bed rest, make sure that your leg is raised. To enhance the effect, combine folk methods of treatment with local medication.
Local treatment:
- Ointments containing heparin: Lyoton-gel, Gepatrombin. Improve blood circulation, expel the fluid that stagnates in the tissues, inhibit the growth of the thrombus. Apply to the affected area 2-3 times a day.
- Ointments with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Indomethacin Ointment, Dip-Relief, Indovazin. Relieve pain, effectively relieve inflammation. Use a small amount of the drug 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment should not exceed 10 days.
- Ointments with rutoside: Venoruton, Rutozid. Improve the condition of the venous wall, reduce puffiness, reduce soreness. Apply 2 times a day, a small amount of gel rubbed until completely absorbed. After the improvement comes, ointment or gel is used once a day.
Prevention
Preventive measures are as follows:
- wearing comfortable shoes and clothes that do not compress the limbs;
- rejection of bad habits;
- playing sports;
- dropping excess weight;
- Rest, especially with regards to the feet, is advised sometimes to sleep with raised legs and do a massage.
So, thrombophlebitis should not be taken lightly, since the complications of this disease can be very serious. It is important to give up self-treatment and begin to follow the advice of doctors. This will help to remain a physically active person.
Forecast
Many patients who underwent the first episode of DVT develop a relapse of the disease. The frequency of recurrence depends on the treatment:
- Without the use of anticoagulant therapy for 3 months, venous thromboembolism develops in 50% of patients.
- When conducting anticoagulant therapy, the risk of recurrence during the year is about 8%.
- The risk of recurring thrombosis reduces the use of compression knitwear.
The probability of development of PE is dependent on the location of thrombi - the higher they have climbed through the veins of the leg, the greater the danger. In the absence of treatment from PE, about 3% of patients with DVT die.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



