 Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by connective tissue damage and vessels and, as a consequence, involvement in the pathological process of virtually all organs and systems of the body.
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by connective tissue damage and vessels and, as a consequence, involvement in the pathological process of virtually all organs and systems of the body.
In the development of systemic lupus erythematosus, a certain role is played by hormonal disorders, in particular, an increase in the amount of estrogens. This explains the fact that the disease is more often registered in young women and adolescent girls. According to some data, in the emergence of pathology, an important role is played by viral infections, intoxications with chemicals.
This ailment relates to autoimmune diseases. Its essence lies in the fact that the immune system starts to produce antibodies for some stimulus. They adversely affect healthy cells, as they affect their DNA structure. Thus, due to antibodies, a negative change in connective tissue and vessels occurs.
Causes
What causes contribute to the development of systemic lupus erythematosus, and what is it? The etiology of the disease is unknown. In its development, the role of viral infection, as well as genetic, endocrine and metabolic factors is assumed.
Patients and their relatives have lymphocytotoxic antibodies and antibodies to double-stranded RNA, which are markers of a persistent viral infection. In the endothelium of the capillaries of damaged tissues (kidneys, skin), virus-like inclusions are detected; on the experimental models the virus was identified.
SLE occurs mainly in young (20-30 years) women, but cases of the disease are common in adolescents and older people (more than 40-50 years). Only 10% of men are affected, but the disease is more severe for them than for women. The provoking factors are often insolation, drug intolerance, stress; women - childbirth or abortion.
Classification
The disease is classified according to the stages of the disease:
- Acute systemic lupus erythematosus. The most malignant form of the disease, characterized by a continuous-progressive course, a sharp increase and a multiplicity of symptoms, resistance to therapy. In this type, systemic lupus erythematosus often occurs in children.
- Subacuteis characterized by a periodicity of exacerbations, however, with a lesser degree of symptomatology than with acute SLE. The defeat of the organs develops within the first 12 months of the disease.
- Chronic formis characterized by a long-term manifestation of one or more symptoms. A combination of SLE with an antiphospholipid syndrome with a chronic form of the disease is especially characteristic.
Also during the disease, three main stages are distinguished:
- The minimum. There are minor head and joint pains, a periodic increase in body temperature, malaise, as well as the initial skin signs of the disease.
- Moderate. Significant damage to the face and body, involvement in the pathological process of blood vessels, joints, internal organs.
- Expressive. There are complications from internal organs, brain, circulatory system, musculoskeletal system.
Systemic lupus erythematosus is characterized by lupus crises, in which the activity of the disease is maximal. The duration of the crisis can be from one day to two weeks.
Symptoms of Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus manifests itself in a large number of symptoms, which is caused by tissue damage of almost all organs and systems. In some cases, manifestations of the disease are limited exclusively to skin symptoms, and then the disease is called discoid lupus erythematosus, but in most cases there are multiple lesions of the internal organs, and then they speak of the systemic nature of the disease.
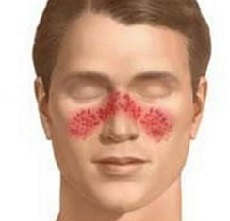
At the initial stages of the disease, lupus erythematosus is characterized by a continuous course with periodic remissions, but almost always turns into a systemic form. Often there is erythematous dermatitis on the face like a butterfly - erythema on the cheeks, cheekbones and always on the back of the nose. Appears hypersensitivity to solar radiation - photodermatosis is usually rounded, are of multiple character.
The defeat of joints occurs in 90% of patients with SLE. In the pathological process involved small joints, usually fingers fingers. The defeat is symmetrical, patients are concerned about pain and stiffness. Deformation of the joints is rare. Aseptic (without an inflammatory component) necrosis of bones are common. The head of the femur and the knee joint are affected. In the clinic symptoms of functional insufficiency of the lower limb predominate. When involving the pathological process of the ligamentous apparatus, unstable contractures develop, in severe cases dislocations and subluxations.
General symptoms of SLE:
- Soreness and swelling of the joints, muscle pain;
- Unexplained fever;
- Chronic fatigue syndrome;
- Rashes on the skin of the face of a red color or a change in the color of the skin;
- Pain in the chest with deep breathing;
- Reinforced hair loss;
- Whitening or blue skin of the fingers or hands in the cold or under stress (Raynaud's syndrome);
- Hypersensitivity to the sun;
- Swelling (swelling) of the legs and / or around the eyes;
- Enlargement of lymph nodes.
To dermatological signsdiseases include:
- A classic rash on the bridge of the nose and cheeks;
- Spots on limbs, trunk;
- Baldness;
- Fragility of nails;
- Trophic ulcers.
Mucous membranes:
- Redness and ulceration (appearance of ulcers) of the red border of the lips.
- Erosion (surface defects - "mucous membrane") and ulcers on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
- Lupus-cheilitis - marked dense swelling of the lips, with densely attached to each other grayish scales.
Defeat of the cardiovascular system:
- Lupus myocarditis.
- Pericarditis.
- Endocarditis of Liebman-Saks.
- The defeat of the coronary arteries and the development of myocardial infarction.
- Vasculitis.
With lesions of the nervous systemthe most frequent manifestation is asthenic syndrome:
- Weakness, insomnia, irritability, depression, headaches.
With further progression, it is possible to develop epileptic seizures, memory and intellect disorders, psychoses. Some patients develop serous meningitis, optic neuritis, intracranial hypertension.
Nephrological manifestations of SLE:
- Lupus-nephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidneys, in which thickening of the glomerulus membrane occurs, fibrin is deposited, hyaline thrombi are formed. In the absence of adequate treatment, the patient can develop a persistent decline in kidney function.
- Hematuria or proteinuria, which is not accompanied by pain and does not bother a person. Often, this is the only manifestation of lupus from the urinary system. Since currently diagnosing SLE is timely and effective treatment begins, acute renal failure develops only in 5% of cases.
Gastrointestinal tract:
- Erosive-ulcerative lesion - patients are concerned about lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, pain in various parts of the abdomen.
- Infarction of the intestine due to inflammation of blood vessels that supply blood to the intestines - a picture of "acute abdomen "with high-intensity pain localized more often around the navel and in the lower abdomen.
- Lupus hepatitis - jaundice, an increase in liver size.
Lung infection:
- Pleurisy.
- Acute lupus erythematosus.
- The defeat of the connective tissue of the lungs with the formation of multiple foci of necrosis.
- Pulmonary hypertension.
- Pulmonary embolism.
- Bronchitis and pneumonia.
It is almost impossible to assume lupus before going to the doctor. Consult for advice if you have an unusual rash, fever, joint pain, fatigue.
Systemic lupus erythematosus: a photo
How does systemic lupus erythematosus look like, we offer detailed photos for viewing.
Diagnostics
If you suspect a systemic lupus erythematosus, the patient is referred to a rheumatologist and dermatologist for advice. To diagnose systemic lupus erythematosus, several diagnostic diagnostic systems have been developed.
Currently, the system developed by the American Rheumatic Association is preferred as being more modern.
The system includes the following criteria:
- butterfly symptom:
- discoid rash;
- the formation of ulcers on the mucous membranes;
- kidney damage - protein in the urine, cylinders in the urine;
- brain damage, convulsions, psychosis;
- increased sensitivity of the skin to light - the appearance of a rash after exposure to the sun;
- arthritis - affection of two or more joints;
- polyserositis;
- decrease in the number of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets in a clinical blood test;
- the detection of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) in the blood.
- the appearance in the blood of specific antibodies: anti-DNA antibodies, anti-Sm antibodies, false positive reaction Wasserman, anticardiolipin antibodies, lupus anticoagulant, positive test for LE cells.
The main goal of treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus is the suppression of the autoimmune reaction of the body, which underlies all the symptoms. Patients are assigned different types of drugs.
Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus
Unfortunately, a complete cure for lupus is not possible. Therefore, therapy is selected so as to reduce the manifestation of symptoms, to stop the inflammatory as well as autoimmune processes.
The tactics of treating SLE are strictly individual and can change with the time of the disease. Diagnosis and treatment of lupus - often combined efforts of the patient and doctors, specialists of various specialties.
Modern drugs for the treatment of lupus:
- Glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone or others) are potent drugs that fight with inflammation in case of lupus.
- Cytostatic immunosuppressants (azathioprine, cyclophosphamide or others) - drugs that suppress the immune system, can be very useful in lupus and other autoimmune diseases.
- Blockers of TNF-α (Infliximab, Adalimumab, Etanercept).
- Extracorporeal detoxification (plasmapheresis, hemosorption, cryoplasmosorption).
- Pulse therapy with high doses of glucocorticosteroids and / or cytostatics.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - can be used to treat inflammation, swelling and pain caused by lupus.
- Symptomatic treatment.
If you suffer from lupus, you can take several steps to help yourself. Simple measures can make exacerbations less likely, and also improve the quality of your life:
- Refuse from smoking.
- Exercise regularly.
- Adhere to a healthy diet.
- Beware of the sun.
- Adequate rest.
The prognosis for life in systemic lupus is unfavorable, but the latest advances in medicine and the use of modern medicines give a chance for an extension of life. Already more than 70% of patients live more than 20 years after the primary manifestations of the disease.
At the same time, doctors warn that the course of the disease is individual, and if one part of the patients develops SLE slowly, then in other cases, the rapid development of the disease is possible. Another feature of systemic lupus erythematosus is the unpredictability of exacerbations, which can occur suddenly and spontaneously, which threatens with severe consequences.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



