 Giardiasis is a common infectious disease of the human body, caused by the intestinal unicellular parasite lamblia. Giardiasis is found in adults and children all over the world.
Giardiasis is a common infectious disease of the human body, caused by the intestinal unicellular parasite lamblia. Giardiasis is found in adults and children all over the world.
Lamblias are unicellular microscopic parasites that can reproduce in the small intestine of a person. When infection with this parasite and the presence of clinical symptoms of the disease requires adequate treatment of Giardiasis.
The disease has both a light and a heavy current. In some cases, lamblia carriers themselves do not get sick, but can infect others, as their body serves as a safe container for pathogens.
The causative agent of Giardiasis
What it is? Lamblium is a unicellular parasite, which, under favorable conditions, shows great activity. The causative agent of giardiasis can exist in two forms: trophozoids and cysts. Trophozoids actively multiply, causing the appearance of negative symptoms. Cysts are rounded formations that protect unformed trophozoids from aggressive factors.
The main way of infection with lambliasis is fecal-oral. Cysts with feces of a human or animal fall into the external environment. They are able to maintain viability in water bodies for several months. The causative agents of giardiasis can withstand freezing, raising the temperature to 50 ° C. They die by boiling. Infection with Giardiasis is possible with the use of tap water, when washing fruits and vegetables with unboiled water. In the summer, you can get infected by buying in a pond that is infected with Giardia cysts.
It is very rare to consider the contact-household way of infection. But, nevertheless, it is possible if hygiene rules are not observed in everyday life.
Classification
- Lamblingship(asymptomatic giardiasis) - there are no signs of disease, but at the same time a person allocates lamblia to the environment.
- Intestinal form- signs of impaired bowel function.
- Hepatobiliary form- a violation of the liver, biliary tract.
- Giardiasis as a Concomitant Disease, when the main chronic disease (atopic dermatitis (skin allergy), celiac disease (a genetic disease in which the gluten protein causes damage mucosa of the small intestine, and the absorption process is disturbed)), causes a decrease in immunity, and various infections, for example giardiasis, are attached.
Symptoms of Giardiasis
In adults, the symptoms of lamblia can vary and depend on various factors, such as the amount of lamblia in the body, the duration of infection, the age of the patient. In general, the symptoms of infection with giardiasis in adults are expressed as disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
The duration of the incubation period of giardiasis is from 1 to 3 weeks. A typical symptom of giardiasis in adults is gastrointestinal syndrome. Since parasites are localized in the small intestine, this leads to a disruption of many functions of the digestive tract.
In the acute form of the manifest giardiasis, pain predominates in the navel and / or right hypochondrium, signs of dyspepsia disorders - nausea, belching, bloating, a feeling of fullness of the stomach, loss of appetite, etc. The pains do not depend on the intake of food, they are constantly aching, sometimes they are sharp. Typical diarrhea with a frequency of bowel movements up to 3-5 times during the day.
Watery and frothy stool, observed at the beginning of the disease, then becomes fat and semi-shaped. Often diarrhea alternates with constipation. The duration of the acute phase is no longer than 7 days, after which recovery occurs or the course of the disease becomes subacute or chronic.
So, let's consider the mainmanifestations of intestinal form of Giardiasis:
- ambiguous pain in the right part of the epigastric region;
- soreness in the navel area, not associated with meals;
- paroxysmal pain with nausea and vomiting;
- feeling of a full stomach, accompanied by bloating;
- deterioration of appetite;
- eructation;
- steatorrhea - a large amount of fats in the feces (usually with enteritis);
- heartburn;
- problems with stool: diarrhea (sometimes of a foamy nature) can be replaced by constipation and vice versa.
Hepatobiliary formtoo often occurs in adult patients. Usually it is expressed by cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), as well as by dyskinesia (a violation of the motor function) of the bile ducts. In these cases, the main symptoms of the disease are:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- belching with bitter aftertaste;
- soreness when touching the abdomen in the gallbladder;
- The skin manifestations of Giardiasis are limited to a slight jaundice and itching.
Characteristic are also general symptoms: pallor of the skin (even with normal hemoglobin concentration in the blood), weakness, irritability, bruises under the eyes, "seizures" around the mouth, allergic manifestations.
Chronic lambliasis
The launched form of giardiasis is found mainly in adults and children of school age. It is characterized by a recurrent course.
Considersigns of giardiasis in chronic form:
- deterioration of the general state of the human body (lag in the physical development of the younger generation);
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract (unstable and irregular stools, aching abdominal pain, nausea, lack of appetite, etc.);
- cholecystitis and colitis;
- deterioration of well-being in the form of headaches, malaise, painful thinness, hypotrophy;
- a decline in strength and a lined tongue;
- uneven skin color (in case of constipation);
- allergic reactions (itching on the skin, hives, etc.);
- A bronchial asthma, an arthritis and many other things.
Treatment of giardiasis is quite long. In order to destroy all lamblia, the number of which in an adult can reach several million, several courses of antiparasitic drugs are required. It is also necessary to restore the intestinal microflora, detoxify.
Lambliasis analysis
Giardia is difficult to diagnose without laboratory confirmation.If suspected of giardiasis is directed to:
- a blood test (antibodies to lamblia are detected);
- stool examination (detection of cysts);
- duodenal sounding - in the contents of the lumen of the duodenum find lamblia.
The most accessible method of laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis is coprological examination. However, it should be noted that lamblia cysts in the stool can not be detected. In addition, it is desirable to conduct a study of duodenal contents. And also the serological diagnosis of giardiasis is carried out, when specific antibodies are detected in the blood 2-4 weeks after infection.
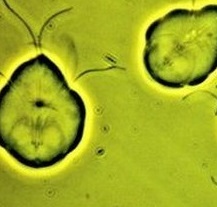
Lambliasis: photo
As the lambliasis looks, we offer detailed photos to view.
How to treat giardiasis
In adults, the treatment of giardiasis should be performed only by a physician with an infectious disease specialist or gastroenterologist and in no way independently at home.
Scheme of treatment of Giardiasisis carried out in 3 stages:
- Improved intestinal activity, elimination of toxicosis, increased immunity.
- Antiparasitic treatment with drugs.
- Strengthening defensive forces, creating conditions that prevent the proliferation of lamblia.
A special diet is included in the number of obligatory measures, due to which it is possible to create certain conditions that prevent the lamblia from multiplying. The menu of such patients should include porridge, dried fruits, vegetable oil and washed vegetables. You should significantly reduce the use of carbohydrates.
The first stage of treatment
Treatment of Giardia at the first stage lasts no more than two weeks and includes such events as:
- Diet, which helps stop the development of the lamblia parasite. The food is based on the restriction of refined carbohydrates, gives preference to cellulose and lean dishes.
- Removing signs of toxicosiswith the help of enterosorbents (Enterosgel, Polyphepanum, Polysorb, activated carbon).
- Reception of enzyme preparationsto improve digestion (Creon, Mezim-forte, Pancreatin).
- Reception of cholagogue preparations and herbs. Such treatment is carried out to improve the outflow of bile.
- Taking antiallergic drugs(Diazolin, Cetrin, Loratadine, Desloratadine).
The second stage of treatment
itbasic antiparasitic therapy. The patient is prescribed a course of drugs, whose action is aimed at the destruction of protozoa. For this purpose, derivatives Furazolidone, Metronidazole, Ornidazole, Tinidazole, Albendazole are used. The doctor will select the necessary medicine on an individual basis.
In this case, the specialist will take into account possible contraindications, the patient's condition, determine the duration of taking and dosage of the drug. Simultaneously with drugs from parasites, at this stage continue to receive enterosorbents and antihistamines.
The third stage of treatment
This stage is intended to consolidate the achieved result and includes the following within 2-3 weeks:
- Antialliasis diet.
- Multivitamins, adaptogens.
- Enzyme preparations.
- Probiotics (Bifiform, Bifidumbacterin, Linex, etc.).
Diet for giardiasis
In the fight against the disease from the diet, it is necessary to exclude such foods: whole milk, pasta, flour products, sweets, bakery and sausage products. From cereals, you can only eat buckwheat, corn and rice.
Milk must be replaced with curdled milk or kefir. It is very useful for giardiasis to drink cranberry or cranberry mors. Meat should be low-fat and boiled, and fruits and vegetables can be eaten in any quantity. It is not recommended to use mayonnaise as a dressing, it is better to use vegetable oil.
It is very important to adhere to separate food and to ensure that the body receives all the necessary nutrients and trace elements.
Treatment during pregnancy
All drugs used to treat giardiasis can have a negative impact on the development of the fetus. For this reason, treatment for lamblia in pregnant women either is postponed for the period after delivery, or, at least, is transferred to the second trimester of pregnancy and is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
Macmirror for giardiasis: reviews
Macmirror is a combination drug containing a preparation of the nitrofuran series (similar to the same furazolidone). Like all nitrofurans, it is active against the simplest, the same lamblia.
However, nitrofuran preparations are not a means of choosing the treatment of giardiasis, t. Their activity against them wants the best. Macmirror is well-approved for the treatment of trichomoniasis, as for lambliasis, then the reviews about it are contradictory.
Prevention of Giardiasis
Prevention of lamblias invasion includes a set of standard measures recommended to protect against infections with a fecal-oral transmission mechanism:
- Do not drink raw (unboiled or not purified otherwise) water.
- Do not swallow water while swimming in open water and explain to children that this can not be done.
- Carefully wash all the fruits and vegetables served on the table, as well as your hands before eating.
- Do not let your pet (cats, dogs) lick your face and hands, and demand the same treatment of animals from children.
It is much easier to prevent invasion, than to carry out the subsequent treatment of giardiasis.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



