- What happens in the body during an attack?
- Causes of
- How does dumping occur?
- Classification of seizures
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
- Related videos
Surgical interventions for stomach diseases can be accompanied by complications. One of them is dumping syndrome. It appears, according to different data, in 10-30% of operated patients after removal of part of the stomach, the intersection of the innervation of the vagus nerve, but also in non-operated patients with chronic diseases.
The essence of pathological disorders is a sharp acceleration of transportation of unprepared contents from the stomach to the intestine without the necessary digestion. Attacks( dumping attacks) are caused by the effects of a digestive failure, lack of nutrients, loss of fluid, imbalance of hormonal provision.
What happens in the body during an attack?
A dumping attack is usually associated with eating, an attack occurs immediately after or during a meal. Because of the loss of part of the stomach in the remaining organ, the functions( secretions of gastric juice, motility, mixing and movement of food, storage) are disrupted. As a result, the unprocessed lump of food is immediately sent to the small intestine. Here there is an accelerated cleavage of proteins( hydrolysis).
The flow from the duodenum to the lean concentrated fluid( hypertonic solution) is accompanied by a significant absorption of water from the extracellular space, blood plasma. The gut is overfilled, stretched, reacts with diarrhea.
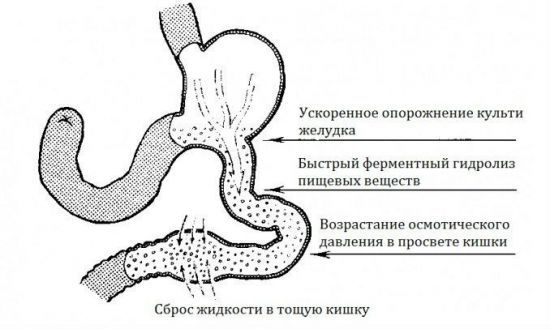
The main links in the formation of the dumping syndrome ultimately disrupt the whole digestion process.
. Transition of fluid and electrolytes into the intestines contributes to the redistribution of blood supply to the internal organs: increased blood filling of the liver, cerebral and arterial ischemia, and the widening of peripheral capillaries.
In response to stretching, the production of the hormone serotonin increases. Together with the drop in the volume of circulating plasma( hypovolemia), it causes vascular manifestations( a feeling of heat, severe weakness, palpitation, sweating, shortness of breath).
Accelerated absorption in the small intestine of glucose leads to activation of intrasecretory functioning of the pancreas, increase in the production of the hormone insulin, under its influence hypoglycemia develops with weakness, headache, dizziness, and violation of consciousness.
In the blood plasma of patients during an attack, the content of various biologically active substances( kinins, substance P, enteroglucagon, vasoactive intestinal peptide, neurotensin) increases. At the same time, excitation of the parasympathetic department of the nervous system is registered, this helps to increase the level of acetylcholine.
All the regulating systems of the body are involved in the mechanism of the dumping syndrome. Completely it has not been studied yet. But it is believed that the main violation is the blocking of feedbacks from "control centers".This is confirmed by the effect on the neuropsychological status of patients.
Causes of
The study of the syndrome showed that it is observed in patients who underwent stomach surgery, and in those who have never been operated on. The difference in probable causes will be considered for these two groups of patients. What operations cause dumping syndrome?
Of the operations on the stomach, the most common are resection( removal of part of the organ) for non-healing ulcers, tumors, stenosis of the pylorus. Less often, vagotomy is performed( excision of the vagus nerve) with recurrent ulcer disease.
The main cause of post-resection dumping syndrome is determined by the loss of body volume and a violation of the ability of the remaining stump to provide adequate digestion of food, delay the lump for the necessary time and evacuate to the duodenum.
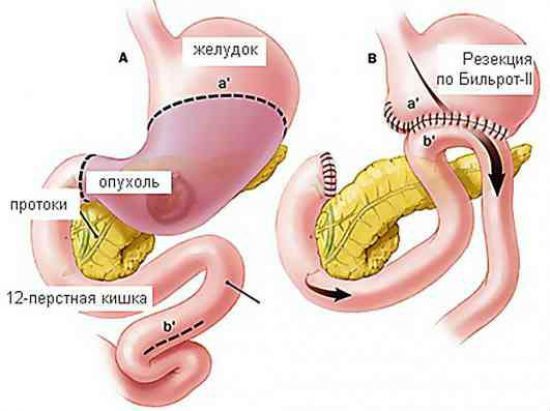
The greatest changes relate to surgical intervention with the removal of the anthrum and the pylorus, because it is the pyloric sphincter that provides the physiological regulation of the transition of food chyme to the duodenum
The existing resection options include the possibility of connecting the end-to-end stomach stump:
- with the duodenum( the method of resection by Billroth I) - here the conditions for dumping syndrome occur less frequently, since the intestinal part of the digestive tract remains intact;
- with jejunum( a method of resection by Billroth II), if it is necessary to simultaneously remove the duodenum - the most dangerous variant, undigested food is immediately sent to the jejunum and the mechanism of the syndrome is triggered.
Patient monitoring shows that after a pyloric resection with a part of the pyloric section, 20 to 80% of cases are complicated by a dumping syndrome during the first year. The connection between the degree of risk of postoperative dumping syndrome and mental temperament is interesting: more often it develops in choleric and melancholic people, it is not observed in sanguine and phlegmatic patients.
With vagotomy, the main trunk or branches of the vagus nerves are dissected. This manipulation tries to remove the stimulating effect on the production of acid by the lining of the gastric mucosa and to achieve scarring of the ulcer.
If the lower branches intersect, the function of the pyloric zone is traumatized, the process of food passage through the gatekeeper is artificially disrupted. Therefore, the plastic of the pylorus is additionally performed, a stoma( opening) is created between the stomach and the small intestine. In such cases, dumping syndrome is observed in 4-10% of patients.
After gastrectomy( removal of the entire stomach) due to a common tumor, the development of the complication is most likely, since with the complete exclusion of the stomach from the digestive process, the ingested food is immediately sent to the intestine.
The choice of the method of surgical intervention depends on the specific disease, the location of the ulcer and tumor, the state of the stomach tissues. Doctors try to use the least traumatic variant.
Why do people who are unheeded get sick?
Dumping syndrome is rarely seen in unoperated individuals, so its causes can not be related to postoperative anatomical organ changes. In these cases, the stomach volume is preserved. In therapy, a functional type of dumping syndrome is known, which accompanies temporary gastric juice secretion, motor-evacuation activity.
Disease can complicate the course:
- of chronic gastritis and enteritis;
- peptic ulcer disease;
- endocrine pathology( changes in gastric activity due to impaired neurohumoral regulation).
Chronic gastroenteritis proceeds according to the type of dumping syndrome
How does the dumping syndrome manifest itself?
Symptoms of dumping of the syndrome are manifested by attacks on the background of food intake or 15-20 minutes after it. More often associated with sweet and dairy dishes. The patient has a sudden weakness, dizziness, sweat, a feeling of heat. Symptoms are caused by vascular and neurovegetative disorders. Attacks can be short-lived or last up to several hours. Complaints are divided by character into 5 groups.
Caused by impaired vascular tone and disruption of the autonomic nervous system - palpitations, pallor of the face or redness, a feeling of heat and hot flashes, weakness, hand tremors, dizziness with darkening in the eyes, blurred vision, tinnitus, cold sweating, increased urine output,rarely - loss of consciousness.
Dyspeptic - loss of appetite, belching and nausea, vomiting, loud rumbling in the abdomen, diarrhea then constipation. Manifestations are caused by a general eating disorder in the gastrointestinal tract and impaired secretory activity of the pancreas.
Associated with a violation of the assimilation of food, vitamin deficiency, metabolic changes - weight loss, anemia, severe physical weakness, reduced ability to work, men have impotence. Pain syndrome - is formed by concomitant inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder, liver, pancreas, spikes in the abdominal cavity.
Psychoneurological changes - are detected by the nature of the person, there is irritability, imbalance, a tendency to crying, complaints of insomnia, headaches, memory loss, a sharp change of mood.
Some of the symptoms appear during seizures, others - become permanent, keep between bouts. The course of dumping syndrome is long. Attacks in patients appear in most cases in the first 12 months after the operation, half a year they are most vivid. May be provoked by the expansion of a sparing diet, new foods, milk, large portions, excess carbohydrate food.

After 2-3 years of the disease, permanent symptoms are added to attacks, the person's personality changes
Classification of attacks
Some authors divide symptoms of seizures depending on the prevalence of hormones and neurotransmitters( catecholamines, acetylcholine) entering the blood. Sympathoadrenal type is characterized by:
- dry mouth;
- atony of the intestines, propensity to constipation;
- tachycardia;
- bloating;
- increase in pressure;
- pallor of the face;
- excited state, a sense of anxiety;
- tremor of the hands;
- convulsions and numbness in the limbs;
- headaches;
- chills.
Vagotonic type differs:
- with increased salivation;
- with nausea;
- abdominal pain;
- diarrhea;
- a rare heart rhythm and low blood pressure;
- with reddening face;
- increased sweat excretion;
- feeling of lack of air;
- nasal congestion;
- weakness in muscles;
- by dizziness;
- with a feeling of drowsiness.
There are three degrees of severity during dumping attacks. Easy - the frequency of seizures no more than 1-2 times a month, usually occur in violation of diet, accompanied by diarrhea. Continue to half an hour, pass by yourself. Deficiency of weight of the patient is up to 5 kg.
Medium - attacks occur 3-4 times a week, last from one to one and a half hours, accompanied by severe cardiovascular disorders( tachycardia, hypertension with a decrease in diastolic pressure), diarrhea.
In the interictal period, the patients show signs of disturbed metabolism, reduced working capacity, people suffer from insomnia, aggressive and quick-tempered. Lack of weight is determined up to 10 kg. During the examination, anemia, loss of electrolytes, a decrease in voltage on the ECG are detected.
Severe - weakness is so pronounced that patients can not sit, just lie, the attack causes each meal, last 2.5-3 hours. Possible loss of consciousness, a sharp drop in pressure( collapse).The patient is exhausted, during the interictal period, he suffers from avitaminosis, metabolic disorders, and is disabled. Body weight is reduced by more than 10 kg.
Even more severe( grade 4) is characterized by the addition of internal degeneration, cachexia of the patient, marked anemia and protein-free edema. Patients need care.

Patients with dumping syndrome are forced to eat lying
Depending on the elapsed time from food, seizures are distinguished. Early - dumping attack is symptomatic during or immediately after eating, usually cause severe weakness, the course depends on the type. The continuation of nutrition worsens the patient even more. The state of health improves when lying down.
Late - signs develop after two to three hours after a meal, as much as possible with symptoms of hypoglycemia:
- face pimple;
- dizziness with darkening in the eyes;
- sweating;
- by hand tremor;
- marked weakness;
- cardialgia;
- feeling of fear of death.
Diagnostics
For correct diagnosis, a physician should have information about a stomach operation, its volume and prescription. The doctor draws attention to the description of complaints and their paroxysms, the connection with food.
Laboratory studies show: anemia due to hypovitaminosis, a violation of the electrolyte exchange of sodium, potassium, chlorine, calcium, a decrease in the amount of protein in the plasma, an increase in the activity of the enzyme amylase, in the stool masses( increased release of unassembled fat).
When measured during an attack, a sharp decrease in central venous pressure and minute blood volume is recorded. X-ray examination with a contrasting substance shows a shortened stump of the stomach, increased release of the barium suspension( jet), a transition of the contrast to the intestine after 5-15 minutes, an increase in the diameter of the dilated loop of the small intestine, rapid movement along the intestine, and increased peristalsis.
By the time of the barium suspension in the small intestine, the degree of severity of the syndrome is set:
- for mild( grade I) - not less than 5 hours;
- medium( II degree) - up to 3-3.5 hours;
- severe( grade III) - up to 2-2,5 hours.
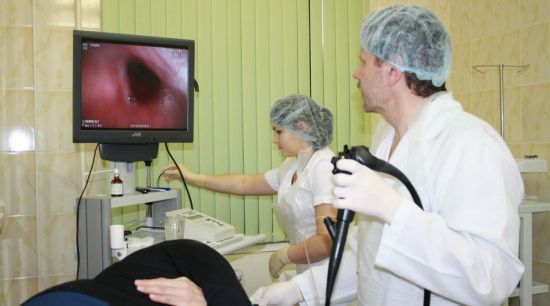
Fibrogastroscopy shows an anastomosis between the stomach and intestine of round shape, large diameter( gaping), although in normal course it should be a slit
To confirm the diagnosis, a provocative test is performed. It allows you to assess the severity of the syndrome. The patient is measured by the initial pressure, pulse rate, the volume of circulating plasma is taken into account by blood analysis.
The measurements are then repeated after the administration of the concentrated glucose solution. If the attack did not immediately manifest itself, then the measurements are repeated after 15 minutes and then after a few hours. The syndrome is characterized by hypoglycemia.
The course of dumping syndrome is aggravated by neuropsychic disorders. Therefore, the patient may need counseling psychoneurologist. The most often diagnosed changes in the mental state: asthenic, neurasthenic, hysterical, depressive, hypochondriacal type.
Treatment of
In the treatment of dumping syndrome, it is necessary to use the possible ways of correcting disturbed digestion, neuro-mental status.
Conservative methods
It is conducted to patients with the first-second degree of severity of the syndrome. The diet is designed to slow the evacuation of food. Recommended meals 6 times a day, limited portions. Solid and liquid foods are used separately. First the patient should eat the second course, and after half an hour - the first.30 minutes before the start of eating, it is recommended to drink a glass of tomato juice. It promotes the excitation of pancreatic secretion.
The composition of food sharply limits the amount of carbohydrates, sugar is replaced with sorbitol. From the diet, simple carbohydrates should be completely excluded: honey, sweets, jam, refined carbohydrates: soft bread and baked pastries, cereals, pasta, milk, sour cream, smoked products. Fats are allowed in small quantities. After eating, the patient needs to lie down for 30 minutes.
Common restorative drugs - intravenously injected glucose with a calculated dose of insulin under the skin, B vitamins, nicotinic acid. In the state of moderate and severe severity, patients are shown transfusion of albumin solution, native plasma, erythrocyte mass, plasma substitutes.

Injection of Atropine is used to slow intestinal motility half an hour before a meal
Pepsin, gastric juice, enzyme preparations( Pancreatin, Panzinorma, Creon) are recommended as replacement therapy. With significant weight loss, corticosteroids, anabolic hormones are recommended. With a soothing goal, barbiturates, sedatives are used.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is indicated for severe degree of dumping syndrome, unsuccessful conservative treatment. The essence of repeated intervention: plastic anastomosis, creating conditions for greater involvement of the duodenum in the process of digestion of food. Use a transplant from your own small or large intestine.
The operation is called "reconstructive gastroejunoduodenoplasty."Before the operation, the patient is trying to prepare medicines, nutrient intravenous solutions. There are also different types of operational reconstruction:
- reduction in the diameter of the gastrointestinal anastomosis;
- creation of an additional anastomosis between the leading and withdrawing loop of the small intestine;
- formation of an additional reservoir of paired intestinal loops and others.
To choose the optimal surgical option, surgeons take into account the degree of severity, the nature of functional disorders of the digestive system and the whole organism, the age of the patient, the period after the first operation.
The result of a new intervention is a decrease in the intensity and frequency of seizures, improving digestion, increasing body weight. The best effect is the elimination of dumping syndrome. Treatment of dumping syndrome in mild form gives good results. It is important to notice negative symptoms in a timely manner and consult a doctor.



