 Cholecystitis along with pancreatitis is one of the most common diseases of the abdominal cavity. Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder, while pancreatitis is a disease of the pancreas. These two ailments often occur simultaneously.
Cholecystitis along with pancreatitis is one of the most common diseases of the abdominal cavity. Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder, while pancreatitis is a disease of the pancreas. These two ailments often occur simultaneously.
Now about 15% of adults suffer from cholecystitis, the symptoms of which are bothering them in everyday life. This is due to the inactive way of life, the nature of nutrition: the excessive use of an animal rich in food, the growth of endocrine disorders. Therefore, how to treat cholecystitis worries many people.
The most common cholecystitis in women, they face symptoms of this disease 4 times more often than men. In most cases, this is the result of taking contraceptives or pregnancy.
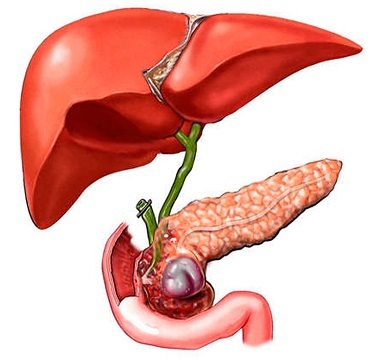
And so, what is cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder, an organ designed for the deposition of bile, which along with other digestive enzymes (gastric juice, small intestine and pancreas enzymes) actively participates in the process of processing and digestion of food.
With this disease, surgeons (with acute form) and therapists (with chronic) often face. In most cases, cholecystitis develops in the presence of gallstones, and almost 95% of cases are diagnosed simultaneously with cholelithiasis. Depending on the form of the disease (acute, chronic cholecystitis), the symptoms of the disease and the methods of treatment will vary.
Causes of cholecystitis
What it is? Most often, cholecystitis develops with the penetration and development of microbes (E. coli, streptococci, staphylococcus, enterococci) in the gallbladder and this justifies the use of antibiotics in the development of acute or exacerbation of chronic form.
TOnon-infectious causesthe occurrence of cholecystitis include:
- biliary dyskinesia;
- nature of nutrition (consumption in large quantities of sweet, fatty, smoked, fried foods, fast food).
- stones in the gallbladder and ducts;
- diabetes mellitus, obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hormonal disorders in the body;
- pregnancy;
- reflux esophagitis;
- heredity and congenital pathologies of the gallbladder.
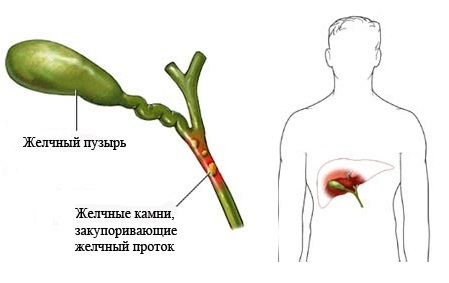
Very often the development of cholecystitis occurs and as a consequence of an impaired outflow of bile. It can occur in a person who suffers from cholelithiasis. The provoking factor of stagnation of bile in the gallbladder in women is pregnancy, as the enlarged uterus squeezes the gallbladder.
The trigger mechanism for the manifestation of the disease is always a disorder in the diet of the patient with cholecystitis. In such cases, symptoms of the disease are detected in approximately 99 percent of patients.
Symptoms of cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis, the symptoms of which often develop in the presence of gallstones and are a complication of cholelithiasis.
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis develop rapidly, they are often called "hepatic colic since the pain syndrome is located precisely in the liver.
The main signs of the acute stage of the disease are:
- Continuous pain in the right hypochondrium, which can give to the right side of the chest, neck, in the right arm. Often before the onset of pain, an attack of biliary colic occurs;
- Nausea and vomiting, after which there is no relief;
- Sensation of bitterness in the mouth;
- Increased body temperature;
- In case of complications, jaundice of the skin and sclera.
Often the pain is accompanied by nausea and vomiting of bile. Usually there is an increase in temperature (up to 38 C and even up to 40 C), chills. The general condition worsens considerably.
The provoking factor giving points for the development of acute attack of cholecystitis is a powerful stress, overeating with acute, fatty foods, alcohol abuse. If you did not understand in time how to treat cholecystitis, then it will be chronic and will bother you for a long time.
Symptoms of chronic cholecystitis
Chronic cholecystitis occurs mainly for a long time, sometimes it can last for many years. The aggravation and occurrence of its symptoms are facilitated by provoking factors - malnutrition, alcohol, stress, etc.
Distinguish chronic tubeless (non-calculous) and chronic calculous cholecystitis. The clinical difference between them from each other is due almost exclusively to the fact that with calculous cholecystitis periodically adds a mechanical factor (migration of stones), which gives a brighter picture disease.
Symptoms of a disease in a chronic form during an exacerbation are no different from the symptoms of cholecystitis in acute form, in addition, that the onset of biliary colic occurs more than once, and from time to time with gross errors in nutrition.
The symptoms that an adult experiences from time to time in the chronic form of this ailment:
- pains of a dull character in the right hypochondrium;
- vomiting, nausea;
- bloating;
- a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- diarrhea after eating (due to impaired digestion of fatty foods).
In women, the signs of cholecystitis occurring in chronic form are amplified by sudden fluctuations in the hormonal background of the body, a few days before the onset of menstruation, against the background of pregnancy.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis is based on the collected history.
The doctor conducts palpation of the abdominal cavity, and also finds out whether there is symptomatology of hepatic colic. With the help of ultrasound revealed an increase in the gallbladder and the presence in its ducts of stones. For an extended study of the bile ducts, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is prescribed.
A blood test shows an increased white blood cell count, a high level of ESR, bilirubinemia, and also disproteinemia. Biochemical analysis of urine shows increased activity of aminotransferases and amylase.
Treatment of cholecystitis
 Patients with acute cholecystitis, regardless of the condition, must be hospitalized in the surgical department of the hospital.
Patients with acute cholecystitis, regardless of the condition, must be hospitalized in the surgical department of the hospital.
The treatment regimen for cholecystitis includes:
- bed rest;
- hunger;
- detoxication therapy (intravenous injection of detoxifying blood substitutes and saline solutions);
- anesthetics, antibiotics, antispasmodics, drugs that suppress the secretion of the stomach.
The patient needs bed rest. To relieve pain, antispasmodics and analgesics are prescribed. With a pronounced pain syndrome, Novocain blockades are performed or Novocaine electrophoresis is administered. Disintoxication is carried out by intravenous injection of solutions of 5% glucose, solution, gemodeza with a total amount of 2-3 liters per day.
Antibiotics of a broad spectrum of action are prescribed. All without exception, patients with acute cholecystitis showed a strict diet - in the first 2 days you can drink only tea, then it is allowed to go to a diet table 5A. At the stage of exacerbation, the treatment of cholecystitis is primarily aimed at relieving severe pain, reducing inflammation, and eliminating manifestations of general intoxication.
In severe cases, surgical treatment is indicated. Indication for removal of the organ (cholecystectomy) is an extensive inflammatory process, and the threat of complications. The operation can be performed by an open or laparoscopic method to select a patient.
How to treat cholecystitis with folk remedies
When treating the chronic form of cholecystitis at home, medicinal plants can be used, but only as an adjunct to the basic treatment. And so, here are some folk remedies, they should be used only after consulting a doctor.
- Take 2 teaspoons of chopped sage medicinal leaf, brew 2 cups of boiling water. Infuse for 30 minutes, drain. Take 1 tablespoon every 2 hours for inflammation of the gallbladder, liver.
- Flowers immortelle-30 grams, yarrow-20 grams, wormwood-20 grams, fennel or dill-20 grams, mint-20 grams. Mix everything and crush it thoroughly. Two tea spoons of the collection to fill with water (cold) and insist for 8-12 hours. Reception: Take 1/3 cup three times daily before meals.
- Take 4 parts of the roots of dandelion medicinal, 4 parts of rhizome rhizomes erect, 2 parts of flowers tansy, 2 parts of peppermint leaves, 2 parts of herb flaxseed and 1 part of grass celandine. 1 tbsp. Collect a glass of boiling water, insist 30 minutes, drain. Take 1 / 4-1 / 3 tbsp. 3 times a day for 20 minutes before meals.
- Air. A teaspoon of the crushed rhizomes of aira pour a glass of boiling water, insist 20 minutes and strain. Drink 1/2 cup 4 times a day.
- Radish juice: grate the black radish or grind it in a blender, squeeze the pulp well. The resulting juice is mixed with liquid honey in equal parts, drink 50 ml of the solution daily.
- Take evenly the root of chicory, herb celandine, a sheet of walnut. 1 tablespoon of the collection pour 1 glass of water, heat 30 minutes, cool and strain. Take 1 glass 3 times a day for cholecystitis and cholangitis.
One of the fees should be taken during the entire period of exacerbation, and then one month, with interruptions to one and a half months, at this time should be taken one plant that has either choleretic or spasmolytic properties.
.Diet in chronic cholecystitis
How else to treat cholecystitis? First of all, these are strict rules of nutrition. With this disease, it is strictly forbidden to eat a large amount of saturated fat, so there may be speeches and hamburgers, french fries, fried meat and other fried foods, as well as smoked products.
You need some increase in meals (up to 4-6 times), as this will improve the outflow of bile. It is desirable to enrich the food with oat bread, cottage cheese, egg protein, oatmeal, cod, yeast drinks.
Prohibited products:
- leguminous crops;
- fatty meat, fish;
- chicken eggs;
- pickled vegetables, pickles;
- sausages;
- spice;
- coffee;
- baking;
- alcoholic beverages.
In nutrition with cholecystitis should be given priority to products that reduce cholesterol. You can eat:
- meat and poultry (lean), eggs (2 pcs. in Week),
- sweet fruits and berries;
- of stale products is recommended stale foods;
- vegetables: tomatoes, carrots, beets, zucchini, potatoes, cucumbers, cabbage, eggplant;
- in the finished dish you can add vegetable oil,
- butter (15-20 g per day), sour cream and cream in small quantities;
- sugar (50-70 grams per day, along with added to the dishes).
Observe the diet is necessary even for 3 years after the case of exacerbation of the disease or within a year and a half with dyskinesia bile ducts.
Forecast
The prognosis is conditionally favorable, with adequately conducted treatment the work capacity will be fully preserved. The greatest danger can be complications associated with rupture of the gallbladder and the development of peritonitis. In case of its development, even with adequate treatment, a lethal outcome is possible.
It is also necessary to pay great attention to the observations of the attending physician, since the clinical dynamics has its own peculiarities in each specific case.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



