 Trophic ulcer is a disease characterized by the formation of skin or mucosal defects that occurs after rejection necrotic tissue and characterized by a sluggish course, a small tendency to healing and a tendency to recur.
Trophic ulcer is a disease characterized by the formation of skin or mucosal defects that occurs after rejection necrotic tissue and characterized by a sluggish course, a small tendency to healing and a tendency to recur.
As a rule, they develop against the backdrop of various diseases, differ in persistent long-term course and are difficult to treat. Recovery directly depends on the course of the underlying disease and the possibility of compensating for the disorders that led to the onset of pathology.
Such ulcers do not heal for a long time - more than 3 months. Most often trophic ulcer affects the lower limbs, so treatment should begin when the first signs are found at the initial stage.
Causes
Violation of the blood supply to the skin area leads to the development of microcirculation disorders, lack of oxygen and nutrients and gross metabolic disturbances in the tissues. The affected area of the skin is necrotic, becomes sensitive to any traumatic agents and infection.
Provoke occurrenceTrophic ulcers on the leg are capable of such risk factors:
- Problems of venous circulation: thrombophlebitis, varicose veins of the lower extremities and others (both diseases contribute to stagnation of blood in the veins, disrupting nutrition of the tissue and causing necrosis) - ulcers appear on the lower third of the shin;
- Deterioration of the arterial blood circulation (in particular, with atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus);
- Some systemic diseases (vasculitis);
- Any kind of mechanical damage to the skin. It can be not only an ordinary, domestic trauma, but also a burn, frostbite. The same area includes ulcers that are formed in addicted people after injections, as well as the effects of irradiation;
- Poisoning by toxic substances (chromium, arsenic);
- Skin diseases, for example, chronic dermatitis, eczema;
- Violation of the local circulation at prolonged immobility due to trauma or illness (bedsores are formed).
When diagnosing a disease, the disease that caused the formation is very important, since the tactics of treating the trophic ulcers on the leg and the prognosis is largely dependent on the nature of the underlying venous pathology.
Symptoms of trophic ulcers
The formation of ulcers on the leg, as a rule, is preceded by a whole complex of objective and subjective symptoms, indicative of a progressive violation of venous circulation in the extremities.
Patients notice an increase in edema and heaviness in calves, an increase in gastrocnemius muscle cramps, especially at night, the appearance of burning sensation, "heat," and sometimes itching of the shin. During this period, in the lower third of the shin, a network of soft cyanotic veins of small diameter increases. Violet or purple pigment spots appear on the skin, which, merging, form a vast zone of hyperpigmentation.
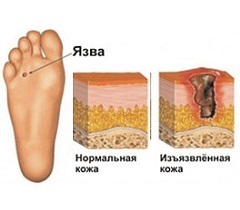
In the initial stage, the trophic ulcer is superficial, has a moist dark red surface covered with a scab. In the future, the ulcer expands and deepens.
Individual ulcers can merge with each other, forming extensive defects. Multiple launched trophic ulcers in individual cases can form a single wound surface along the whole circumference of the shin. The process extends not only in breadth, but also in depth.
Complications
Trophic ulcers are very dangerous for their complications, which are very serious and have poor prospects. If you do not pay attention to the trophic ulcers of the extremities in time and start the treatment process, the following unpleasant processes can subsequently develop:
- erysipelas;
- lymphadenitis, lymphangitis;
- sepsis;
- gas gangrene;
- skin cancer.
On a mandatory basis, the treatment of trophic ulcers on the legs should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician without any independent activity, only in this case it is possible to minimize the consequences.
Prevention
The main preventive means for preventing the occurrence of trophic ulcers is the immediate treatment of primary diseases (circulatory and lymph drainage disorders).
It is necessary not only to apply the drugs inside, but also to apply them externally. The local effect will help to stop the pathological processes, treat the existing ulcer and prevent the subsequent destruction of tissues.
What is dangerous disease?
Progressing trophic ulcers may eventually occupy significant areas of the skin, increase the depth of the necrotic effect. Gnoyrodnaya infection, got inside, can provoke the appearance of erysipelas, lymphadenitis, lymphangitis, septic complications.
In the future, the advanced stages of trophic ulcers can develop into gas gangrenes, and this is the cause of urgent surgical intervention. Long-term non-healing wounds, exposed to aggressive substances - salicylic acid, tar, can develop into malignant degenerations - skin cancer.
Treatment of trophic ulcers on the leg
In the presence of trophic ulcers on the leg, one of the main stages of treatment is to identify the cause of the disease. For this purpose, it is necessary to consult with such doctors as phlebologist, dermatologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, vascular surgeon or general practitioner.
The late stages of the disease are usually treated in surgical hospitals. However, in addition to identifying and eliminating the cause of trophic ulcers, one must also not forget about daily care for the affected area.
How to treat a trophic ulcer of the lower extremities? Use several options, depending on the neglect of the pathological process.
- Conservative therapy, when the patient is prescribed such drugs as phlebotonics, antibiotics, antiaggregants. They will help cure most of the symptoms of the disease. Patients often prescribe the following drugs: Tocopherol, Solcoseryl, Actovegil. This medication can be prescribed only by a doctor.
- Local Therapy, with which you can cure the damage to tissues and skin. With diabetes, ointments containing antiseptics and enzymes are used. These remedies heal wounds and provide local anesthesia. Ointments that increase blood circulation are forbidden to apply to the open surface of a trophic ulcer. Such ointments as Dioxysol, Levomecol, Curiosine, Levosin exert a wound-healing effect. Ointment is applied to the compress and whether special bandages are made.
- Surgical intervention, which is produced after the healing of ulcers. In the course of it, the blood flow in the veins in the affected area is restored. This operation involves shunting and phlebectomy.
To treat wounds use such drugs: Chlorhexidine, Dioxydin, Eplan. At home, you can use a solution of furacilin or potassium permanganate.
Operative intervention
 Surgical treatment of trophic ulcers of the lower extremities is indicated for extensive and severe skin lesions.
Surgical treatment of trophic ulcers of the lower extremities is indicated for extensive and severe skin lesions.
The operation consists in removing the ulcer with the surrounding non-viable tissues, and further closing the ulcerative defect, in the second stage, an operation is performed on the veins.
There are a fewvarious surgical methods:
- Vacuum therapy, which allows you to quickly remove pus and reduce edema, as well as create a moist environment in the wound, which will greatly prevent bacteria from developing.
- Cathering - suitable for ulcers that do not heal for a very long time.
- Percutaneous stitching - suitable for the treatment of hypertensive ulcers. Its essence is in disconnection of venous-arterial fistulas.
- Virtual amputation. The metatarsal bone and metatarsophalangeal joint are cut off, but the anatomical integrity of the foot is not impaired - but the foci of bone infection are removed, which makes it possible to effectively combat the neurotrophic ulcer.
When the size of the ulcer is less than 10 cm², the wound is closed with its own tissues, tightening the skin daily for 2-3 mm, gradually bringing the edges together and completely closing it for 35-40 days. On the wound site remains a scar, which must be protected against any possible injuries. If the area of the lesion is more than 10 cm², apply skin plastic, using the patient's healthy skin.
Medication Therapy
The course of treatment with drugs necessarily accompanies any operation. Treatment with medicines is divided into several stages, depending on the stage of the pathological process.
At the first stage (the stage of a wetting ulcer) the course of drug therapy includes such drugs:
- Antibiotics of a wide spectrum of action;
- NSAIDs, which include ketoprofen, diclofenac, etc .;
- Antiaggregants for intravenous injection: pentoxifylline and reopoglyukin;
- Antiallergic drugs: tavegil, suprastin, etc.
Local treatment at this stage is aimed at cleansing the ulcer from the dead epithelium and pathogenic microorganisms. It includes such procedures:
- Wash the wound with solutions of antiseptics: manganese, furacilin, chlorhexidine, decoctions of celandine, string or chamomile;
- Use of dressings with medicinal ointments (dioxycol, levomikol, streptolaven, etc.) and carbonate (special bandage for sorption).
In the next stage, which is characterized by the initial phase of healing and the formation of scars, healing is used in healing ointments for trophic ulcers - solkoseril, actevigin, ebermin, etc., as well as antioxidant preparations, for example, tolkoferon.
Also at this stage are used specially developed for this wound coverings of the swederm, geschispon, algimaf, algipore, allein, etc. The treatment of the expressed surface is carried out by curiosin. At the final stages, drug treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying ailment, which provoked the appearance of trophic ulcers.
How to treat a trophic ulcer on the leg at home
When starting treatment for trophic ulcers according to folk recipes, it is necessary to consult with your doctor.
At home, you can use:
- Hydrogen peroxide. It is necessary to drip onto the ulcer peroxide, then sprinkle streptocicide on this place. On top you need to put a napkin, previously soaked in fifty milliliters of boiled water. In this water, add two teaspoons of peroxide. Then cover with a pack and bandage with a handkerchief. Change the compress several times a day. And sprinkle the streptocide, when the wound becomes moist.
- Healing balmin the treatment of trophic ulcers in diabetes mellitus. It includes: 100 g of juniper tar, two egg yolks, 1 tablespoon of rose oil, 1 teaspoon of purified turpentine. All this must be mixed. Turpentine pour slowly, otherwise the egg will curdle. This balm is applied to the trophic ulcer, then covered with a bandage. This folk remedy is a good antiseptic.
- Powder from driedleaves of the Tartar. Rinse with rivalol solution. Powder with cooked powder. Apply a bandage. In the morning of the next day, sprinkle powder again, but do not wash the wound before this. Soon the ulcer will begin to heal.
- Trophic ulcers can be treatedantisepticsWipe off wounds with warm water and soap, apply antiseptic and bandage. These dressings alternate applications of a solution of sea or table salt (1 tbsp. l. for 1 liter of water). Gauze is folded in 4 layers, moistened with saline solution, lightly squeezed and applied to the wound, on top of the compress paper, hold for 3 hours. The procedure should be repeated twice a day. Between applications, the break is 3-4 hours, at this time the ulcers should be kept open. Soon they will begin to diminish in size, the edges become dense, which means that the healing process is going on.
- Garlic poultices or compressesapply with open sores. Take multi-layer gauze or a terry towel, soak in hot broth of garlic, squeeze out excess liquid and immediately attach to a sore spot. On a poultice or a compress put a dry flannel bandage and a hot water bottle or a bottle of hot water to keep the heat longer.
- Necessarymix egg white with honeyso that these ingredients are in the same proportion. Whip everything and apply to ulcers, including the veins that are hurting. Then cover the back side of the burdock leaves. There should be three layers. Wrap the cellophane film and bandage it with a linen cloth. Leave the compress on overnight. You need to do this treatment five to eight times.
Remember that in the absence of timely and correct therapy, complications such as microbial eczema, erysipelatous inflammation, periostitis, pyoderma, arthrosis of the ankle joint, etc., can develop. Therefore, use only folk remedies, while ignoring the traditional treatment is not worth it.
Ointments for treatment
To treat this disease, you can also use a variety of ointments, both natural and purchased in the pharmacy. Effectively heal wounds and exert anti-inflammatory effect ointments arnica, comfrey, as well as room geranium.
Ointment of Vishnevsky is also often used. Of the ointments that can be bought in the pharmacy, they particularly distinguish dioxycol, levomecol, as well as streptolaven and a number of analogues.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



