 Arthritis is a disease of the joints, accompanied by their inflammation, the symptoms and treatment of which are as clearly described in the medical literature. The name of the disease comes from the word "athron", which in Greek means "joint".
Arthritis is a disease of the joints, accompanied by their inflammation, the symptoms and treatment of which are as clearly described in the medical literature. The name of the disease comes from the word "athron", which in Greek means "joint".
During arthritis, inflammatory changes occur in the inner joint synovium. In this place there is a development of synovitis, often an inflammatory effusion - exudate - begins to accumulate.
Modern medicine means by arthritis a whole group of diseases, united by common signs and features. The main clinical manifestations of the disease are swelling and pain. Similar problems suggest that the cartilaginous tissue is affected, which is accompanied by changes in the joint capsule. In this case, a person experiences pain in them and there is a restriction in the movement.
What it is?
Symptoms of different types of arthritis are more or less similar. Signs of arthritis are pain in the inflamed area, redness, fever over the inflamed joint, stiffness and difficulty of movement. You may have to face other troubles, such as fatigue, weight loss, swollen lymph nodes, fever. In some cases, patients may encounter difficulties in walking and self-care.
Although the disease is common among adults, in some cases young people are also prone to arthritis. In the United States alone, arthritis suffers from more than 42 million people, and one in six because of this disease became disabled. It should be noted that among the causes of disability in this country arthritis is in the first place.
Various anti-inflammatory drugs are used to reduce inflammation and pain. It is best to combine medication and curative gymnastics in the treatment. Reduce pain, swelling and inflammation can massage therapy. According to statistics, arthritis shortens life by about 10 years, but rarely becomes a direct cause of death. To date, unfortunately, there are no drugs that could completely cure rheumatoid arthritis.
Causes of Arthritis
How does arthritis develop, and what is it? The disease can occur due to various factors, including joint wear, which occurs with time.
Also, pathology is promoted by joint infections and traumas, allergies and autoimmune processes with the formation of antibodies that destroy the body's own tissues - the components of the joint. Often arthritis occurs after an infection of the upper respiratory tract - tonsillitis, influenza, SARS, etc.
Arthritis and arthrosis - what's the difference?
The names of these joint diseases are consonant, but the symptoms accompanying them, the pathological process and the treatment are different. So what's the difference, let's understand:
- Osteoarthritis, or deforming osteoarthritis (DOA) is a chronic degenerative disease that flows wavyly. One of the main characteristics of this disease is the destruction of the cartilaginous tissue in the joint.
- Arthritis, on the contrary, is an inflammatory disease of the whole organism; and inflammation of the joints in arthritis - only "The tip of the iceberg," under which are hidden some other processes occurring within the body.
Osteoarthritis and arthritis are characterized by the nature of pain and discomfort during movements, concomitant symptoms and age of patients.
Classification
In modern medicine, it is common to subdivide the disease into several types, the symptoms and methods of treatment of which will depend directly on the type of arthritis and the causes that caused it.
- Rheumatoid - it accounts for more than 45% of diseases in which the causative agent is staphylococcal infection.
- Gouty - he's also a "gout." A fairly common form of the disease, associated with the deposition in the body of salts and uric acid.
- Reactive - develops after the transferred diseases and is accompanied by severe pain.
- Rheumatic - inflammation of the joints, caused by rheumatism. In this case, the temperature rises, the elbows, knees and hip joints blush and blush.
- Traumatic - affects the largest joints, which is the greatest load: shoulder, elbow, knee, ankle.
- Infectious - most often caused by intestinal infections (typhoid fever, salmonellosis, dentinaria).
- Psoriatic is a chronic joint disease caused by psoriasis.
- Chlamydia - caused by chlamydial infection after suffering urethritis, pneumonia, prostatitis and other inflammatory processes.
Arthritis can often lead to disability. If the first manifestations of the disease occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of Arthritis
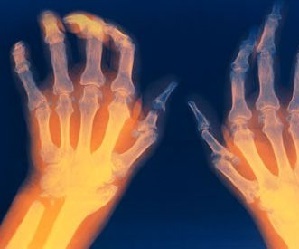 Arthritis, the first symptoms of which are most often felt on small joints, for example, fingers or toes. Many experts believe that this disease was originally directed to them.
Arthritis, the first symptoms of which are most often felt on small joints, for example, fingers or toes. Many experts believe that this disease was originally directed to them.
Symptoms of arthritis can include redness, swelling and a change in the structure of the joint, which can lead to damage, pain and loss of joint function.
The main signs of arthritis, which should alert an adult:
- joint pain;
- edema in the joint region;
- swelling of the joints;
- stiffness and limitation of movements in the joint region;
- redness of the skin around the joint;
- numbness of the joints, especially in the morning;
- local temperature increase.
A person with arthritis quickly becomes fatigued, with the pain intensified when the patient is physically stressed, sometimes the joints "crunch." In the analysis results, there is an increase in the number of leukocytes and ESR, and the presence of a c-reactive protein can also be observed. Unfortunately, the same type of symptomatology for different causes of the disease makes it difficult to accurately and timely diagnose.
Stages of development
In the dynamics of the pathological process in arthritis, four stages are distinguished:
- Clinically, the disease does not manifest itself, but the x-ray images of the joints have the first signs of inflammation. Sometimes there is a slight stiffness of movements and periodic pain during exercise.
- Progressing inflammatory process leads to thinning of the tissues of the joint structures and erosion of the heads of bones. There are swelling in the area of the affected joints; often there is a local increase in temperature and redness of the skin, the movements are accompanied by a crunch.
- Gradual destruction of the joint structures leads to a considerable deformation of the joints, limited mobility, constant pain and partial loss of joint functions, which are partly compensated by muscle tension.
- Pathological changes in the joint tissues are irreversible; the diseased joint is completely immobilized. When knee joints are affected, contractures are formed, and ankylosis develops in the hip joints - fusion heads of articular bones due to the filling of the joint capsule with a replacement bone or fibrous tissue.
How exacerbation manifests itself
Rheumatoid arthritis has two phases of flow. Remission is a period of relative well-being, when the symptoms of the disease become less pronounced or completely disappear. On the contrary, during an exacerbation, there are not only signs of inflammation of the joints, but also general reactions.
Exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Loss of appetite;
- An increase in temperature to 37-38.5 ° C
- Pronounced weakness and apathy;
- Severe pain in the affected joints. It becomes constant and does not depend on the time of day. NSAIDs, most often, do not have any effect;
- Possible the appearance of chest pains, difficulty breathing, feelings of discomfort in the eye area, decreased vision.
It is important to recognize the exacerbation of arthritis as early as possible, since during this period all the organs of the patient suffer. Special treatment is needed to relieve all the symptoms and return the disease to the phase of remission.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of arthritis is a rather difficult task. This is due to the fact that the causes that cause inflammation in the joints can be different. Some types of arthritis are widespread and easily diagnosed, and there are those in which the correct diagnosis can only be an experienced doctor, after a thorough examination of the patient.
The cause of arthritis development can be any infectious process (local or general), joint trauma, allergy, autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders. There are also inflammatory joint diseases, the etiology of which is still not clear enough, an example of such a pathology is "Rheumatoid arthritis "To select the therapy for arthritis treatment, it is necessary to diagnose and determine which factor led to the development of the pathological process.
Diagnosis of arthritis consists of the following data:
- Thorough history of the disease.
- Revealing its connection with allergic, infectious diseases, trauma.
- A characteristic clinical picture of arthritis.
- The laboratory method of examination (when examining the patient reveals signs of inflammation, increased levels of uric acid, the presence of antibodies to hemolytic streptococcus group A, etc.).
- Instrumental diagnostics (radiography, ultrasound, computer or magnetic resonance imaging).
- Investigations of synovial fluid.
In recent years, for more accurate diagnosis of arthritis, use arthroscopy, which allows a thorough examination of the joint cavity, take a synovial fluid intake for its subsequent analysis. The main method of instrumental diagnosis for arthritis is radiography. It is usually performed in two projections, according to indications, X-rays can be made and additional projections that allow more detailed identification of local changes occurring in the affected joints.
To clarify the changes in articular tissues, which are usually poorly discernible in X-ray examination, for example, epiphyses, computer or magnetic resonance imaging is used. The main difficulty in the diagnosis of arthritis is that none of the methods of laboratory or instrumental diagnosis of the disease can not uniquely and accurately deliver the correct diagnosis. To diagnose arthritis, to identify its cause, and therefore, the correct choice of the prescribed treatment, a comprehensive examination of the patient is necessary. All data obtained during the survey, then should be associated with the clinical picture of the disease.
Effects
Complications of arthritis are early and late. To early complications include phlegmon, panartritis (acute purulent arthritis). Late complications include osteomyelitis, sepsis, contractures and pathological dislocations.
Treatment of arthritis
The sooner the arthritis treatment begins, the more effective it will be. This is due to the fact that the first and second stage of the development of the disease is not characterized by a pronounced degree of deformation of the joints. First of all, the treatment of the disease depends on the nature and causes of those who caused it. In general, the treatment of arthritis is aimed at reducing pain, eliminating inflammation and preventing the progress of the disease.
And so, how to treat arthritis and what are the most important therapies? Mainly use such basic components:
- Pharmacological methods of treatment: the use of anti-inflammatory non-steroid ointments, creams and gels; intra-articular injection of glucocorticosteroids.
- Vitaminotherapy, the reception of macro and microelements, diet therapy, the reception of amino acids (methionine, arginine), necessary for the construction of new tissues.
- Non-medicamentous methods of treatment: selection of orthopedic footwear, reducing loads on joints, getting rid of harmful habits, therapeutic exercises, massage, hydrotherapy, acupuncture and electric stimulation of muscles.
- Surgical methods of treatment or arthroplasty are used only in the most neglected forms of arthritis.
- In the case of complicated forms, the introduction of stem cells can be used.
For patients with arthritis, specialized complexes of exercise therapy have been developed, which are aimed at developing flexibility and strength. They are additionally supplemented by aerobic exercises. Perhaps some patients will find that such a load is too great for a person with aching joints. However, this is not quite true. First, you should start practicing during remission, and secondly, the complex is selected individually, taking into account the degree of damage to the joints. Regular classes give simply amazing effect.
In addition, they need to adhere to a special diet, about which we will talk just below.
Physiotherapy
The following methods are highly effective:
- Galvanic currents;
- Irradiation of the joint with ultraviolet waves;
- Diathermy - the effect of low-frequency current on the joint region, with the purpose of heating it;
- Electrostimulation by Gerasimov is a new way of physiotherapy, the principle of which is to stimulate tissues around the joint with a low-frequency current. The course of treatment is 3-6 procedures, and the effect of it persists for several years. After therapy, patients notice a decrease in the severity of pain, stiffness and signs of inflammation (swelling and redness of the joints).
It should be noted that physiotherapy does not replace medical treatment, but only supplements it. Otherwise, rheumatoid arthritis will progress steadily and lead to damage and curvature of the joints.
Modern preparations
The last generation of drugs against rheumatoid arthritis are drugs that selectively reduce activity of inflammatory substances in the body: interleukins, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and others. They proved their effectiveness not only during pharmacological tests, but also in real clinical practice. Another plus is the rare occurrence of adverse reactions.
The main representative of this group of drugs:
- Infliximab (synonyms - Remicade, Flammages);
- Etanercept (synonym - Enbrel);
- Adalimumab.
Why are these medicines not widely used? The point is the price. The cost of 20 ml of the drug, on average, is 4, 00-50000 thousand. rub. Not every hospital or patient can afford it.
How to treat arthritis with folk remedies
In addition to traditional methods, the treatment of arthritis can be supplemented with folk remedies. There are a lot of recipes in the arsenal of folk healers. However, when starting home treatment, you need to be patient.
- Take 1 tbsp. l. salt and dissolve in a glass of boiled water. In a small mold, freeze in the freezer. The resulting ice should be placed on the affected joint and kept until completely thawed. Without washing off, wrap the joint for 3-4 hours with a woolen scarf (handkerchief).
- Treatment with a mixture of juices - grind one medium beet, one large apple and 2 carrots. Squeeze the juice from the pulp, add a third of a teaspoon of ginger powder, carefully mix all the ingredients and drink during the day, 3 portions of this mixture.
- Twenty tubers of cyclamen should be cooked in 10 liters of water. For one procedure, 1 to 2 liters of decoction is enough. Such therapeutic baths for hands and feet should be done daily for 30 minutes until the condition improves.
- Take the bay leaf package and put half of it into a saucepan. Pour 300 ml of boiling water and boil for 5 minutes. After wrap it up better and let it brew for three hours. After 3 hours filter and drink before bed. And so 3 days in a row. In a week it is necessary to repeat the course.
- We take the flowers of black elderberry - 1 part. Birch leaves - 4 parts. Willow bark - 5 parts. Shredded ingredients are mixed, 1 tablespoon of the mixture is poured into a glass of boiling water. The infusion is wrapped up. Half an hour later the product is ready. You need to take half a glass of infusion 4 times a day before meals.
- This method consists in laying mustard plasters on a sore spot to warm up the joints, thus relieving the patient of pain.
Diet for arthritis
Adults suffering from different forms of arthritis are recommended a special diet that helps reduce acidity.
It is recommended to include in your diet:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- fresh juices;
- mackerel, trout, salmon;
- fish fat;
- mineral water;
- dairy products.
A balanced diet for arthritis should be rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids from the Omega 3 group and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
It should be removed from the diet strong tea, coffee, reduce alcohol consumption. Refuse to eat meat, mushroom and fish broths; all kinds of smoked products; salted and fried fish; caviar; all varieties of legumes. Lovers of muffins, chips and jams will have to choose between their health and nutritional preferences.
The main thing that must be remembered: a diet for arthrosis and arthritis should be balanced, low-calorie, and also contain vitamins and minerals.
Prevention
For complex prevention of arthritis, it is necessary to observe such rules:
- Keep track of weight, since excess weight increases the wear and tear of the joints;
- Do not smoke and do not drink alcohol - it also affects the joints negatively;
- Maintain a correct posture, which reduces the burden on the joints;
- Lift the weights correctly, without bending the spine to the left and to the right, avoiding injuries and unnecessary loads on the joints and muscles;
- Regularly engage in physical exercises, since a well-developed "muscle corset" reduces the burden on the joints;
- Reduce the intake of sugar and other easily digestible carbohydrates of carbonated beverages;
- Do breaks in work associated with prolonged sitting / standing. In breaks, do light exercises;
- Correctly organize the workplace so that it was comfortable to sit, you did not have to bend forward, throw your head back, strain your back and neck.
It is also worth eating balanced, including in the diet of polyunsaturated fatty acids (fatty fish, fish oil) and calcium (dairy products, fish), also exclude animal fats (the source of "bad" cholesterol), there are more vegetables and fruits. Omega-3-unsaturated fatty acids facilitate the symptoms of arthritis (in particular, due to the synthesis of anti-inflammatory molecules - resolves). A study of 2112 patients with confirmed x-rays of the knee osteoarthritis showed that a higher intake of magnesium corresponds to a significant reduction in the risk of osteoarthritis (P = 0.03)
Forecast
In the early stages of acute infectious arthritis is well treatable until the full restoration of the function of the joint.
If the development of the inflammatory process is associated with endogenous factors, recovery is more difficult to achieve, but it is possible slow the rate of progression of the disease, prevent the development of complications and avoid disability.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.


