 Vasculitis is an autoimmune inflammation of the vessel wall. This syndrome can affect any vessels of different caliber: arterioles, veins, arteries, venules, capillaries.
Vasculitis is an autoimmune inflammation of the vessel wall. This syndrome can affect any vessels of different caliber: arterioles, veins, arteries, venules, capillaries.
In the course of its development, pathology leads to complications from various organs, which is caused by a violation of normal blood flow to these parts of the body. Depending on what and how the disease provoked, vasculitis is divided into primary and secondary.
In most cases, the disease is benign. Everyone can get an infection - an adult or a child. Vasculitis has a large number of subspecies and classifications, they differ in severity, localization and etiology. Separately, hemorrhagic vasculitis is excreted, affecting the vessels of the skin, kidneys, digestive tract, joints.
Causes of vasculitis
What is this disease, and what are the causes of vasculitis: the main cause of this disease is the inflammation of the walls of blood vessels. The most common is vasculitis on the legs, the treatment of which must begin in a timely manner.
- The etiology of primary vasculitis has not yet been accurately established. The main possible cause is considered autoimmune disorders.
- Secondary vasculitis can manifest itself against a backdrop of chronic, acute infections, vaccination, oncology diseases, severe overheating or cooling, thermal damage to the skin, incl. sunburn.
Often, the disease occurs due to an allergic reaction to medications. Currently, more than 150 medicines are known, the administration of which triggers the development of vasculitis. These drugs include: sulfanilamide preparations, radiocontrast agents, B vitamins, tuberculostatics, analgesics, drugs iodine, antibiotics, etc. In addition, attention should be given to allergic manifestations after the administration of certain vaccines, serums. Especially it concerns children.
Each of these factors can cause the beginning of the process of changing the antigenic structure of the tissue, which forms the basis of the vessels. As a result, an autoimmune process starts, in which the body begins to perceive the body's own tissues as foreign. As a result, the human immune system begins to attack its own tissues, damaging the blood vessels.
Classification
There are a large number of different types of vasculitis, each of which is accompanied by the defeat of a certain type of vessels and its own specific symptoms. The most common of them.
- Hemorrhagic vasculitis. It flows with the symptoms of superficial vasculitis, is characterized by the defeat of capillaries of the skin, joints, gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. It is based on increased production of immune complexes, increased vascular permeability and damage to the wall of capillaries.
- System- a disease that occurs with the defeat of large and small blood vessels. Often occurs as an allergy or in response to the presence of an infection in the body. It is treated with Prednisolone, Pyrazolone, acetylsalicylic acid.
- Wegener's granulomatosis- Vasculitis, in which the small vessels of the upper respiratory tract, lungs and kidneys are affected.
- Urtkarny- can act as an independent ailment of an allergic nature, and as a manifestation of systemic diseases. Externally, urticarial vasculitis is very similar to the manifestation of urticaria, only blisters with this disease last much longer (1-4 days).
- Allergic- Vascular damage during various allergic reactions.
In addition, vasculitis can be primary - develops as an independent disease, and secondary - occurs as a manifestation of another disease.
Symptoms of vasculitis
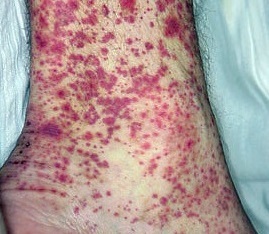 With vasculitis, the symptoms may be different. They depend on the nature of the lesion, the type of vasculitis, the localization of the inflammatory process, and also on the severity of the underlying disease.
With vasculitis, the symptoms may be different. They depend on the nature of the lesion, the type of vasculitis, the localization of the inflammatory process, and also on the severity of the underlying disease.
In case of skin lesions, a rash appears on its surface. If the nerves are affected, the sensitivity of the person is lost, aggravated or completely disappears. When the blood circulation of the brain is broken, a stroke occurs.
Among the common symptoms of vasculitis in adults, we can note weakness and fatigue, loss of appetite, pallor, increased body temperature, and more. The first sign of the disease are small, hardly noticeable, gradually progressing hemorrhages on the skin, other manifestations are absent or occur later.
Symptomatology in lesions of the lower extremities:
- rash and hemorrhagic spots;
- bloody blisters;
- increased body temperature;
- joint pain or muscle pain;
- weakness;
- itching of the skin in the affected area.
The disease is characterized by a long and chronic course with periodic exacerbations, difficulties in treatment and progression.
Treatment of vasculitis
 Treatment of vasculitis, as well as diagnosis of the disease, should be done by a rheumatologist. Only he is able, with the help of the symptoms that the patient indicates, to draw a conclusion about which form of vasculitis is before him and to prescribe an individual treatment.
Treatment of vasculitis, as well as diagnosis of the disease, should be done by a rheumatologist. Only he is able, with the help of the symptoms that the patient indicates, to draw a conclusion about which form of vasculitis is before him and to prescribe an individual treatment.
It should be borne in mind that virtually all types of vasculitis have a chronic progressive nature, so therapy should be comprehensive and long-lasting.
To treat vasculitis prescribe drugs that inhibit the production of antibodies that reduce the sensitivity of tissues: cytostatics (cyclophosphamide), glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone). Procedures such as hemosorption and plasmapheresis may be prescribed. The necessary treatment for hemorrhagic vasculitis is antibiotics. Patients with obliterating forms of vasculitis, thrombosis of large arteries, development of stenosis of the main arteries showed surgical treatment.
As for the primary allergic vasculitis, in most cases it passes independently, without requiring absolutely no special treatment. When the disease affects organs vital for life (brain, heart, lungs, kidneys), the patient needs intensive and aggressive therapy.
If there is a desire to use any folk remedies for vasculitis, then they also need to be discussed with your doctor.
The prognosis of the disease can be varied. As a rule, vasculitis affects only the skin. But there are some types of diseases that can seriously harm vital organs, and lead to death. In patients with vasculitis without specific treatment with immunosuppressive therapy, the prognosis is not favorable, a 5-year survival rate is 10% of the total number of patients.
Diet with vasculitis
The diet of a patient with vasculitis is made taking into account the causes that led to the development of the disease. First of all, such a diet is aimed at excluding the possibility of allergic reactions. Therefore during an exacerbation and some time after it the patient should adhere to a strict hypoallergenic diet.
Do not refuse to eat fresh vegetables, fruits (except those that provoke allergies), fermented milk products, in particular cottage cheese, dried fruits, various cereals. For example, some drugs increase blood pressure, which means that consumption of coffee, fatty meat, canned foods, smoked products, muffins, salt should be limited.
The nature of cooking is also important. When exacerbating you can not eat fried foods, it is better to switch to boiled or stewed. In general, a diet with vasculitis should be made on the basis of the form of the disease and the individual characteristics of the body, so when compiling a diet diet is very important to listen to the views of the doctor.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.


