Inflammation of the lungs in children: symptoms and treatment of newborns and infants
- Symptoms in children 1-3
- Symptoms in infants
- Treatment

Inflammation of the lungs is an acute infectious disease of the respiratory system.Inflammation of the lungs in children can be primary and develop independently or secondary, that is, develop as a consequence of another infectious disease that was transferred earlier, for example, sinusitis or the flu.
A child of any age, even just born, can get sick of this infection.Today, there are many medicines to treat this disease, so the disease can be called not so dangerous than a few dozen years ago.
However, it is not necessary to relax, since pneumonia is a serious illness that must be treated on time and correctly, so as not to lead to a fatal outcome.
- The cause of the disease can be bacteria, viruses, fungiand all kinds of parasites. In the lungs of a child, these organisms are through breathing.
- The main factors of the disease are viral infections, as a result of which the immunity of the child becomes weak.
- Respiratory infectionsincrease the amount of mucus and reduce their bactericidal activity, and air enters the lungs not so clean and moist. All this kills epithelial cells and reduces the immunity of the baby, so that all microbes and viruses calmly penetrate the respiratory tract, leading to an inflammatory process in the lungs.
At infection, in the lungs there is an edema of the small bronchus, because of which the air enters the body badly. And it is here that the process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. The gas exchange process is hampered and oxygen is supplied to internal organs in insufficient quantity for normal functioning.
Important
A doctor who determines a child's lung inflammation should always determine the form and severity of the disease. Only in this way can an adequate treatment be prescribed that will give results and facilitate the treatment process.
Inflammation can be of several types:
- Croupous- One lung is affected. Can be left-handed or right-handed. The baby immediately jumps to a temperature of 39-40 degrees. In the lungs and abdomen, pain is felt, a moist cough with phlegm appears, red rashes appear on the body;
- Focal. It is diagnosed in children aged 1-3 years. It affects the entire area of the lung. This form is considered secondary and appears as a result of the transferred bronchitis. The first symptoms are high fever, dry and deep cough. This type of disease can be cured only by prolonged intake of the necessary drugs. Treatment lasts 2-3 weeks;
- Segmented. Partially affects the child's lung. When this child does not want to eat and play, sleeps badly, the temperature appears 37-38 degrees. Coughing can be practically non-existent, because of what often this type of illness is difficult to detect from the first days of appearance;
- Staphylococcal. This type of infection infects newborns and babies up to one year. The main symptoms are shortness of breath, vomiting, coughing and wheezing with heavy breathing. ESR and leukocytosis in the blood test will be above the norm. With timely and correct treatment, the disease will begin to recede after 1.5 - 2 months. After that, the baby undergoes a 10-day rehabilitation.
Inflammation: symptoms in children from one year to three
 According to statistics, babies are more likely to suffer from inflammation.All this is explained by the underdeveloped respiratory system in children under three years old. The weight of the baby's organs is only being formed and developing, so they can not fully resist the infections. In children up to the age of three, lung tissue is not yet mature, the respiratory tract is small and narrow, and the mucous membranes are saturated blood vessels, which instantly swell as a result of infection, which leads to a deterioration in lung ventilation.
According to statistics, babies are more likely to suffer from inflammation.All this is explained by the underdeveloped respiratory system in children under three years old. The weight of the baby's organs is only being formed and developing, so they can not fully resist the infections. In children up to the age of three, lung tissue is not yet mature, the respiratory tract is small and narrow, and the mucous membranes are saturated blood vessels, which instantly swell as a result of infection, which leads to a deterioration in lung ventilation.In addition, the ciliated epithelium still can not quickly remove phlegm, which becomes more numerous in the disease. As a result, the infection safely penetrates into the body, settles in the organs and multiplies, leading to severe inflammation.
About the inflammation of the lungs, parents can guess by certain signs and symptoms.If the disease does not recede, but on the contrary gaining strength. If the child's immunity weakens day by day and all the treatment procedures performed do not lead to the desired result, it is necessary to urgently show the child to the doctor and think about serious medication.
Important
It is not necessary in such cases to engage in self-medication and risk the health and life of the baby. This can only worsen a child's condition, and time for quick and painless treatment will be missed.
- Symptoms of pneumonia in children aged two and three years are the same.
- Parents should identify them in the shortest possible time and urgently call the doctor at home.
- Within 3-5 days from the onset of the development of a cold or flu, the child's condition does not improve, the temperature constantly rises and cough intensifies.
- The child refuses to eat, does not sleep well, is capricious and does not want to do anything about a week after the onset of the illness.
- The main symptom is a strong strangling cough.
- There may also be shortness of breath and a small temperature, indicating an inflammatory process in a small body.
- The child begins to breathe frequently and intensively, but can not breathe normally.
Important
Children 1-3 years should do 25-30 breaths, at an older age the norm is reduced to 25 breaths per minute.
With pneumonia the baby breathes more often than usual.There is a cough, runny nose, fever and temperature. If more than three consecutive days the fever keeps, you need to take antipyretic drugs.
Inflammation of the lungs: symptoms of pneumonia in infants
Mom must constantly monitor the condition of her baby, as the inflammation of the lungs in newborns manifests itself immediately and it will be seen from the behavior of the child.
If the baby whimpers all the time, behaves sluggishly and indifferent to the world around him or cries all the time, does not want to eat and at the same time the temperature rises to the baby, it is necessary to show the child to the doctor.
Most often pneumonia is diagnosed in infants who are on artificial feeding. As well as this disease, children with diathesis, rickets and other diseases are susceptible.The main symptoms that talk about the inflammation of the lungs in infants:
- Temperature. In the first year with pneumonia, the temperature may not be high, in contrast to older children. It can keep within 37 degrees, sometimes rising to 37.5 degrees. In addition, the temperature at this age will not indicate the severity of the disease;
- Unnatural behavior. The kid behaves uneasily, reacts badly to others, refuses food and breast, while in his sleep he constantly turns and cries. Vomiting, diarrhea, runny nose and a strong cough may also occur;
-
Breath. The baby becomes painful to breathe. When coughing, purulent and mucous formations are prominent. There is shortness of breath and rapid breathing. Sometimes foam and discharge can go from the nose and mouth.
Important
The norm in newborns is 50 breaths per minute. From two months to one year, children make 25-40 breaths. If the number of breaths becomes larger, the baby may have pneumonia.
You can also observe how the skin is drawn into the child during breathing. Usually this happens from the patient's lung. To do this, you need to undress the baby and see how the skin behaves between the ribs;
- Cyanosisnasolabial triangle. This symptom is manifested by blue skin over the upper lip and under the nose. Especially the skin turns blue during breastfeeding.
Treatment of pneumonia in children
Children under three years of age who have been diagnosed with pneumonia can be treated both in the hospital and at home. It all depends on the severity of the disease and the condition of the small patient.
The doctor should identify the type of pneumonia, on the basis of which the risks of complications will be determined.
- Inflammation of the lungs in children can be treated at home, if the baby is not intoxicated, not breathing and the work of internal organs.
- In addition, the doctor should be sure that the child's living conditions will be favorable for his treatment and will not provoke complications.
- In this case, the doctor must come to the patient every day until the condition of the baby can not be called satisfactory, but stable. If the child's improved condition lasts several days, the doctor can come to the patient once or twice a day.
Treatment of newborns and children up to3-хyears should be spent in a hospital.Also, under the constant supervision of doctors should be children with respiratory failure, rickets, immunodeficiency. Immediate hospitalization is carried out by children who do not experience any improvement within 1-2 days of treatment.
Children with pneumonia are assigned bed rest in a ventilated room with an air humidity of 50-60%.
- The trunk and head of the child in a horizontal position should rise.
- It is necessary to drink a lot, so that the blood liquefies and sputum forms, which removes the entire infection from the body.
- A complex treatment is prescribed, the basis of which is antibacterial therapy.
 Before prescribing antibiotics, it is necessary to determine the presence of allergic reactions to any kind of medications from the baby and its close relatives. Initially, a wide-spectrum antibiotic is chosen which the child will take until, until all the test results are obtained and the pathogen and type of disease are determined.
Before prescribing antibiotics, it is necessary to determine the presence of allergic reactions to any kind of medications from the baby and its close relatives. Initially, a wide-spectrum antibiotic is chosen which the child will take until, until all the test results are obtained and the pathogen and type of disease are determined.Usually, the course of taking antibiotics is7-10 days.In severe forms, the course can be prolonged. In addition, antifungal agents and probiotics with vitamins are prescribed to support the body and enhance immunity.
If antibiotics do not improve the patient's condition for two days, the drug is urgently changed to another. After the temperature subsides and ceases to rise, dyspnea and wheezing during breathing will also decrease, the treatment continues for a couple of more days. Reception of antibiotics is terminated only after the complete cure of the child.
In order for the sputum to leave the baby's body well, stimulating and coughing means are used, thanks to which the bronchial secretion is diluted and eliminated from the body.
To do this, use plant, synthetic and semi-synthetic medicines, the basis of which are medicinal plants.
Also, antipyretic agents may be prescribed:
- Babies up to 3 months at a temperature of 38 degrees and febrile convulsions;
- At a temperature of 39-40 degrees;
- With toxicosis and poor condition of the child.
After recovery from a serious illness, the rehabilitation process begins, during which the child is prescribed curative breathing exercises, warm inhalations and chest massage.
The doctor must always monitor the condition of the baby and his internal organs.After recovery, you need to pass the necessary tests to determine the need to take medication to restore the normal functioning of all the organs of the child. During the year the baby should visit the pediatrician every month.
Interesting Facts
Every year, according to statistics, 150 million children aged 1-5 years and younger suffer from such an ailment as pneumonia. Of these, 70% of all cases are associated with viruses that can be treated without antibiotics, 20% are infected with bacteria, and only 10% of all diagnosed diseases require treatment in the hospital.
A doctor can determine the presence of pneumonia in a child according to the main signs, the results of a blood test and a lung X-ray. And first of all it is necessary to determine the causative agent of the disease. Dr. Komarovsky argues that pneumonia in children is not necessarily treated in a hospital.
Medical assistance is necessary only in the event of a child's poor state and if it begins to suffocate. There are specific symptoms in which you urgently need to see a doctor.
Dr. Komarovsky singles out a few:
- Cough became the main symptom of the disease;
- Impairment after improvement;
- Any catarrhal disease that lasts more than a week;
- Coughing attacks with deep breathing;
- Pronounced pallor of the skin;
- Shortness of breath and lack of antipyretic effect.
As it turns out, it is not always necessary to prick injections. There are many analogues in syrups and tablets, which also act effectively. Therefore, if a child can swallow tablets, it is not necessary to give him injections.
To prevent the disease the child must live and develop under normal conditions, eat balanced and walk more often outdoors.
gajmorit.com
Symptoms of pneumonia in children
Pneumonia in a child is an acute infectious disease that occurs with inflammation of the respiratory parts of the lungs. The disease is accompanied by the accumulation of inflammatory fluid in the pulmonary vesicles-alveoli. Symptoms of pneumonia in children are similar to those in adults, but are supplemented by severe fever and intoxication.
The term "acute pneumonia in children" is out of use in medicine, because the very definition of the disease includes a characterization of an acute process. The International Council of Scientists-Experts decided to divide pneumonia into groups according to other signs that determine the outcome of the disease.
How dangerous is pneumonia?
Despite the progress in medicine, the incidence of lung inflammation in children remains high. Pneumonia is a life-threatening, life-threatening condition. Infant mortality from pneumonia remains high enough. In the Russian Federation, pneumonia> up to , 00 children dies within a year. Basically, this terrible number unites infants who died from pneumonia in the age of 1 year.
The main causes of the fatal outcome of pneumonia in children:
- Later, parents applied for medical help.
- Later, the diagnosis and delay of the correct treatment.
- Presence of concomitant chronic diseases that worsen the prognosis.
In order to timely establish an accurate diagnosis and take measures to treat a dangerous disease, you need to know its external signs - symptoms.
The main symptoms of pneumonia in children:
-
 Fever - increase in body temperature to high digits (> 38 ° C).
Fever - increase in body temperature to high digits (> 38 ° C). - Dyspnoea - increased frequency of respiration more than 40 per minute (in children 1-6 years).
- Cough dry or with phlegm.
- Appearance of cyanotic coloring of the skin of the lips, nasolabial area, fingertips.
- Changes in respiratory noise in the lungs during listening (wheezing, hard breathing).
- Intoxication, expressed general weakness, refusal to eat.
The increase in body temperature in a child is the first symptom of many diseases, for example, a common viral infection (ARI). In order to recognize pneumonia, we must remember: an important role is played not by the height of the fever, but by its duration. For microbial inflammation of the lungs it is characteristic continuation of fever for more than 3 days against the background of competent treatment of a viral infection.
If we evaluate the significance of the symptoms for the diagnosis of pneumonia in children, the most terrible sign will be the appearance of dyspnea. Shortness of breath and tension of additional muscles are more important signs than having wheezing when listening to the chest.
Cough is a symptom of pneumonia in children. In the early days of the disease, cough can be dry. With the resolution of acute inflammation of the lung tissue, the cough will become productive, moist.
If a child with a respiratory viral infection (ARI) has similar symptoms, an urgent call for a doctor is necessary. Underestimation of the severity of the baby's condition can lead to sad consequences - the development of acute respiratory failure and death from pneumonia.
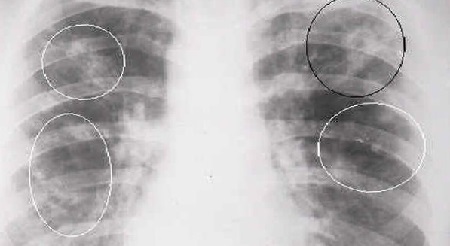
The doctor will examine the small patient, prescribe an examination and an effective treatment. Listening to the lungs in the early days of the disease may not reveal characteristic signs of inflammation. The presence of disseminated wheezing when listening is often a symptom of bronchitis. To clarify the diagnosis for suspected pneumonia, an X-ray of the lungs is necessary. X-ray symptoms of pneumonia are darkening (infiltration) of pulmonary fields, which confirms the diagnosis.
Laboratory Symptoms of Pneumonia
Valuable information about the fact of inflammation in the body carries a general blood test. Signs that increase the presence of pneumonia: a high content of white blood cells in 1 cu. mm blood (more than 15 thousand) and an increase in ESR. ESR is the sedimentation rate of red blood cells. This analysis reflects the amount of inflammatory metabolic products in the liquid part of the blood. The magnitude of ESR shows the intensity of any inflammation processes, including inflammation of the lungs.
How to determine the risk of a child with pneumonia?
The following factors are identified that increase the risk of lung inflammation in children:
- Delayed physical and mental development of the child.
- Low weight of a newborn baby.
- Artificial feeding of a baby under the age of 1 year.
- Refusal of vaccination against measles.
- Pollution of air (passive smoking).
- Overcrowded dwelling, where the baby lives.
- Smoking of parents, including mother's smoking during pregnancy.
- Lack of microelement of zinc in the diet.
- Mother's inability to care for an infant.
- Presence of concomitant diseases (bronchial asthma, heart disease or digestive system).
What forms can the disease have?
 Pneumonia in children is different for reasons and mechanism of occurrence. The disease can affect the entire lobe of the lung - this is a shared pneumonia. If the inflammation occupies a part of the lobe (segment) or several segments, it is called segmental (polysegmental) pneumonia. If the inflammation is covered by a small group of pulmonary vesicles, this variant of the disease will be called "focal pneumonia".
Pneumonia in children is different for reasons and mechanism of occurrence. The disease can affect the entire lobe of the lung - this is a shared pneumonia. If the inflammation occupies a part of the lobe (segment) or several segments, it is called segmental (polysegmental) pneumonia. If the inflammation is covered by a small group of pulmonary vesicles, this variant of the disease will be called "focal pneumonia".In inflammation, passed to the respiratory tissue of the bronchi, the disease is sometimes called bronchopneumonia. The process, caused by viruses or intracellular parasites such as chlamydia, is manifested by swelling (infiltration) of the perivascular tissue of the lungs from both sides. This type of disease was called "bilateral interstitial pneumonia." These symptoms of difference can be determined by medical examination and X-ray examination of sick children.
Inflammation of the lungs in children doctors are divided according to the conditions of origin for domestic (out-of-hospital) and hospital (hospital). Separate forms are intrauterine pneumonia in newborns and pneumonia with a pronounced lack of immunity. Community-acquired (home) pneumonia is called inflammation of the lungs, which has arisen in ordinary home conditions. Hospital (nosocomial) pneumonia is a case of illness that occurs after 2 or more days of the child's stay in the hospital for another reason (or within 2 days after discharge from there).
Mechanism of the development of pneumonia
The entry of a microbial pathogens into the respiratory tract can occur in several ways: inhalation, swallowing of nasopharyngeal mucus, dissemination through the blood. This way of introducing a pathogenic microbe depends on its kind.
The most frequent causative agent of the disease is pneumococcus. The microbe enters the lower parts of the lungs by inhaling or swelling of mucus from the nasopharynx. Intracellular parasites, such as mycoplasma, chlamydia and legionella, enter the lungs by inhalation. The spread of infection through the blood is most typical for infection with Staphylococcus aureus.
The type of causative agent that causes pneumonia in children depends on several factors: the age of the child, the place of origin of the disease, and also from the previous treatment with antibiotics. If within 2 months before the present episode the baby has already taken antibiotics, then the causative agent of the current inflammation of the respiratory tract can be atypical. In 30-50% of cases, community-acquired pneumonia in children can be caused by several types of microbes at the same time.
General rules for the treatment of pneumonia in children
 Treatment of the disease the doctor begins with the immediate appointment of antimicrobials to any patient with suspected inflammation of the lungs. The place of treatment is determined by the severity of the manifestation of symptoms.
Treatment of the disease the doctor begins with the immediate appointment of antimicrobials to any patient with suspected inflammation of the lungs. The place of treatment is determined by the severity of the manifestation of symptoms.Sometimes with a mild course of the disease in children of older age groups, treatment at home is possible. The decision on the place of treatment is made by the doctor, according to the patient's condition.
Indications for treatment in a hospital of children with pneumonia are: severity of symptoms and a high risk of an unfavorable outcome of the disease:
- The age of the child is less than 2 months, regardless of the severity of the symptoms.
- The age of the baby is younger than 3 years with lobar pneumonia.
- Inflammation of several lobes in a child of any age.
- Severe concomitant diseases of the nervous system.
- Pneumonia of newborns (intrauterine infection).
- The small weight of the baby, the delay of its development in comparison with peers.
- Congenital malformations of organs.
- Chronic concomitant diseases (bronchial asthma, heart disease, lung, kidney, cancer).
- Patients with decreased immunity from various causes.
- Impossibility of careful care and accurate performance of all medical appointments at home.
Indications for the urgent placement of a child with pneumonia, in the department of children's intensive care:
- Increases in the number of breaths> 60 in 1 min for babies under the age of one year, and for children older than the year, dyspnea> 50 per 1 min.
- The retraction of the intercostal spaces and the jugular fossa (fossa at the beginning of the sternum) with respiratory movements.
- Moaning breathing and violation of the right rhythm of breathing.
- Fever that does not respond to treatment.
- Violation of the child's consciousness, the appearance of convulsions or hallucinations.
In uncomplicated course of the disease, body temperature decreases within the first 3 days after initiation of treatment with antibiotics. External symptoms of the disease gradually decrease in intensity. X-ray signs of recovery can be seen in the pictures of the lungs no earlier than 21 days after the start of antibiotic treatment.
In addition to antimicrobial treatment, the patient must comply with bed rest, plenty of drinking. Expectorants are prescribed if necessary.
Prevention of pneumonia
Protection from respiratory viral infection plays an important role in preventing the incidence of pneumonia.
It is possible to carry out vaccination against the main pathogens of pneumonia in children: a hemophilic rod and pneumococcus. At present, safe and effective vaccine-tablets are developed against microbes that cause pneumonia and bronchitis. Preparations from this class "Bronchovax" and "Ribomunil" have a children's dosage. They are appointed by the doctor to prevent such a dangerous disease as pneumonia.
ingalin.ru
Signs of pneumonia in children
 Inflammation of the lungs, or pneumonia, is a disease that many have heard of. It can develop in a child with weakened immunity, after hypothermia, as well as in a child who has had an acute respiratory viral infection. But this should not be frightened, because according to statistics, only 0.5% of the total number of affected children develops this disease. Symptoms of pneumonia in children may differ depending on age, so if you suspect this ailment, you need to seek medical help urgently.
Inflammation of the lungs, or pneumonia, is a disease that many have heard of. It can develop in a child with weakened immunity, after hypothermia, as well as in a child who has had an acute respiratory viral infection. But this should not be frightened, because according to statistics, only 0.5% of the total number of affected children develops this disease. Symptoms of pneumonia in children may differ depending on age, so if you suspect this ailment, you need to seek medical help urgently.Signs of pneumonia in a child under one year of age
Very often, especially in infants, the first symptoms of this formidable disease are mistaken for an ordinary cold. Even experienced parents are not in a hurry to seek help from a doctor, whereas precious time can be missed. Signs of pneumonia, both in a one-year-old child and a young child, are manifested in the following:
- cyanotic skin;
- body temperature in the range of 37-38 degrees;
- strong and paroxysmal cough;
- rapid accumulation of sputum;
- refusal of food, tearfulness, irritability.
If you start treating this disease in time, the signs of pneumonia in infants quickly go to recession, and treatment is recommended to be carried out at home. Inflammation of the lungs is treated with antibiotics, even in such small children, so compliance with the regime of the day, proper nutrition, as well as the introduction of foods containing lactobacilli in the diet is mandatory. When all these simple rules are fulfilled, the baby will feel much better in a couple of days, and the general course of treatment will be from 5 to 7 days.
Symptoms of pneumonia in children from a yearSymptoms of pneumonia in children 2 years and older do not differ much from those that are present in infants. Here, one can also observe symptoms typical for pneumonia:
- Increased body temperature.This is one of the first signs in children, which adults pay attention to when they are pneumonia. The temperature fluctuates between 37 and 38 degrees, and by evening, as a rule, it is higher than in the morning. However, there are exceptions, when the child may have decreased or, conversely, a very high (up to 40 degrees) body temperature.
- Persistent cough.In a child, for example, 3 years and older, the primary signs of pneumonia are a strong, pertussis or paroxysmal cough and pallor of the nasolabial triangle. In toddlers, it can be both dry and with sputum secretion. It can contain impurities of pus, mucus or blood. With such symptoms, the doctor must send the crumb to the X-ray of the lungs.
- Pain in the chest and lack of air.Common signs of pneumonia in children 5-6 years of age and toddlers of close age are pain under the shoulder blades, with coughing or breathing, from one side, and also, especially when walking or exercising, the state of "lack of air".
-
External signs.If the baby is silent, not complaining at all, then it is possible to suspect pneumonia due to rapid fatigue of the crumbs, severe sweating, rapid rapid breathing and capriciousness. In children, the accuracy of movements decreases and there may be a violation of coordination,
 that sometimes leads to a dead end parents and others.
that sometimes leads to a dead end parents and others. - Refuse to eat.This sign, as a rule, is accompanied by a digestive disorder, nausea and vomiting. And even if the baby manages to feed a little, he will lose weight quickly enough.
So, parents need to remember that any deviations in the behavior of the child should be alarming, and especially when they concern health. Cough, fever, lack of air, rapid breathing - these are the symptoms in which a doctor's consultation should be immediate.
WomanAdvice.ru
Pneumonia in children - symptoms

Pneumonia in children, especially the first years of life, is a common disease that affects the lungs. Duration of treatment, the likelihood of relapse and the transition of pneumonia to the chronic stage are good reasons to understand the need for early diagnosis of the disease. About the existing forms of the disease and how to recognize the child pneumonia, we will explain in this article.
How to determine pneumonia in a child?
Determine the symptoms of pneumonia possible, but not always it is possible in the early stages, especially in infants. The thing is that in the first days of the disease the symptoms are very similar to acute bronchitis.
- For bronchitis and pneumonia in children, the secondary type of development of the disease is more typical (on days 5-7 after the ORVI, ORZ in children).
- Severe dry cough, shortness of breath and chest pain.
- High body temperature.
Only a specialist can make a final diagnosis.
How does pneumonia manifest in children?
Manifestations of pneumonia in children can vary significantly. It depends on the type of pathogen. The severity of the disease and the brightness of the manifestation of symptoms are due to the extent of lung damage.
Calling pneumonia can:
- viruses;
- bacteria;
- worms;
- allergies;
- fungi, etc.
For viral pneumonia in children, the symptoms in the form of cough, high fever, poorly amenable to medication, characteristic wheezing and other things persist. But atypical pneumonia, which is caused by chlamydia and mycoplasmas, you can and completely confuse with the usual ARI.
The first signs of atypical pneumonia in children:
- prolonged dry cough;
- sneezing, a bad cold;
- a feeling of perspiration in the throat;
- high body temperature, but in some cases the temperature may remain within normal limits;
- loss of appetite;
- wheezing, not typical for normal pneumonia.
Symptoms of radical pneumonia in children also have their own characteristics. If other areas of the lung are affected, the disease is diagnosed more easily. Determine the localization of wheezing in this disease is extremely difficult. If the inflammation started in the basal part of the lung, additional tests should be performed, since in the pictures the basal pneumonia is similar to tuberculosis and bronchial cancer. Temperature, cough, loss of appetite and other symptoms are inherent in radical pneumonia, but the disease itself is protracted.
Symptoms of pneumonia in infants
In infants, it is especially difficult to diagnose pneumonia in the early stages, even for specialists. In the first two days of the disease, a cough or breathing with a characteristic noise is not observed in the child and there are no wheezing when listening to the lungs. Pneumonia in infants can also occur without fever. Given that the baby's respiratory system is just beginning to improve, the picture of the disease can develop into a serious and the treatment then has a very long time. But nevertheless signs of a pneumonia at thoracal children, let and not so strongly pronounced, are available.
- The child loses his appetite. A kid can often ask for a breast, but at the same time he practically does not suck.

- The nasolabial triangle of the baby acquires a bluish tinge. This is especially noticeable during sucking.
- The skin between the ribs of the baby begins to retract. To determine this, it is necessary to put the child to undress it and see if the given symptom is present.
- Rapid breathing. Babies who get pneumonia start breathing more often. So, in children up to 2 months there are more than 60 breaths per minute, for children up to a year there are more than 50 breaths, and in children after a year - more than 40 breaths per minute.
- Behavioral changes. The child can become sluggish and apathetic, the periods of sleep at the same time increase noticeably in time. There may be another option, when the child, by contrast, is a lot of naughty, crying and screaming.
WomanAdvice.ru