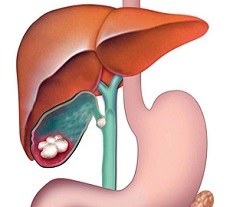
 Calculous cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder associated with the deposition of stones formed from cholesterol, dyes of bile and calcium impurities. These deposits are localized in the bile lumen and ducts.
Calculous cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder associated with the deposition of stones formed from cholesterol, dyes of bile and calcium impurities. These deposits are localized in the bile lumen and ducts.
Problems with the outflow of bile cause deterioration of blood circulation in the walls of the gallbladder, resulting in the release of numerous substances that cause inflammation. Over time, the process of multiplying bacteria.
The course of calculous cholecystitis has a chronic character with a periodic transition to an acute condition (in which bile colic and jaundice can be observed). In contrast, non-calculous cholecystitis is not associated with the deposition of stones, and can be either acute or chronic.
Statistics
Since the middle of the twentieth century, the number of patients with chronic heart failure has doubled every 10 years and is about 10% of the population of most developed countries: in our country, HCM suffer about 15 million. human; in the USA - more than 30 million people.
Among patients older than 45 years, cholelithiasis is found in every third. As a result, the number of operations related to HCW in the United States in the 1970s was annually more than 25, 00, in the 1980s more than 40, 00, and in the 1990s, up to 50, 00.
Now in the US, the number of cholecystectomies and operations on the biliary tract is about 1.5 million. per year and exceeds the number of all other abdominal interventions (including appendectomy).
Causes
Why does calculous cholecystitis occur, and what is it? The main cause of calculous inflammation of the gallbladder is the presence of concrements in its lumen. They are formed due to qualitative changes in the balance of bile: cholesterol crystallizes, there is a general stasis of secretion with the attachment of the inflammatory component. The formation of the stones themselves leads, first of all, to a violation of the outflow of bile, that is, its stagnation.
Certain conditionspromote the formation of stones:
- excessive consumption of fatty and carbohydrate food;
- prolonged interruptions in nutrition, hunger diets with a lack of vitamins;
- trauma and consequences of the transferred operations on the organs of the abdominal cavity;
- impaired motor function;
- acute viral hepatitis;
- hereditary predisposition;
- endocrine disorders (diabetes, climax, obesity, long-term use of contraceptives, treatment with hormonal drugs).
Also, among the factors predisposing to the development of calculous cholecystitis, dyskinesia of bile excreting pathways, chronic gastritis, duodenitis, pancreatitis, liver cirrhosis, Crohn's disease, helminthiases.
Symptoms of calculous cholecystitis
Calculous cholecystitis has two forms - chronic and acute. Disease historywith acute manifestation of calculous cholecystitisbegins to develop with the following symptoms:
- most often, there is a so-called biliary colic. Severe pain, which starts right under the ribs, is transmitted to the right shoulder or arm;
- you vomit, there is vomiting with bile;
- the body temperature rises;
- you feel a weakness in the body;
- there is a cold sweat;
- possibly jaundice;
- there is a sharp drop in blood pressure.
In chronic calculous cholecystitis is not in the stage of exacerbationSymptoms are more softer. Patients can complain about:
- characteristic dull, aching pain in the region of the right hypochondrium of a permanent character or arising 1-3 hours after the intake of abundant and especially fatty and fried foods.
- the pain irradiates upward, into the region of the right shoulder and neck, right shoulder blade. Periodically, there may be a sharp pain resembling a biliary colic. However, sometimes even expressed inflammatory changes in the gallbladder may not be accompanied by symptoms of biliary colic.
- usually chronic calculous cholecystitis is not accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
- Such phenomena as nausea, irritability, insomnia are not uncommon.
- jaundice is not characteristic.
Period of exacerbationcomplicated by additional symptoms:
- sharp cutting pain in the liver, can give in the scapula, sternum, mid-epigastric zone, right shoulder;
- severe nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- weakness;
- swelling and tension of the abdomen;
- spasms of the peritoneal muscles;
- problems with the stool, more often - constipation.
In accordance with ultrasonic signs,4 stages of calculous cholecystitis:
- the initial or pre-stone stage is characterized by the presence of biliary stasis, thick bile and microliths in the gallbladder. In half the cases, the pre-stone stage is reversible.
- concrement stage
- stage of chronic calculous cholecystitis
- stage of complications of calculous cholecystitis
As can be seen, depending on the symptoms of calculous cholecystitis, the methods of treating the disease will differ substantially.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of "calculous cholecystitis" is based on the symptoms named by the patient and on clinical studies. For this, an overall blood and urine test is performed. Assigning ultrasound, CT (computed tomography) and X-rays (cholecystography) are done. A study of the level of enzymes of the pancreas and liver samples is carried out, and feces are analyzed. In some cases, duodenal probing with bile sampling may be prescribed.
Also calculous cholecystitis followsdifferentiate from the following pathologies:
- dyskinesia of the biliary tract;
- adenomyomatosis;
- acuminate cholecystitis;
- cholesterosis of the gallbladder;
- right-sided renal colic;
- chronic hepatitis;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- chronic gastritis;
- chronic colitis;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- stomach ulcer and 12p. guts.
Treatment of chronic forms usually takes place at home, with exacerbations, the patient is hospitalized or, depending on the condition, treatment in a day hospital.
Complications
Among the complications of calculous cholecystitis the most significant are:
- Choledocholithiasis (obstruction by concrements of the common bile duct);
- subdiaphragmatic abscess;
- empyema and perforation of the gallbladder;
- stenosis of the pharyngeal papilla;
- acute or chronic pancreatitis;
- reactive cholangitis, hepatitis;
- peritonitis.
Only timely and competent therapy of the disease will help to avoid unpleasant consequences of cholecystitis.
Treatment of calculous cholecystitis
Therapy depends on the form of the disease. Treatment of acute calculous cholecystitis is carried out in a hospital. Self-medication at home is prohibited. As a rule, spasmolytic, antibacterial, detoxification therapy, anticholinergic, antiemetics are prescribed. After stabilization of the condition, surgical treatment is performed in a planned manner.
If all the treatment is not beneficial, then they decide to perform a surgical operation. During surgical treatment can remove both the body itself with stones, and only stones. The choice of the type of operation depends on the condition of the organ, the size and amount of gallstones.
As for chronic calculous cholecystitis, the basis of treatment is strict adherence to diet in the offensive and interstitial periods, Exclusion from food nutrition rich in carbohydrates and fats, reducing to a minimum the salt and spices, total refusal of alcohol.
After the abatement of exacerbation, litholytic therapy is prescribed - the use of medications that dissolve stones in the gallbladder - ursosana, henofalk, lithofalk. These drugs allow you to treat calculous cholecystitis without surgery at home. Also, if necessary, prescribe antispasmodics.
Operation
There are several types of surgical intervention for the treatment of calculous cholecystitis:
- Laparoscopy. Several cuts are made on the abdomen, special instruments and an optical instrument are introduced through them - a laparoscope that transmits an image to the monitor. Extensive opening of the peritoneum is not required, therefore the period of postoperative recovery is shortened and the appearance of the operated person does not suffer.
- Percutaneous cholecystostomy. In the gallbladder, a drainage tube is inserted through a small incision on the abdomen. Applied for the course of elderly and severe patients who have complications of acute cholecystitis.
With the impossibility of minimally invasive intervention, resort to open cholecystectomy or cholecytectomy from mini-access. Open cholecystectomy, as a rule, is shown in complicated forms of calculous cholecystitis. In some cases, weakened or elderly patients with complications have cholecystotomy or percutaneous cholecystostomy.
Forecast
With calculous cholecystitis, the prognosis for life is conditionally favorable, with adequately conducted therapy the work capacity will be preserved to the fullest. The greatest danger is the complications associated with the development of peritonitis due to rupture of the gallbladder. In this case, even with adequate treatment, a lethal outcome is possible.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



