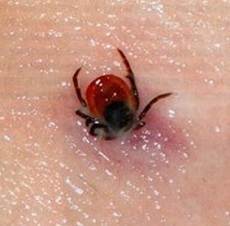
 The tick is a subclass of arthropods from the class of arachnids, the length of the body of an individual of medium size is 0.5 mm.
The tick is a subclass of arthropods from the class of arachnids, the length of the body of an individual of medium size is 0.5 mm.
Activation of insects begins in the spring and early summer, the risk of being bitten increases in warm, dry weather. When you bite through the wound, an anesthetic is injected into the body, as a result of which the insect attacks pass absolutely unnoticeable for a person.
Ticks are known as carriers of tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis and other dangerous diseases. If a person is bitten by an infected tick, the virus quickly enters the bloodstream and infects the entire body.
Preventative inspection
These parasites at a distance of 10 to 15 m feel that there is a person. And near the paths the mite awaits more readily than in the forest more often.
After a walk,examine the body for mites:
- an area that is located behind the person's ears;
- neck, thorax and armpits;
- inguinal region and genital organs;
- small of the back;
- the scalp.
The main danger for a person is the infection of diseases,the carrier of which is a tick:
- typhus tick-borne typhus;
- Tularemia;
- erlichiosis;
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- ku-fever;
- Lyme disease.
At the site of the bite, redness and swelling occur in some cases, allergic reactions may occur.
Symptoms of tick bite in humans
The tick has a peculiar organ - the hypostome (proboscis), which penetrates the skin of the victim and is attached to the wound with a special saliva, it simultaneously and anesthetizes (that's why a person does not feel the moment of bite), and fixes the proboscis in the wound. The size of the mite is about 0.3-0.4 mm, the female is 1 mm larger. Sucking blood, the mite increases in size by 2-3 times.
You can identify the main symptoms in humans associated with a tick bite, they can manifest themselves after 2-3 hours, namely:
- chills;
- redness of the place, where there is a bite;
- fear of light;
- headache;
- increased weakness and drowsiness;
- painful sensations in the joints of a person.
The following symptoms of a tick bite in a person can be such factors:
- skin rashes;
- severe itching;
- increase in human body temperature to 39-40 degrees Celsius;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- there is a clear tachycardia;
- you can see an increase in lymph nodes, namely regional ones.
In addition to these symptoms, it is necessary to consider the presence of secondary signs, which provoked the tick with its bite, namely:
- nausea;
- profuse vomiting;
- hoarse voice;
- heavy breathing and shortness of breath;
- severe headache accompanied by dizziness;
- the presence of peculiar nervous disorders, for example: hallucinations.
Ticks are carriers of many diseases, among them tick-borne encephalitis, tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease), rickettsiosis and other infections. When you find a sucking mite - remove it as soon as possible! To tighten with removal it is impossible. The longer the mite drinks blood, the more infection will enter the body.
The first signs of Borreliosis and tick-borne encephalitis
Lyme disease (borreliosis):
- redness of the skin in the bite of the parasite;
- gradual increase in the size of the red spot;
- the transformation of redness from a rounded spot into a ring with a pale cyanotic center.
Tick-borne encephalitis:
- general and muscular weakness in the neck, arms and legs;
- a feeling of numbness in the neck and face;
- chills, fever;
- nausea, vomiting;
- severe headache;
- dyeing the skin of the face, neck, mucous membrane of the mouth and eyes in red.
At occurrence of the given symptomatology it is necessary urgently to address to the doctor infektsionistu or to the therapist of a polyclinic, in a reception branch of an infectious hospital, and at a serious condition - in an ambulance.
How does a tick tick a person: photo
The place around the bite has a color from pink to reddish, it depends on the reaction of the body. In the center there will be a noticeable deepening into the interior of the skin.
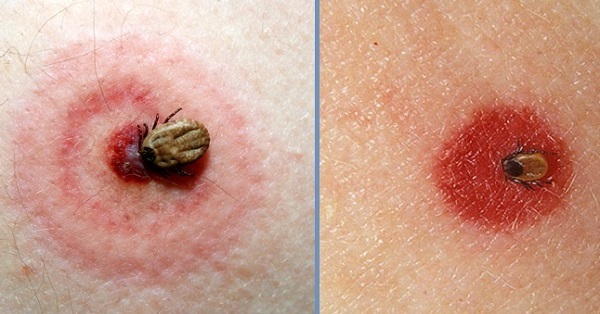 If there is redness in the bite - this can be a normal allergic reaction. But the red spots that have reached a diameter of 10-12 cm, can be a symptom of Lyme disease.
If there is redness in the bite - this can be a normal allergic reaction. But the red spots that have reached a diameter of 10-12 cm, can be a symptom of Lyme disease.What to do with a tick bite?
Since the tick is a vector of serious diseases, when you return home after hiking in a park or forest, do not immediately lie on a sofa. It is important to carefully examine yourself and your loved ones for the presence of a tick on the body.
If the tick was found, then it should be pulled out of the human body as soon as possible. There are several ways to do this at home.
- You can try to "unscrew" the insect from the skin. In this case, the movements must be made counter-clockwise. Keep the mite as close to the skin as possible to prevent the abdominal rupture. Fingers with a bandage or gauze.
- Another variant -use of improvised means, for example, clothes from clothing. It needs to tighten the proboscis at the distance as close to the skin as possible, and, following the swinging movements, slowly remove the tick. Some remove tick with nails or matches.
If you did not have the opportunity to go to a medical institution and conduct an analysis of the tick, then it is advisable to observe the injured person within a month.
It is also worth knowing that the incubation period for Lyme Disease from the onset of infection to the onset of symptoms usually 1-2 weeks, but it can be much shorter (several days), or longer (from months to years). In the case of tick-borne encephalitis, it is considered that from the moment of getting the virus into the blood before the onset of the first manifestations of the disease passes from 1 day to a month. The average period is 1-3 weeks, since the forms of the development of the disease are different.
Consequences of a tick bite for a person
The tick bite itself is not dangerous to humans. Serious consequences after a bite can occur only if the insect has been infected.
The tick can be a source of quite a large number of diseases, so by removing the tick, keep it for investigation for infection with tick infections (tick-borne encephalitis, tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease), if there is a possibility for other infections), usually it can be done in an infectious disease hospital. It must be understood that the presence of infection in the tick does not mean that a person will get sick. An analysis of the tick is needed for calmness in case of a negative result and vigilance - in the case of a positive.
Here is a list of diseases that a tick can transmit:
- Tick-borne encephalitis;
- Lyme borreliosis;
- Tick-borne haemorrhagic fevers;
- Ehrlichiosis;
- Anaplasmosis;
- Tick-borne typhus;
- Ridiculous rickettsiosis;
- Tsutsugamushi fever;
- Ku-fever;
- Rickettsiosis tick-paroxysmal;
- Babesiosis rights.
Most often found on the territory of Russia and represent a serious danger to human health - tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis. Of course, the probability of getting infected with a tick bite is not too high, because 90% of the mites, according to the studies, are sterile. However, it is present.
Consequences of a bite of an encephalitis tick
Adverse outcome:
- A persistent decline in the quality of life with the progression of symptoms (continuous progression, abortive - recurrent).
- A persistent organic syndrome with a significant decrease in the quality of life in the form of a defect in motor functions without progressive symptomatology.
- Promote the progression of symptoms: binge, stress, fatigue, pregnancy, etc.). Prolonged persistent changes in the form of epilepsy, hyperkinesis - an occasion to determine III, II, I group of disability.
Favorable outcome:
- Chronic weakness, lasting up to 2 months, followed by a complete restoration of the body's functions.
- Infection of moderate severity with recovery to 6 months.
- Infection in severe form with a recovery period of up to 2 years without paresis and paralysis.
Helpful information
- If you have kept a live tick for analysis, it will be taken to the laboratory at an infectious hospital or at a sanitary epidemiological station.
- If you are vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis, then it gives protection from infection with the virus.
- 10 days after the bite, blood can be examined by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis.
- After 14 days, the blood is tested for antibodies to tick-borne encephalitis.
- Antibodies of borreliosis can be detected in the blood only 30 days after infection.
Prevention
Of course, do not deprive yourself of the pleasure of walking around the city under the canopy of trees, because ticks can overtake and in the city. Simply, going to the forest, you need to adhere to certain rules of prevention, so as to maximally protect yourself from these bloodsucking insects:
- Avoiding places of congestion of ticks that prefer to dwell in moist thickets of plants.
- The manifestation of extreme caution during the maximum activity of such dangerous insects is the period from the beginning of May to the middle of September.
- Wearing closed clothing, and on open areas of the body - rubbing special creams and funds against tick bites, which will not allow insects to have access to the human body.
Prevention of the consequences associated with a tick bite is based on:
- Vaccination (preventive measure), when a person is infected, it can not be used.
- Specific immunotherapy is a curative measure (the introduction of immunoglobulin only in case of infection or suspected infection after a bite).
- Use of special clothing and devices to prevent ticks from getting on the body.
- Use of means for repelling, destroying ticks.
- Health insurance to pay for possible treatment.
Also remember, when you bite the infection is usually not transmitted immediately. The longer the tick will stay on the body, the greater the chance of getting encephalitis or borreliosis.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



