 Inflammation of the tongue - glossitis, can be the result of many factors. There is a place for both traumas and pathogenic microorganisms.The term glossitis can be used to designate a change in the surface of a tongue that occurs under the influence of a shortage vitamins, anemia, acute infection, some types of dermatosis, as well as with anomalies in the structure of the tongue.
Inflammation of the tongue - glossitis, can be the result of many factors. There is a place for both traumas and pathogenic microorganisms.The term glossitis can be used to designate a change in the surface of a tongue that occurs under the influence of a shortage vitamins, anemia, acute infection, some types of dermatosis, as well as with anomalies in the structure of the tongue.
Sometimes chronic glossitis can form. This is facilitated by frequent and prolonged action on the language of chemical stimuli, traumatizing the tongue with sharp edges of seals or prostheses, and destroyed teeth. Chronic course of the disease provokes dysbiosis, decreased immunity.
Taking into account the main causes of the disease, treatment of glossitis is almost always based on the elimination of the underlying cause infection, which allows you to minimize the likelihood of other common oral diseases.
Causes
Why does the glossitis appear, and what is it? The inflammatory process affecting the tissues of the tongue is called glossitis. By this term all language pathologies are meant, including those that are not inflammatory. Glossitis can manifest itself, but mostly it is a sign of any disease of the body.
The causes that can cause glossitis, are quite diverse:
- infectious agents, they are most often represented by bacteria and viruses;
- trauma of the tongue as a result of burns (hot drink, biting of the tongue, impact on the tongue of substandard seals, orthodontic constructions, etc.);
- local allergic reactions (toothpaste, food colorings, etc.);
- anemia;
- deficiency in the body of vitamins B, E, iron;
- malnutrition;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus);
- AIDS (candidiasis and herpetic infection).
Chronic glossitis occurs as a result of traumatism of the tongue with the pointed ends of the destroyed teeth, pointed edges of seals or dentures, frequent and prolonged action on the language of electric current, chemical stimuli. Chronization of glossitis is facilitated by a decrease in local and general immunity and dysbacteriosis, as well as the state of the body in which autoantibodies are formed.
Symptoms of glossitis
Symptoms of glossitis in the tongue are so obvious that it is simply impossible to miss them. In addition, if you study the photos of patients, you can understand that the manifestations will be noticeable externally, since they affect the color and form of the language.
The main signs of glossitis in adults:
- an unpleasant smell arises in the mouth;
- when chewing, the tongue hurts;
- in the throat appears perspiration and sensation of a lump;
- the mucous membrane swells;
- salivation increases;
- sometimes reddish specks may appear on the tongue;
- discomfort in the mouth;
- the tongue becomes inactive and dry.
If glossitis is not treated, then it becomes chronic. In chronic glossitis, the tongue swells strongly and tightly, its structure changes. With neglected forms of glossitis, mushroom-like growths grow on the tongue.
When glossitis is complicated by phlegmon, the swelling of the tongue and suppuration become more pronounced and spread to the bottom of the mouth and neck. The pain syndrome increases, the process of food intake becomes more complicated until the patient completely refuses to eat. Difficulty speech and breathing, possible attacks of suffocation. General signs of intoxication with glossitis complicated phlegmon, become more pronounced: regional lymph nodes increase, temperature rises, weakness appears.
Classification
Depending on the symptoms, different forms of glossitis are distinguished in the language:
- Desquamative glossitis. A characteristic feature of this disease is the "geographical" language, which has a pinkish-red "mottled" appearance, which resembles the contours of the continents on a geographical map. The sites of exfoliation, sloughing of the epithelium are called desquamation sites. The cause of desquamative glossitis development is the deterioration of nutrition of the mucous membrane tissues of the tongue, due to which they peel off. Usually desquamative glossitis is not accompanied by complaints. Sometimes there is a feeling of a slight tingling, most often when the lesions are localized on the lateral surfaces or the tip of the tongue. Often desquamative glossitis develops with exudative diathesis, blood diseases, digestive organs, metabolic disorders, helminthic invasions, in pregnant women.
- Folded glossitis- congenital pathology of the tongue. It is expressed by folds in the tongue, the deepest fold extending longitudinally along the middle line of the tongue. This form of glossitis does not cause unpleasant sensations, therapeutic measures are required only with a large number of folds and are conducted for aesthetic purposes.
- Purulent-phlegmous glossitis. Inflammation extends to deeper layers of the body, as well as beyond. In this case, you can grope enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, which are also involved in the process. Also, the patient feels a general malaise, the body temperature rises to high figures and lasts until the positive dynamics occurs in the treatment of pathology. This form of glossitis sometimes requires prompt intervention and mandatory therapy with antibacterial agents.
- Slight Glossitismanifests itself overgrowth of the filiform papillae with further cornification. This form of glossitis occurs with frequent traumatization of the tongue and candidiasis. Also, villous glossitis can provoke the taking of certain medicines and smoking.
- Rhomboid (middle) glossitis- occurs against a background of low acidity of gastric juice, which is caused by chronic diseases of the digestive system. On the surface of the tongue appear thickening of the epithelium of bright red or cyanotic color. The rhomboid glossitis is dangerous because it often turns into a chronic form and has a recurring character. Depending on the intensity of the inflammatory process, treatment may require surgical intervention or radiosurgical methods.
- Phlegmose (deep)Glossitis affects all layers, as well as nearby tissues and areas (cheeks, lymph nodes). With this form an abscess is formed, all signs of inflammation are noted, an abscess may start.
- Ulcerative formmost often develops after catarrhal (if the disease is not treated). In this case, ulcers develop on the surface of the tongue, which can bleed for damage. Edema becomes more pronounced.
Vivid and specific clinical manifestations of glossitis allow the dentist to diagnose a visual examination. To determine the nature and depth of the lesion, as well as to identify the disease that caused glossitis, apply biochemical, histological, bacteriological, serological and cytological diagnostic methods.
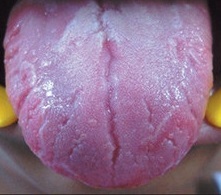
Glossitis - photos
How does glossitis look in the language, we suggest viewing detailed photos of the symptoms.
How to treat glossitis in the tongue?
Depending on the cause of glossitis in the language, the final treatment regimen is determined. As for the general recommendation for treatment, the specialists will recommend the following:
- constant rinsing of the mouth, especially after eating, brushing your teeth at least twice a day;
- avoiding too hot, flavored, spicy food, irritating and so damaged mucous;
- mashed potatoes, grated soups and viscous cereals - the daily diet of a person suffering from glossitis.
To reduce the pain during eating, the patient is shown rubbed soups, mucous porridges and a variety of purees. Before and after meals, as well as during the day, rinses of the mouth with a solution of Furacilin, a weak solution of potassium permanganate or 0.05% solution of Chlorhexidine are shown. If the pain syndrome is pronounced in the case of glossitis, then resort to applications with anesthetics - a 2% solution of Trimechain, Pyromecaine or Lidocaine. If there are signs of dryness of the tongue to reduce pain, the surface of the tongue is smeared with a mixture of anesthesin and glycerin.
In the treatment of glossitis of the tongue folk remedies are widely used herbs that have anti-inflammatory effect: chamomile, sage, calendula officinalis, etc. Based on these herbs are prepared decoctions for rinsing the mouth.
Prevention
Glossitis is easier to prevent than treat with drugs, so we want to list a few simple rules that will minimize the risk of developing an inflammatory process:
- be sure to observe the hygiene of teeth and oral cavity;
- in the morning and in the evening brush your teeth with the toothpaste your dentist recommends;
- Do not allow injuries to teeth, gums and mucous membranes;
- regularly check with an experienced dentist;
- do not abuse nicotine and alcohol;
- refuse overly spicy dishes.
When the first signs of glossitis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor, because the earlier treatment is started, the faster the glossitis will heal.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



