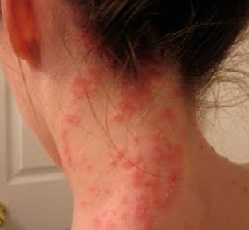
 Allergic urticaria is a skin reaction to an allergen. The main symptom is large blisters that look like insect bites, or a nettle burn.This disease is accompanied by a severe itch, so treatment should begin in a short time.
Allergic urticaria is a skin reaction to an allergen. The main symptom is large blisters that look like insect bites, or a nettle burn.This disease is accompanied by a severe itch, so treatment should begin in a short time.
Since rashes can have a variety of causes, this disease is one of the most difficult to diagnose. In this regard, the patient undergoes a thorough examination, appointed by the doctor an allergist-immunologist. Particular difficulty is a chronic urticaria, lasting more than 2 months.
Young children are the most vulnerable group in relation to this disease. Over the years, reactions of this kind have been significantly suppressed, but what is remarkable is that a thirteen-year age is a fatal moment for people prone to allergies. These age-old "surprises" are especially relevant for the female part of the population.
Causes
The emergence of urticaria is most affected by people who have other allergy symptoms (bronchial asthma, hay fever, food allergy, etc.)
The main causes of urticaria:
- heat, cold, pressure, sweat;
- some drugs, such as aspirin, codeine, ibuprofen or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- some food additives, such as dyes and preservatives.
In 20% of cases, allergic urticaria is associated with the immune system reaction to food and contact with plants and animals. In the remaining 80% of patients it is difficult to determine the causes of urticaria, blood tests and skin tests, as a rule, give negative results.
Classification of the disease
Allergy in the form of urticaria can manifest with varying degrees of severity and under different circumstances, on the basis of which the doctors have identified several of its types.
- Acute - characterized by a sudden onset, the appearance of itching and burning of the skin, and then the appearance of blisters and hyperemia. The name is due to the coincidence of symptoms with nettle burn. Blisters can be large and small in size. Elements can merge, acquiring a giant size. In such cases there is a violation of the general condition with the appearance of fever, chills.
- Chronic - manifestations worry the patient for a long time. However, they are not so pronounced, and sometimes patients do not notice them at once, which delays the moment of seeking help.
- Edema Quincke - proceeds in an acute form, it is also called giant urticaria. It makes itself felt suddenly. On the body appears limited puffiness, which seizes the sexual organs or face. In the area of swelling, the skin acquires a dense elasticity, becomes white or pink in color. Sore place is constantly itching, burning is felt. After a few hours or 24 hours, the puffiness passes by itself. If the case is severe, then a fatal outcome is possible.
- Recurrent - characterized by the appearance of blisters at different sites with different time intervals. Clinically, in addition to skin manifestations, weakness, malaise, headache, fever, myalgia, and arthralgia may occur.
Symptoms of an allergic urticaria
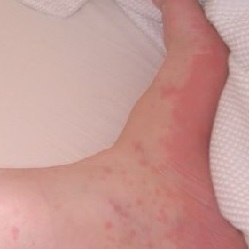 In the case of urticaria, the main symptom that distinguishes it from other types of allergic reactions is the onset of blisters on the skin (see Fig. a photo).
In the case of urticaria, the main symptom that distinguishes it from other types of allergic reactions is the onset of blisters on the skin (see Fig. a photo).
In appearance, the blister resembles the protruding part of the skin like a trace from an insect bite or a burn left by the nettle. The affected place is accompanied by itching. There may be redness. Most often the rash has a symmetrical character.
The number of blisters is also individual, it varies from a few spots to a hundred. In severe cases, there are so many spots that they merge and cover the entire skin. Very rarely there are symptoms such as vomiting and nausea. They indicate irritation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, which is very dangerous.
How to treat allergic urticaria
Success in the treatment of allergic urticaria by 90% depends on whether it will be possible to identify the cause - a specific allergen, and eliminate it. With the constant presence of an irritant factor in the blood, there will be a sufficient number of immunoglobulins, which are detoxifying. This means that the rash does not go away.
How to treat allergic urticaria at its first manifestations:
- Eliminate the allergen that caused an inadequate immune response of the body. In the case of medications, a lifelong ban on the appropriate group of drugs is introduced to the patient.
- Intravenous enter calcium gluconate to relieve swelling.
- Start taking drugs that block the production of histamines.
- In the case of chronic urticaria, autolymphocytotherapy is prescribed-a six-fold subcutaneous injection of the lymphocytes of the patient's own blood.
Compliance with all treatment options eliminates the symptoms of acute urticaria. On the skin there are no traces, edemas of mucous and itching disappear.
If urticaria causes a lot of factors or contact with a significant factor can not be ruled out, then it is necessary to take antihistamines (claritin, diazoline, telfast). For particularly severe forms of urticaria, short-term glucocorticoid drugs are used.
Locally to reduce the itching and rash apply ointments based on zinc oxide (zinc paste, cindol), in heavier cases, the doctor may prescribe ointments and creams containing corticosteroids, for example, advantan, elokom.
Diet is extremely important for recovery
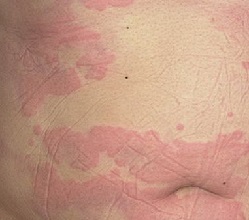 You can treat allergic urticaria by excluding certain foods from your diet, in other words, the patient needs a strict diet.
You can treat allergic urticaria by excluding certain foods from your diet, in other words, the patient needs a strict diet.
Which products should be removed is determined by an experimental method: it is necessary to exclude one or another product, while monitoring the reaction of the organism.
Below is a list of products that most often cause an allergic reaction:
- meat, offal, eggs, animal fat;
- fish, caviar of fish, shrimp, mussels, squid;
- tomatoes, celery, potatoes, radish, pumpkin, sea kale, mushrooms;
- sharp varieties of cheese, pickled cheese;
- nuts, berries, citrus fruits;
- exotic fruits, all fruits are red;
- canned food, crackers, chips, hamburgers, instant soups;
- chocolate, coffee with flavor additives (dry cream, amaretto, caramel);
- spicy foods and spices (onion, garlic, coriander, mint, mustard, pepper).
Hypoallergenic diet is always selected individually, and lasts from three weeks for adults and not more than one week for children.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



