Content
-
1Fracture of calcaneus: treatment and rehabilitation
- 1.1The causes and signs of fracture of the calcaneus
- 1.2First aid for suspected fracture of calcaneus
- 1.3Treatment of calcaneus fracture
- 1.4Fracture of calcaneus without bias or slight shift
- 1.5Fracture of calcaneus with significant displacement
- 1.6Fractures of the calcaneus with a significant number of fragments
- 1.7Rehabilitation after a fracture of the calcaneus
- 1.8Gentle load at a fracture of the calcaneus bone during the period of fixation with a plaster bandage
- 1.9Increase in load after removal of gypsum with fracture of calcaneus
-
2Fracture of calcaneus with and without bias: symptoms, treatment, how many heals
- 2.1Causes - fracture or bruise
- 2.2Classification of fracture
- 2.3Symptoms of trauma
- 2.4First aid for suspected fracture
- 2.5Signs of chronic heel fracture
- 2.6Diagnosis after injury
- 2.7Treatment is determined by the type of injury
- 2.8Conservative therapy
- 2.9Surgery
- 2.10Skeletal traction
- 2.11Surgical operations
- 2.12Rehabilitation
- 2.13When can I step on an injured leg?
- 2.14To which doctor to apply
-
3Classification, signs and methods of treatment of calcaneus fractures
- 3.1Symptoms and Diagnosis
- 3.2Classification of injuries
- 3.3Causes of traumatization
- 3.4Methods of treatment
- 3.5Gypsum bandage
- 3.6Operation
- 3.7Possible complications
- 3.8Rehabilitation process
-
4Fracture of the heel with and without displacement: symptoms, treatment, recovery
- 4.1Causes
- 4.2Main symptoms
- 4.3Varieties of fractures
- 4.4Diagnostics
- 4.5Heel fracture treatment
- 4.6Recovery after fracture
-
5Fracture of calcaneus
- 5.1Causes and mechanisms
- 5.2Fractures of the calcaneus body
- 5.3Supports of the adenopathy
- 5.4Heel of the heel
- 5.5Symptoms and clinical manifestations
- 5.6Heel of the heel
- 5.7First aid
- 5.8Treatment depending on the stage of the fracture
- 5.9Without bias
- 5.10Compression fractures
- 5.11Intra-articular fractures
- 5.12Fractures of calcaneal tubercle
- 5.13Rehabilitation period and recovery
Fracture of calcaneus: treatment and rehabilitation
Fracture of the calcaneus - the injury is quite unpleasant, because for a long time it can reduce the ability to work and the normal activity of the victim.
The length of the recovery period depends not only on the complexity of the fracture, but also on the correctness of the method of treatment, the effectiveness of rehabilitation measures.
The causes and signs of fracture of the calcaneus
In most cases, the fracture of the calcaneus is compression-like and occurs as a result of an unsuccessful jump or fall to the feet without depreciation.
The first signs of a fracture of the calcaneus are pain until the impossibility of stepping on the leg and the appearance of swelling or swelling.
Due to the tension of the tendon at the fracture site, movements of the ankle leg are limited.
Similar symptoms may indicate another type of injury, but accurate diagnosis is possible only on the basis of radiographic examination.
First aid for suspected fracture of calcaneus
If there is a suspicion that the victim may have a fracture of the calcaneus, first of all it is necessary to ensure the immobility of the injured limb and the speedy delivery of the patient to the medical institution. If this is possible, the suffering of the victim should be alleviated by giving him an analgesic medicine.
Treatment of calcaneus fracture
The determining factor in choosing the method of treatment of the fracture of the calcaneus is the degree of violation of the natural geometry of the location of the bones.
In a special way connecting certain conditional points of the foot bones, the so-called Beler angle is obtained, which is normally 20-40 degrees and decreases in the traumatized foot.
Quite easy is the treatment of fractures of the calcaneus with a slight displacement. In other cases, resort to special techniques to restore the geometry of the foot.
Fracture of calcaneus without bias or slight shift
If, at a displacement caused by a fracture, a decrease in the Beler angle does not exceed 5-7 degrees from the normal position, a fixation of the limb with gypsum is sufficient to treat the fracture. For a full fixation, the cast is applied from the toes to the knee joint or (if necessary) to the middle of the thigh.
Fracture of calcaneus with significant displacement
In more complex cases of calcaneal bone fractures, the angle of Beler can not only significantly decrease, but also be reduced to zero and even becomes negative.
For a full reposition (matching parts of a broken bone) resort to special measures.
Changing the position of the foot and using a special wooden wedge as a support of the sole, they achieve the matching of the fragments of the calcaneus bone, in which there will be no flattening of the foot (decreasing the angle of Beler).
This procedure is rather painful, therefore it is conducted under anesthesia. The success of the reposition is checked by a control radiograph, after which a plaster cast is applied to the foot.
Not always compression fractures allow such a repositioning.
The possibility of the procedure depends on the angle and type of bone cleavage and, in certain cases, is associated with the risk of repeated divergence of parts of the bone.
Compression fractures, the type of which does not allow repositioning, requires in-patient treatment by stretching.
Fractures of the calcaneus with a significant number of fragments
If a large amount of fragments is formed in the fracture of the calcaneus, an operation is required to combine them. Multiple fractures after combining or, if necessary, osteosynthesis, are treated permanently with the help of Elizarov's apparatus.
Rehabilitation after a fracture of the calcaneus
Rehabilitation after a fracture of the calcaneus is not easy for several reasons.
First, it is this type of fracture that is characterized by a high degree of probability of discrepancy of parts of the bone for violations in treatment.
Secondly, the heel is the supporting part of the body, and it is quite difficult to reduce the load on it.
The time of finding a leg in a plaster bandage with different types of fractures differs markedly and is not less than 12 weeks.
The control of the fusion of the fragments is carried out using an X-ray.
In order to avoid atrophic processes and at the same time minimize the risk of divergence of parts of the bone, the injured leg is gradually loaded.
Gentle load at a fracture of the calcaneus bone during the period of fixation with a plaster bandage
For the first time the physical load is permissible not earlier than 5-6 weeks after repositioning. At this time, the leg is still fixed with gypsum, and to ensure a gentle loading regime it is recommended to use crutches or special wire-frame devices.
Increase in load after removal of gypsum with fracture of calcaneus
After the gypsum is removed you can not immediately return to the usual rhythm of life.
If the work of the victim is associated with standing on his feet or walking on foot with constant movements, then fully able to work can be considered restored no earlier than 5-6 months. For "sedentary" occupations this period may be somewhat less.
The first time after the removal of gypsum, walk with crutches, transferring weight to them and avoiding resting completely on the damaged foot.
Restoration of muscle tissue after a long period of movement restriction is facilitated by physiotherapy, massage and self-massage of the limb.
With caution, after consulting with a surgeon, you can perform simple exercises - pull the sock, make a circular motion of the foot.
A source: http://bolivspine.com/bolezni/bolezni-kostej/perelom-pyatochnoj-kosti-lechenie-i-reabilitatsiya.html
Fracture of calcaneus with and without bias: symptoms, treatment, how many heals
Fracture of calcaneus refers to rare injuries and is observed in 3% of all fractures. This is due to the fact that this bone is very durable and even in the elderly it is necessary to have a very serious traumatic effect to break it.
In this article we will acquaint you with the causes, classification, signs, methods of diagnosis, first aid and treatment of calcaneus fractures.
Such an injury refers to severe injuries, since
heel bone is subject to considerable load - it is basic, carries the main load during walking and performs a damping function in the process of movement.
To select the method for its recovery, an individual approach and a long rehabilitation are necessary, ensuring the complete restoration of its anatomical structure and functions.
As a rule, with fractures of the calcaneus, the fragments move, and the trauma becomes severe. In more rare cases, the damage is not accompanied by a shift, is light and fuses quickly.
Such fractures are often combined with other injuries: a fracture of the talus, ankle or spine.
The presence of combined injuries always significantly complicates and prolongs treatment and recovery period.
Causes - fracture or bruise
The following factors can lead to a fracture of the calcaneus:
- unsuccessful landing or falling to the feet from a height;
- heel compression in case of a traffic accident or work-related injuries;
- a strong blow with a blunt object;
- intensive and prolonged workload, leading to "fatigue" bone defects (for example, athletes, cadets, newly recruited soldiers).
The most common cause of such a trauma is a fall from a height.
When landing, the entire gravity of the body is projected through the bones of the shank and ankle to the talus bone, and it wedges into the heel bone, splitting it into several parts.
The type of fracture and the nature of displacement of fragments in such cases is determined by various factors: the height of the fall, the mass of the body and the position of the feet when they come into contact with the surface.
Classification of fracture
Like all fractures, the fracture of the calcaneus can be open or closed. The formation of wounds and the outflow of fragments with such injuries is less frequent.
Fractures of the calcaneus can be with or without bias. Displacement of fragments always complicates the course of the trauma, its treatment and the subsequent restoration of leg functions.
By the nature of bone damage, fractures are divided into:
- compression without bias;
- compression with displacement;
- edge with or without offset.
On the localization of a bone fracture, fractures are divided into:
- fractures of the calcaneus calcaneus;
- fractures of the calcaneus.
In the place of fractures, fractures can be:
- intra-articular (in 20% of cases);
- extraarticular.
Symptoms of trauma
During the injury, the patient has intense pain in the heel area. It is of a permanent nature and is greatly strengthened with any attempt to move in the ankle or transfer of body weight to the injured leg.
After that, the following symptoms appear:
- increased pain when feeling;
- edema in the foot area to the Achilles tendon;
- expansion of the heel;
- formation of a hematoma on the sole;
- flattening of the arch of the foot.
In the presence of concomitant injuries of the spine or ankle, a slightly different clinical picture develops, which prevents the detection of a calcaneus fracture.
This is because the signs of other fractures are more pronounced.
With late detection of a violation of the integrity of the calcaneus or improper treatment, the following complications may develop:
First aid for suspected fracture
If a fracture of the calcaneus is suspected, the following measures should be taken:
- Ensure complete immobility of the affected limb.
- If there is a wound, treat it with an antiseptic solution and apply a bandage from a sterile bandage.
- Apply cold to the area of the injury.
- Give the patient an analgesic drug (Analgin, Ketorol, Ibufen or others).
- Ensure rapid transportation of the patient to a medical institution.
Signs of chronic heel fracture
Older fractures of the calcaneus require more complicated surgical treatment and often become the cause of disability. With such neglected injuries, the following clinical picture is observed:
- flat or flat-valgus deformation of the foot is detected;
- heel bone eventually increases in transverse dimension;
- there are no movements of the thumb (not always);
- the rigidity of all toes is determined (not always);
- trophic ulcers on the thumb (sometimes).
When studying X-ray images, the following signs (one or several) are revealed:
- anatomically abnormal bone fusion;
- the presence of pseudoarthrosis (false joint);
- an increase in the transverse dimension of the bone;
- decrease in bone length;
- incorrect arrangement of articular surfaces in the talus joint;
- subluxation of the talus joint;
- signs of arthrosis in the joint of Chopar;
- pronounced flattening of the arch of the foot.
Diagnosis after injury
X-ray examination confirms the presence of a fracture or, on the contrary, excludes it.
Radiography is always performed to detect a fracture of the calcaneus. This method of research is the "gold" standard in the diagnosis of such injuries.
For its carrying out, pictures are taken in the lateral and direct projection, and other bones are also being studied: the talus, medial and lateral ankles.
In the detection of certain symptoms and complaints of the patient, indicating the possible presence of additional injuries, X-rays or CT of the spine are assigned.
Treatment is determined by the type of injury
The tactic of treating the fracture of the calcaneus is determined by the type of injury and the degree of disruption of the natural location of the bones.
To do this, the doctor in a special way connects certain points of the bones on the X-ray and obtains the angle of Beler.
Normally, it is 20-40 °, and with a trauma it decreases or becomes negative.
Conservative treatment of calcaneus fractures is prescribed in the absence of displacement or insignificant displacement of fragments along the physiological axis.
In other cases, the surgical procedure is performed to eliminate bone defects.
Particularly difficult to treat fractures with a large number of fragments.
Conservative therapy
With a decrease in the angle of Beler from the norm by no more than 5-7 °, trauma treatment can be performed by applying a circular cast bandage.
When performing it, a small modeling of the longitudinal arch of the foot is carried out. The dressing is applied from the fingers to the level of the knee or mid-thigh.
If necessary, a closed reposition of the fragments can be performed prior to its application.
When applying the gypsum bandage, flexible metal supports can be used. They are installed between the gypsum and the sole. Their use allows to increase the effectiveness of therapy and ensures the correct formation of bone callus.
The duration of immobilization of the injured leg is about 6-8 weeks. During this time the patient should use crutches. After 4 months, the doctor may recommend dosage for a damaged limb.
To eliminate pain and accelerate the growth of bone fragments, the following drugs are prescribed:
- analgesics: Analgin, Ketanov, etc .;
- preparations of calcium;
- multivitamin complexes.
Before the removal of gypsum, it is necessary to perform a control radiography. After removal of the immobilizing bandage, the patient is provided with an individual rehabilitation program.
Surgery
With more complex fractures, the fragments of the calcaneus bone are displaced and the angle of Beler not only decreases significantly, but can also become negative. In such cases, special techniques are used to correctly reposition the fragments.
Skeletal traction
In some cases, skeletal traction is used to eliminate displacement. Surgical way through the heel bone carried a metal needle. Subsequently, to its protruding end, weights are attached to ensure the juxtaposition of fragments.
After 4-5 weeks, the needle is removed and a plaster bandage is applied to the limb for the correct intergrowth of the fragments. The duration of immobilization is usually about 12 weeks, but the timing may vary depending on the severity of the injury.
After that, control shots are taken, which make it possible to determine the possibility of removing gypsum and starting loads on the leg. After the fusion of fragments, the patient is assigned a rehabilitation program.
Surgical operations
With open and severe fractures with a significant number of fragments and a pronounced displacement of them, surgery is performed - external osteosynthesis. For its implementation, compression-distraction apparatuses are used, which are devices from spheres and spokes.
During the intervention, the surgeon opens up soft tissues and opens three joints: the Tar-heel, the talon-navicular and the heel-cuboid.
Next, he compares the bone fragments and passes through them the spokes, which allow you to hold the bone in the correct position for proper fusion.
If necessary, some places are filled with a bone graft, previously taken from the iliac bone. The need for plastic can arise when it is impossible to compare small fragments.
After this, the displacement of the displaced tendons of the fingers is performed. To fix the spokes used hemispheres. Thanks to them, it is possible to pull the fragments into a physiological position, which ensures proper fusion.
Sometimes, in order to compare fragments of the calcaneus, open reposition operations are performed using metal plates, screws or autografts. Such interventions are less effective, less frequent, and often accompanied by complications.
Metal structures for osteosynthesis of the patient are about 6 weeks. During this period, a strict bed rest is prescribed.
After this, limb immobilization with gypsum is carried out for 2 months.
After performing the control radiography and removing the gypsum, an individual rehabilitation program is appointed.
In the case of chronic fractures of the calcaneus, surgery for a three-joint resection of the foot is indicated.
During this intervention, the surgeon eliminates valgus deformity, forms a complete arch of the foot and restores the normal width of the heel.
The bones that are exposed during the resection operation are held together by special screws.
After this, the wound is sutured and a circular cast plaster is applied to immobilize the limb, as well as during immobilization with "fresh" fractures. The duration of wearing gypsum is determined by control shots. After this, the patient is recommended an individual program for recovery.
Rehabilitation
During treatment and rehabilitation all patients with fractures of the calcaneus are advised to follow a diet with the introduction of a large number of calcium-rich foods: dairy products, herbs, vegetables, berries and fruit.
With fractures without bias or slight displacement, which are treated conservatively, the duration of complete recovery is usually about 3 months. After removal of gypsum, the patient is assigned a rehabilitation program, which includes a set of exercises for therapeutic gymnastics, massage and physiotherapy.
Fractures with displacement or a large number of fragments require a longer recovery period. The cast is worn for about 3 months, and for severe injuries, the period of immobilization can be extended to 5 months.
If it is necessary to prolong limb immobilization, gypsum can be replaced by orthosis. This device is easier and allows reducing the recovery period,
its wearing prevents stagnation of blood in the veins, muscle atrophy and expands motor activity.
During rehabilitation after complex fractures, the patient is given massage courses, therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy (UHF, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, etc.), which improve blood circulation and metabolic processes in injured tissues and accelerate muscle recovery after prolonged bed rest mode.
When can I step on an injured leg?
Remember! You can not step on the heel unless the doctor has allowed it. In the performance of such actions, the proper fusion of the bone may not occur. Especially dangerous are premature loads on the heel with multi-fracture fractures.
With light fractures without bias, the physician can resolve the attack on the forefoot after 4 weeks. In this case, you must follow all the recommendations of the doctor. The ability to step on the heel is determined individually.
For complex fractures, the load on the forefoot is allowed in at least 3-5 months. And the timing, when the patient can fully step on the heel, is also determined by the doctor.
Fractures of the calcaneus are severe and rare injuries and are often accompanied by dislocations of fragments.
For their elimination, conservative and surgical techniques can be used.
After completion of the treatment, an individual rehabilitation program is assigned to fully restore the lost functions of the injured leg.
To which doctor to apply
If you suspect a fracture of the calcaneus, you should consult an orthopedic doctor. After carrying out a radiography the doctor will determine the tactics of treatment. Upon completion, the patient needs a consultation with a rehabilitator to prepare a rehabilitation program.
A source: https://myfamilydoctor.ru/perelom-pyatochnoj-kosti-so-smeshheniem-i-bez-nego-simptomy-lechenie-skolko-zazhivaet/
Classification, signs and methods of treatment of calcaneus fractures
Such an injury, as a fracture of the calcaneus, is very rare. Almost always a fracture is a consequence of falling on straight legs or sharp squeezing.
The heel bone most often affects people who work at height (industrial climbers or installers) or are fond of extreme sports (auto and motorcycle racing, parkour). Those at risk are those who suffer from osteoporosis.
In view of all this, a natural question arises: how to recognize heel fractures and how to properly treat them.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The human foot consists of 26 bones. Heel is considered the most durable and large of them. It has a spongy structure and a large number of nerves and vessels.
This structure makes the fracture very painful.Another feature: almost always, along with a fracture of the calcaneus, damage is rammed and cuboidal.
Fracture of the calcaneus body has several characteristic features:
- Strong pain makes it impossible to stand on the foot. If there is a displacement of bone fragments, it is difficult for a person to walk independently. Appears lameness.
- If the fracture is open, bleeding begins. A symptom of a closed fracture is a hematoma (a bruise, a hemorrhage under the skin).
- Heel strongly swells.
- Limited mobility of the ankle joint.
You can diagnose the fracture in several ways:
- If a fracture is suspected, the doctor first collects the available information. You need to know how the injury was received, from what height the patient fell, whether there were injuries in the past, what medicines the person takes.
- Next is a visual inspection.
- Prove or disprove the diagnosis can be using an X-ray done in three projections. The doctor pays attention to the angle of Belera (part of the calcaneus). If there is no fracture, the angle is 20-40 °. In the opposite case, it decreases or even takes negative values. These data help to assess the condition of the heel and decide on further treatment.
- Another method of diagnosis is computed tomography. The procedure allows you to see the heel bones from all sides and from different angles.
Depending on the data received, the doctor will prescribe the treatment.
Classification of injuries
Fractures of the heel bones are of several types:
- fracture of the lateral process - this element is located on the hillock of the calcaneus;
- fracture, otherwise known as "duck beak
- violation of the integrity of the medial process, which is located on the hillock;
- fracture of the hillock in the place where the tendon is attached.
- fracture with displacement of bone fragments is the most common form when fragments move to one side or diverge in different directions;
- open - bone fragments can damage soft tissues and even come out, such a trauma requires a longer recovery than the rest;
- comminuted - occurs less frequently than other species, when the bone is broken into several (three or more) fragments.
There is still a closed fracture. Soft tissue with such a trauma is not damaged.
Causes of traumatization
Fracture of the calcaneus can be caused by excessive stress, fall, etc. Doctors identify several factors that trigger the appearance of this injury:
- jump from a height to straight legs;
- accidental hit of a foot in a hole on the road during a fast walk or run;
- occupation of sports, in which the heel is an excessive load - football, basketball, skiing, etc.;
- often in medicine they speak of a "fatigue" fracture - this is a consequence of a regular heavy load on the calcaneus, which has been for a long time. Often such a trauma happens in the military.
Methods of treatment
Treatment of fractures of the calcaneus begins with the first aid to the patient:
- It is necessary to lay the victim on his back on a flat surface. In this case, the legs must be bent. To achieve this, a roller, placed under the knees, will help. The roller can be made from a blanket.
- Remove from the damaged foot shoes. Do this as accurately as possible, without causing additional pain to the person.
- If possible, attach a cold compress to the heel.
- If a person does not feel sick, you can give him some pain medication.
- Call the ambulance and talk about what happened, without missing details.
- If possible, take the victim to the emergency room.
The most important thing is to achieve complete immobility of the limb. Treatment will depend on the results of the medical examination and examinations.
Gypsum bandage
If the injury has no complications, a bandage of gypsum is placed on the leg, fixing the bones securely for at least two months - this is the time that is necessary for complete adhesion. It is strictly forbidden to step on foot. If there is no bias, the bandage is superimposed from the foot and up to the knee.
Such heel fractures are considered to be the easiest, since recovery after it takes much less time than in other cases.
Operation
Surgical intervention is possible only after the swelling is completely gone. Recovery after surgery is quite fast.
Operations in the fracture of the calcaneus are of two types:
- connection of bones with the help of open access to them;
- fixation through the skin - the surgeon makes a small incision through which the bones are fixed with special screws.
Usually the leg is fixed for about two to three months. After the plaster bandage or screws are removed and prescribed procedures for rehabilitation.
Possible complications
Make a prediction about how the fracture will grow together and how quickly the bone will recover is difficult, partly because complications sometimes develop:
- The connecting staples irritate the tendons;
- there is irritation of the seam area;
- the wound does not heal;
- pain becomes chronic;
- there are changes in the structure of the joints;
- infections are attached;
- develop thrombosis or arthritis.
If complications occur, immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will adjust the treatment or appoint additional procedures.
Rehabilitation process
Heel bones have the ability to recover even after severe injuries, but it takes a long time. The length of the rehabilitation period largely depends on the complexity of the heel fracture.
In the case of the calcaneus, you must be patient. It happens that one can not step on foot for several months in a row.
Rehabilitation procedures are conducted as they recover:
- After the expiration of two to three days after the injury, you can begin to load the leg, for example, gently moving the ankle joint. If an operation was performed, it can be done only after the wound has healed.
- On the second day, doctors are allowed to neatly knead the heel.
- On the fourth day, you can perform a set of simple exercises sitting on a chair. All exercises are prescribed by a doctor.
- After removing the plaster bandage for kneading the foot, you can use the ball.
- Specialists recommend wearing special shoes. The expediency of its use is determined by the attending physician. The main thing in this case is not to load the damaged leg. Strong loads can destroy the fixing structure and damage the heel bone again.
- After two weeks, you can start walking, using a cane as a support. If there was a bias, walking should be very cautious.
To accelerate the rehabilitation will help massage and baths.
If there was a bias or complications developed, it is possible to fully recover only after 1 to 2 years. During this time it is recommended to protect yourself from difficult physical work and intensive sports activities.
An integral part of the recovery process is a properly chosen diet. The menu should follow several rules:
- In the diet should be foods high in vitamins C, D, E, which perfectly strengthen the immune system and promote the rapid absorption of calcium.
- In the diet should be added milk and sour-milk products, for example, cottage cheese, kefir, etc. They contain a lot of calcium.
- In cooked dishes there should be a lot of proteins.
- It is recommended to limit or completely exclude the use of sweet carbonated and alcoholic beverages, products that contain refined sugar. This substance slows the process of assimilation of calcium.
A balanced diet will help to speed up the healing process and strengthen the bones.
Conclusion
Fractures of the heel bones - serious enough injuries, which are characterized by severe pain and limited mobility.
The process of recovery usually takes a long time. However, it can be speeded up a little, adhering to all the prescriptions of the doctor, watching for food and performing a set of rehabilitation measures.
A source: https://vseonogah.ru/travma/perelom/pyatochnoj-kosti.html
Fracture of the heel with and without displacement: symptoms, treatment, recovery
Human legs are more likely than other parts of the body to be affected by various injuries. Fracture of the heel, although rare, is very difficult in terms of treatment and recovery.
This damage is characterized by a loss of integrity of the calcaneus. Usually, rehabilitation after such injuries takes place in a stationary environment. Until complete healing, it may take several months.
Causes
Fractures of the calcaneus occur as a result of a strong impact on it. Although the person's foot is well secured by ligaments and muscles, external traumatic factors lead to injuries. Most often, the heel bone leads to a fracture of the bone:
- jump or fall from a sufficiently high altitude - during the landing, on the feet, in general, and heels, in particular, have a huge load. The bones can not bear it, and as a result, a fracture occurs;
- severe mechanical shock - can trigger a heel fracture with or without bias;
- injuries from road accidents, air crashes and other natural and man-made disasters;
- excessive physical exertion on the feet, for example, in professional athletes, ballet dancers;
- accompanying sprains or ligament ruptures, which, in the absence of timely hospitalization, can be aggravated by a fracture.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of a heel fracture are very recognizable. It is simply impossible not to notice such a trauma. Recognize it easily by such key features:
- acute pain - occurs immediately after the fracture of the heel and increases with palpation. Sometimes, from strong pain, a person may even lose consciousness;
- impossibility of independent movement. When you try to step on your leg, the pain is greatly increased;
- formation of a hematoma in the affected area. Internal bruising results from a closed fracture of the calcaneus, when bone fragments injure a soft tissue;
- swelling in the foot, ankle joint;
- bleeding - appears with open fractures, when splintered parts of the bone damage the integrity of the skin;
- deformation of the heel of its increase or flattening.
Varieties of fractures
First of all, the fractures of the heels are divided according to the damage to the integrity of the soft tissues. When closed, there is only an external swelling, the presence of a hematoma.
This can make diagnosis difficult. Moreover, according to statistics, victims with closed fractures much later turn to for help.
This greatly aggravates the symptoms and treatment, in this case, it is more difficult to conduct.
All closed fractures are subdivided according to the plane of damage into such types:
- marginal fracture of calcaneus with displacement;
- isolated fracture of calcaneus without bias;
- compression fracture of the calcaneus with angle change;
- compression heel fracture without bias.
For an open fracture is characterized by the presence of lacerations, bleeding. A bone shift, its numerous fragmented fragments, can be visualized.
This kind of fracture is dangerous for further infection of the body, great blood loss.
In this case it is necessary to apply for qualified help to specialists as soon as possible.
Diagnostics
Before beginning treatment of a heel fracture, it is important to diagnose it correctly. It is from this stage that the process of recovery and healing of damage largely depends.
First of all, the doctor examines the problem site and determines the type of fracture. Then conducts palpation of the site. This is necessary to find the possible displacement of the bone.
The most important method in diagnosing any fractures is radiography. It is carried out in 4 projections:
- Lateral.
- Anteroposterior.
- Projection by Harris.
- Projection of Broden.
Each of them is important and necessary for accurate visualization of the fracture, determining the angle to which the bone has shifted.
In addition to X-rays, CT may be needed. It is usually used to plan a surgical operation. This method helps to assess the type of fracture, to locate the location of fragments of bone, accompanying cracks.
Heel fracture treatment
Depending on the type of fracture of the calcaneus, the treatment may differ. Currently, two main methods are used in medical practice: conservative and operational. The first of these is used in the absence of bone displacement, soft tissue damage.
Conservative method primarily involves the need for immobilization of a damaged limb. On it impose a gypsum longite of the big size (from tips of fingers and to a knee). This is necessary to fix the healing calcane bone well.
The term of wearing longiets can vary from 3 to 8 weeks, depending on the degree of damage and individual characteristics of the body. Young people are much faster to remove gypsum than the elderly.
This is due to the fact that the healing speed of bone tissue is somewhat higher.
During the wearing of gypsum, the victim can move independently with the help of crutches.
But do not forget that at the same time a healthy left or right foot is placed a heavy load.
To avoid complications and additional problems, the first few weeks must be followed by bed rest.
Operative treatment implies a surgical intervention. It is necessary with open fractures. Doctors in the course of the operation try to restore the structural integrity of soft tissues, to avoid infection of the body through open wounds.
Sometimes they can use special metal structures, for example, Ilizarov's apparatus, to hold the bone during the fusion in the correct position.
Such work requires a great skill from the doctor, so not everyone is able to perform the operation flawlessly.
Recovery after fracture
After the fracture, everyone cares about how much bone heals and how soon it will be possible to move independently.
To speed up these processes, doctors recommend not neglecting rehabilitation and follow all the prescriptions.
The recovery period occurs immediately after the removal of gypsum longi and it is directed to the development of lost functions of muscles, ligaments.
Among traditional rehabilitation methods it should be noted:
- LFK - is a complex of simple exercises that are designed to restore the former mobility of the joint in the joint bag. Therapeutic gymnastics should be practiced daily, at least for 15-20 minutes;
- massage - improves blood circulation, leads the muscles into tonus. It is carried out in courses of 10 sessions with a break of 2-3 weeks. Self-massage can be used even right after the injury. In this period, the muscles of the thighs should be developed to reduce the edema of the lower limbs;
- Physiotherapy - very effectively helps to restore the leg lost mobility. Usually, such methods as electro, phonophoresis, heating and laser exposure are prescribed;
- Baths - have relaxing, soothing properties. They are used to relieve tension, to alleviate pain. Doctors recommend using medicinal herbs (chamomile, lavender), salt, soda, essential oils to prepare the trays;
- Restoring diet - includes foods high in calcium and animal protein, such as meat, fish, nuts, sesame, cottage cheese, hard cheese;
- comfortable orthopedic footwear - facilitates walking, forms the correct setting of the foot. Moreover, it promotes a uniform distribution of the load along the entire leg.
Fracture of the calcaneus is a severe trauma, which is difficult to treat. If it is found, call an emergency care service or call a trauma doctor. If you quickly start treatment, there is more chance of a speedy recovery.
A source: https://NogoStop.ru/stopa/pyatka/perelom-pyatki.html
Fracture of calcaneus
About 3% of fractures of all bones form. Depending on whether the fall occurred on one limb, or both, fractures of one calcaneus or both occur.
- Anatomy
- Causes and mechanisms
- Symptoms
- First aid
- Treatment
- Rehabilitation
The calcaneus is the largest bone among the bones of the foot. It is located under the talus bone, and protrudes from under it.
The upper side of the calcaneus has three articular surfaces - anterior, middle and posterior (they correspond to the articular surfaces of the talus bone).
The anterior part of the bone has an articular surface for articulation with a cuboid bone. The calcaneus belongs to the sesamoid bones (located in the thickness of the tendons), it has a spongy structure.
Causes and mechanisms
Depending on the direction of the action of the traumatic force and the architectonics of the calcaneus, fractures of the calcaneus, heel, and support of the supraclavicular bone appear.
Fractures of the calcaneus body
Fractures of the calcaneus body are compression, vertical, horizontal, extraarticular and intraarticular with violation of congruence of the posterior-upper or antero-top or both of the joint surfaces.
Compression and multi-lobe fractures of the calcaneus body with significant displacements cause not only a complete flattening of the arch of the foot, but also deformation by the type of the rocking foot, i.e.
the anterior and posterior parts of the calcaneus are displaced cranially, and the middle part of it becomes convex toward the plantar surface.
Supports of the adenopathy
There are both independent trauma, and in combination with compression fractures of the calcaneus body.
Heel of the heel
Among the fractures of the calcaneal hillock there are two types:
- fracture as duck beak;
- vertical fracture of calcaneal hill with displacement proximally (upward).
In the first case, the fracture plane runs horizontally to the calcaneus axis at the border of the lower level of the horizontal bone trabeculae and The gastrocnemius muscle, due to reflex contraction, displaces the upper fragment proximally - on the roentgenogram the deformation resembles the shape duck beak.
The second type of fracture occurs when the traumatic force acts relatively vertically, under sharp angle to the posterior part of the calcaneus or causes a sudden reflex reduction of the calf muscle.
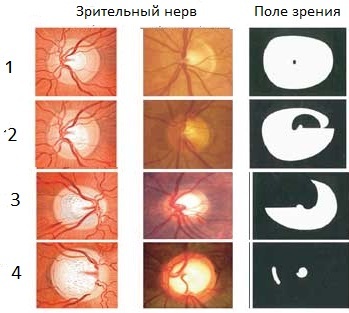
Symptoms and clinical manifestations
Clinical manifestations in fractures of the calcaneus: sharp pain, loss of foot function, significant swelling around the heel conceals and defers its contour.
In fractures without displacement or with a slight displacement of the foot is in the position of plantar flexion. When the fragments are displaced, the heel deformation occurs, the vault is flattened before the deformation occurs as a rocking-foot.
The height of the heel on the side of the injury is less and it seems that the bones in the swelling are lower than on the opposite leg.
The edema overlaps the calcaneal tendon, and it does not contour under the skin. Significant hemorrhage from both sides of the heel.
Palpation of the heel causes a sharp pain not only from the side surfaces, but also the plantar surface. Passive movements and an attempt to pull the foot out from plantar flexion exacerbate the pain.
In fractures without displacement, heel defect is expressed. Hemorrhage on the side surfaces, the victim can not load the foot, the passive movements of the foot exacerbate the pain in the heel area.
With palpation, the pain exacerbates from the lateral and plantar surfaces of the heel, in contrast to the bruises, when the defi- furation is asymmetric, swelling, hemorrhage one-sided - at the scene of the trauma agent, the pain is localized in the place of the bruise, the static function of the foot does not suffer, although the load is felt moderate pain.
The contours of the calcaneal tendon are clear, the height of the calcaneal region on both sides is the same.
X-ray examination confirms the clinical diagnosis.
Heel of the heel
There is a sharp pain in the back of the heel, a stop in the position of plantar flexion due to the contraction of the gastrocnemius muscle, deformation of the back of the heel due to the expansion of the sagittal size.
Attaching the calcaneal tendon is not contoured. When palpation pain worsens in the area of the calcaneal tubercle projection. Active movements in the ankle and impulse strains of the calf muscles are impossible.
When palpation, a diastasis is detected between the heel of the heel and the calcaneus.
X-ray examination specifies the nature of the fracture.
First aid
The patient should be laid on his back, his legs slightly bent at the knees, put a roller under his knees, rolled up from any garment or towel.
Shoes should be removed as soon as possible, because after a few minutes the swelling and pain will only increase.
Apply a cold compress to the injury site, give the patient an anesthetic (for example, an analgin tablet).
If there are suitable improvised means, it is necessary to straighten the leg and fix the ankle and knee joint (for this use boards, sticks, bandages, scarves, etc.).
Treatment depending on the stage of the fracture
Without bias
Fractures of the calcaneus bone without displacement or with insignificant displacements are treated conservatively.
Immobilization is carried out with a plaster bandage in the position of a slight (5-7 °) plantar flexion of the foot.
Immobilization lasts no less than 6-8 weeks.
When applying gypsum boots, the longitudinal and transverse arch must be carefully modeled.
Some authors (MP Novachenko, KM Klimov, FR Bogdanov) advise to gypsum boots to prygipsovat metal stirrups so that the victim could walk without stepping on the foot.
Professor V.A. Yaralov-Yaralyants proposed a special aluminum arch support, which is placed under the arches, when a plaster boot is applied, allowing the injured to load after the gypsum has dried limb.
Workability is restored in 3-5 months. The long fusion of the calcaneus fracture is due to the fact that it does not have a periosteum and the fusion occurs due to the endostasis.
Compression fractures
In compression fractures of the calcaneus body with flattening of the arch, after anesthesia, with% solution of novocaine or 1% solution lidocaine, under the arches of the foot, a pouch with sand is poured and through it, without jerks, the front and back sections of the foot are pulled down, restoring vaults.
In the position of a small plantar flexion (to relax the back of the muscle group) a gypsum boot is applied. If it is impossible to restore the vault closed, apply a skeletal traction.
With vertical fractures of the posterior part of the calcaneus with displacement, treatment with skeletal traction is indicated.
Intra-articular fractures
When intra-articular fractures with a violation of congruence of the anterior and posterior articular planes and support The epithelium is shown operative treatment with the use of bone plastic and restoration of the arch of the foot.
Fractures of calcaneal tubercle
Fractures of the calcaneal tubercle as a duck beak in victims with a well developed muscular system are treated by open comparison with fixation of fragments with screws.
With minor displacements, a closed one-stage comparison is shown.
After anesthesia with a 1% solution of lidocaine or novocaine, the foot is translated into plantar flexion and the surgeon the second hand, resting on the area of attachment of the calcaneal tendon, pushes the fragment down, eliminating it bias.
The reference point of the fragments is the restoration of the back contour of the heel. Then a cotton-gauze pelotus is placed over the tubercle of the calcaneus and a gypsum boot is placed in the position of plantar flexion of the foot. Immobilization lasts 6 weeks.
Rehabilitation period and recovery
The period of immobilization adversely affects the muscles and blood supply to the injured limb.
The patient spends most of his time in bed, resulting in muscle atrophy, bloody vessels narrow, blood flow is limited, because the damaged leg does not require the same amount blood.
To prevent atrophy and its consequences, it is necessary to increase the elasticity and tone of the muscles. The physician rehabilitator selects an individual complex of exercises, taking into account the features of the patient's fracture and vital activity.
To stimulate circulation, massage, physiotherapy, rubbing, and special salt and herbal baths are used.
It is not recommended to start rehabilitation measures in the first week after removal of immobilization (especially physical exertion), in connection with the risk of repeated displacement of bone fragments.
During the rehabilitation period it is especially important to observe the right diet. Food should be rich in calcium, silicon, minerals and, of course, proteins (milk, meat, fish, currants, nuts).
The disability returns about four months after the fracture.
The doctor selects the patient a special arch support, which reduces the load on the heel.
The patient uses it from four to eight months, the period depends on the severity of the transferred trauma. An improperly selected instep can damage your health, so do not try to do it yourself.
A source: http://webortoped.ru/perelomyi/kosti_nizhney_konechnosti/pyatochnoy_kosti.html