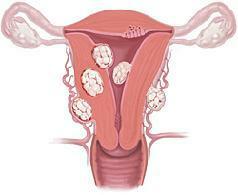
 Varicose veins of small pelvis in women are provoked by a phenomenon such as a reverse transfer of blood to the ovarian vein that occurs when the blood vessels are squeezed.
Varicose veins of small pelvis in women are provoked by a phenomenon such as a reverse transfer of blood to the ovarian vein that occurs when the blood vessels are squeezed.
The starting mechanism of the development of a disease is pregnancy, namely the hormonal changes observed during this period and the growing pressure of the uterus on the vessels of the small pelvis.
This kind of varicose manifests itself in the long and intense pains in the lower abdomen, usually appearing after constant heavy physical exertion or before the menses.
Causes
Why there is varicose veins of the small pelvis, and what is it? In most cases, this disease is diagnosed in women, and most often this ailment is found in patients aged 25 to 45 years.
Quite often, such patients try to cure varicose veins themselves - folk remedies that are used without appointment and specialist advice can lead to undesirable side effects, so you still have to contact a phlebologist.To the factors,provoking the development of this disease, include:
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Unbearable physical activity.
- Problems of a hormonal nature.
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
- Congenital abnormalities of the vascular walls are underdevelopment, aplasticity, weakness.
- Problems of a sexual nature - anorgasmia, pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse, having a psychological origin, often practiced interrupted sexual intercourse.
Varicose veins of the small pelvis are very similar to the condition of varicose veins on the legs. In both cases, valves in the veins suffer, which help the blood flow to the heart. The function of valves is disrupted to prevent reverse blood flow. When the valves collapse, blood stasis stays in the veins of the blood. The veins, which are filled with blood, stretch and intensify even more stagnant phenomena. Pelvic syndrome of venous overload develops mainly near the uterus, fallopian tubes, vulva and even the vagina.
Symptoms of varicose veins of the small pelvis
The presence of varicose veins in women can be indicative of a number of symptoms. The most important of them arecauseless pain in the lower abdomen, the pelvic area, often they are given to the lumbar region or to the perineum. Also, a woman can be bored by mucous discharge in abundant form from the genitals, especially in the second half of the menstrual cycle.
In addition to the main, there are also other, no less important symptoms of small pelvis varicosity in women:
- Dysmenorrhea. The appearance of pain during menstruation.
- In some cases, the function of procreation is impaired.
- Painful irradiation in the zones of the sacrum and waist, as well as in the groin area.
- Sensible course of so-called premenstrual syndromes.
- Appearance of a painful crisis (as a result of psychoemotional stress, physical overstrain, hypothermia).
- The phenomenon of dyspareunia (the appearance of an uncomfortable feeling in the vulva or in the vagina, both during intimacy and at its end).
- The occurrence of pain in the abdomen after prolonged loads (both static and dynamic).
Faced with these symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist. Since this disease can havea lot of unpleasant consequences:
- the activity of organs of the reproductive system is disrupted;
- varicosity can be a contraindication to natural childbirth;
- there is a feeling of anxiety and irritability;
- there is a fear of sexual relations.
It is also worth noting that the above symptoms can be expressed in different ways (weaker or stronger), some women have all the signs of the disease, and someone has 1-2 of them.
Diagnostics
To make the correct diagnosis, a woman undergoes a comprehensive examination.
When a patient complains of pain, arising for an unclear reason, the doctor first determines all the factors that caused the onset of pain syndrome. Carefully examine the patient's legs. So you can detect the appearance of varicose veins. In special cases, consult a vascular doctor.
Methods of diagnostics:
- Laparoscopy. Identify varicose veins in the ovaries.
- Ultrasound of the veins. The study allows you to see the expansion of the veins, their tortuosity.
- Doppler ultrasound. It reveals a decrease in systolic velocity in the veins of the uterus and ovaries.
- Selective ovarycography. The most accurate study. It is performed by the method of introducing contrast through the femoral and subclavian veins.
- CT scan. It allows to exclude pathologies, to reveal varicose veins in the uterus and ovaries, to show their crimp and widening on the screen.
The use of such methods makes it possible to more accurately determine the symptoms of the disease.
Degrees
To standardize the diagnosis and try a differential approach to treatment, AEVolkov was classified varicose veins of the pelvis depending on the diameter of the dilated vessels and venous ectasia.
There are 3 degrees of this disease:
- 1 degree- vein diameter up to 5 mm (any venous plexus of the pelvis), "corkscrew" course of the vessel;
- 2 degree- diameter of the vein 6-10 mm with total type of varicose, loose ectasia of the ovarian plexus (pl.pampiniformis ovarii), VR parametral veins (pl.uterovaginalis), VLV of the articulate plexus of the uterus;
- 3 degree- vein diameter> 10 mm with total BP type or main type of parametric localization.
Depending on the severity of the pathological process in the small pelvis, it is possible to use conservative methods of treatment and surgical interventions.
Treatment of varicose veins of the small pelvis
If a woman is diagnosed with varicose veins of the pelvis, the treatment is aimed at achieving the following goals:
- Termination of the reverse blood flow through the veins of the ovaries.
- Normalization of the tone of the veins, improvement of blood supply of tissues.
- Withdrawal of symptoms: pain, bleeding and so on.
Therapy of HLVMT includestwo main componentsa:
- Course use of medicines for exacerbation.
- Continuous use of curative physical education for the prevention of relapse.
In varicose veins of the pelvic floor 1 or 2 degrees, as a rule, conservative methods of treatment (venotonics, nonspecific anti-inflammatory drugs, therapeutic exercise) are used. Conservative treatment for pelvic venous congenital syndrome is symptomatic, including normalization of conditions labor and recreation with the exception of considerable physical exertion and a prolonged stay in an upright position.
It is worthwhile to understand that even the most qualitative treatment does not provide an opportunity to completely cure varicose veins of the pelvis. But, nevertheless, adequate therapy allows you to get rid of most of the clinical manifestations and significantly improve the patient's condition.
Conservative treatment
Because of the internal location of disease-afflicted veins, medicines are given orally, it is not possible to use venous gels and ointments. The following tools are used:
- Diosmin (detraleks, phlebodia)- to eliminate the increased elasticity of blood vessels, reduce their permeability, prevent brittleness;
- Horse Chestnut Extract (Escuzan)- for removal of puffiness and inflammation;
- Troxerutin (troxevasin)- to improve the outflow of blood from damaged vessels, increase the tone of the veins, reduce edema and inflammation;
- Vitamin C (ascorutin)- to strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
Specialists recommend combining medical therapy with physiotherapy exercises and wearing special compression lingerie. A special need for compression linen occurs during pregnancy.
Surgical intervention
The operation is an extreme measure, which is used in cases when the disease is very neglected and there is a predisposition to VR veins. Operative intervention is chosen depending on the location of the main violations, and provides for such procedures:
- ovarian vein ligation;
- ligation of the genital vein (often in combination with the miniphlebectomy of the perineum);
- operation of Troyanov-Trendelenburg (crossectomy) - in case of defeat, also veins of lower extremities.
In case of need for surgical intervention, the selection of appropriate actions is very individual, as everything depends on the localization of varicose veins.
Exercises
Therapeutic physical training for varicose veins of the pelvis consists of such exercises:
- From the standing position, with the feet standing in parallel, rise to the toes and sink. Repeat up to 30 times.
- From standing position, heels are combined, socks apart. Go up and down 30 times.
- Stand straight, dilute the heel apart, combining socks. Up to socks up to 30 times.
- Make a "bike" and "birch", watching for full leg straightening.
Exercises can be performed anywhere. If you want, you can replace, add or remove any exercises, most importantly, make sure that the body does not overexert. Physiotherapy exercises should be combined with the wearing of compression knitwear.
Folk remedies
The most popular and famous folk remedies:
- Infusion of the tea fungus (chaga).
- Tincture of horse chestnut fruit for oral administration.
- Treatment with leeches, which are put on the area of the sacrum and coccyx.
- Infusion from the root of a dandelion or herbal collection based on the root of a dandelion. It has a venotonic effect.
Considerable role in the treatment of varicose veins is played by the diet - the food should be balanced and contain a sufficient number of animal proteins and vegetable fiber.
Prevention
Also follow a few simple recommendations that will not only serve as a prophylaxis of BPHMT, but also improve the general state of the body:
- Wear special medical tights.
- Daily spend respiratory gymnastics.
- Take a contrast shower, focusing on the hips, perineum, lower abdomen.
- During a sedentary or standing work, take breaks, walk 5-10 minutes every 1-2 hours.
- Add to the diet more vegetables containing vegetable fiber, and vegetable oil. Avoid sharp, salty, and also foods that can cause constipation.
Effects
The most frequent complications of this disease are:
- diseases of the uterus and appendages of an inflammatory nature;
- diseases of the bladder;
- uterine bleeding.
In conditions of disturbed venous outflow, there is a risk of developing venous thrombosis in the pelvis. But the frequency of this type of complications does not exceed 3-5%.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



