 Alveolitis of the hole is an inflammatory process that can develop in a hole (alveolus) of the removed tooth (in connection with this it is sometimes also called postextraction alveolitis). In this case, both the tooth socket itself and the gingival tissue surrounding it are affected.
Alveolitis of the hole is an inflammatory process that can develop in a hole (alveolus) of the removed tooth (in connection with this it is sometimes also called postextraction alveolitis). In this case, both the tooth socket itself and the gingival tissue surrounding it are affected.
Alveolitis of the hole most often acts as a complication after incorrect removal of the tooth, accounting for 25 to 40% of all complications after tooth extraction.
If this procedure was normal, then the healing process of the alveoli proceeds almost asymptomatically, delivering a minimum of discomfort in the first 2-3 days.
What is the alveolitis?
Why does the alveolitis occur, and what is it? This disease is always associated with the removal of the tooth.
The hole formed on the site of the tooth torn out, penetrates the infection, resulting in inflammatory processes begin to occur. Most often, the alveolitis occurs due to a trauma to the wall of the socket or gum.
Causes of the alveolitis of the tooth
Infection of the dental hole after removal can be the result of the following main factors:
- In most cases, the alveolitisappears due to injury to the walls of the well. They are rather thin, so with careless handling, you can damage or completely break them. In addition, with the destruction of bone tissue debris can get into the wound, which will cause infection. The risk of the alveolitis is significantly increased when the wisdom tooth is removed.
- Another common cause of the alveolitis isinfection. Disease-causing bacteria that provoke inflammation can be brought into the open wound after tooth extraction from outside - by dental instruments. The risk of infection in the alveolus increases in people with oral problems (the presence of carious teeth, periodontitis, gingivitis, a large amount of plaque on the teeth). That's why dentists do not recommend to remove the teeth in the presence of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, sore throats, etc.
Also, alveolitis of the socket can develop with:
- decreased immunity;
- inadequate oral hygiene and dental plaque entering the well;
- if there is a part of the root of the tooth left in the hole (for example, the root is broken during the operation);
- non-observance of the doctor's recommendations - removal of a blood clot with particles of solid food, liquid with frequent rinsing, eating hot or spicy food immediately after tooth extraction;
- if there was a cyst in the apex of the root of the tooth, which remained in the hole after removal of the tooth;
- increased bleeding associated with a violation of blood coagulation ability or with severe postoperative bleeding after a traumatic operation.
Alveolitis usually occurs when the tooth is removed due to a neglected form of caries, pulpitis, flux. Also of great importance in its development is played by age. More often such a complication after tooth extraction occurs in the elderly.
At risk of developing the disease include people with a weakened protective function of the body, having a positive HIV status, pathology of the endocrine system and associated with blood clotting disorders.
Symptoms
As a rule, at the initial stage the alveolitis is almost invisible, but it gradually progresses, that is, it spreads in width and depth. The first symptoms of the alveolitis are observed 2-3 days after tooth extraction.
thereforethe main symptoms in the initial stage will be:
- aching pain that may subside with time, but intensify with eating;
- swelling, redness;
- soreness of the gums in the area of the socket;
- can develop edema, especially - after removal of a tooth of wisdom.
Negligible alveolitis can cause more serious symptoms, such as weakness, fever to 37.5 - 38 degrees, increased fatigue. Lymph nodes may become inflamed, denseness of the teeth, an unpleasant smell, a bitter taste may be felt, and pain may be irradiated in the ear or, for example, in the temporal region.
Alveolitis is quite a complicated disease, which is very painful for a person. The more it is launched, the more unpleasant the symptoms of the disease and the more difficult it is to cure. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the slightest suspicion of the alveolitis. The sooner medical care is provided, the sooner the recovery will come and the lower the likelihood of developing serious complications.
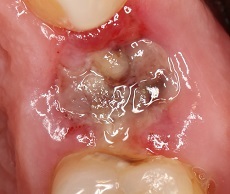
Alveolitis: photo
The photos taken by dentists demonstrate that the alveolitis looks like an empty hole in which there are leftovers of food and particles of dead tissue. While in the hole, healing without complications, you can see a dark red blood clot.
How to treat the alveolitis
Treatment of the alveolitis after the removal of the tooth must begin at a time when the disease has only manifested itself. Otherwise, the duration and price of therapy will be significantly higher. Determine that you have the alveolitis, and not some other disease, can only the dentist. He will give you the appropriate treatment.
Doing this yourself at home, using rinses or antiseptic drugs is unacceptable. You can remove some symptoms and at the same time drive the disease inwards, where it will continue to develop, involving more and more tissues in the process and posing a growing threat to your health.
However, until you have an appointment with the dentist,To reduce painful sensations it is possible by means of anaesthetising preparations:
- Ibuprofen (Nurofen);
- Sedalgin;
- Solpadein;
- Ketonal;
- Ketorolac (Ketanov, Ketorol);
- Xsefokam Rapid.
Before starting treatment, the patient is assigned radiography. A snapshot will indicate the presence of foreign elements or fragments of the tooth in the gum cavity. Furtheranesthesia is performed, and the following manipulations:
- Purification of the socket of the torn tooth and washing of purulent secretions with special solutions.
- Local applications with analgesics and antimicrobial agents.
- Rinsing the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures for the early healing of the wound (after removal of the inflammation).
If the treatment is started on time, then within a week the inflammatory process is stopped, the wound is covered with protective epithelium, which indicates a positive dynamics of treatment. After this, the patient must follow the treatment recommendations and regularly visit a specialist for examination.
Prevention
Preventive measures that help prevent the development of the alveolitis with successful removal of the tooth should be performed by the patient himself. That is, he must carefully follow the recommendations of the doctor.
In order for the healing processes of the hole to pass in normal mode, one should not pick the wound, arbitrarily scrape the gum, squeeze out a blood clot, suck it out and damage something. It is especially important not to chew food for a few days at the side of the jaw where the tooth was removed, so that the blood clot is safe.
The dentist, for his part, can prevent the development of complications, observing the rules of aseptic and antiseptic, and also performing the operation in accordance with the rules of the technique of removal. The formation of a blood clot by compressing the edges of the socket is also a prerequisite for the successful healing of the wound.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



