 The hernia of the esophagus, otherwise called the diaphragm, is the protrusion of its lower part through the aperture opening. Let's figure out what it is, and also consider the symptoms, diet and treatment of hernia of the esophagus.
The hernia of the esophagus, otherwise called the diaphragm, is the protrusion of its lower part through the aperture opening. Let's figure out what it is, and also consider the symptoms, diet and treatment of hernia of the esophagus.
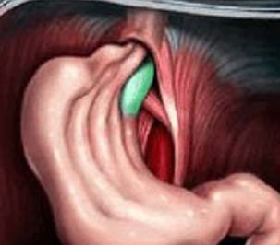
In the human body there is an important organ - the diaphragm, which consists of a muscular septum and divides the abdominal cavity from the chest cavity.
In the diaphragm there is an opening consisting of muscle fibers through which the esophagus passes. Such a hole is called the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. Sometimes, through it in the chest cavity can move and other organs located in the abdominal cavity.
Although the disease is not particularly dangerous, when diagnosing it, you should take care of your health. Therefore, further on, we will consider how to treat the hernia of the esophagus.
Causes
What it is? The cause of the hernia of the esophageal aperture of the diaphragm can be several. In some patients, a hernia is nothing but an innate phenomenon caused by a shortening of the esophagus, others show up the tendency to the appearance of a hernia in old age, the age-related changes in internal organs are evident.
Very often, the cause of this disease is an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, manifested systematically or dramatically. To cause an increase in pressure, in turn, can constipation, heavy physical labor, lifting of weights, abdominal injuries. There are also cases when the appearance of a hernia is caused by diseases of other internal organs - these are the problems of the motility of the stomach, duodenum, gallbladder, etc.
The hernia of the esophagus is much more common in people after 50 years, as there is a natural process of loss of elasticity of muscles and internal organs. By the age of 60, in many, the esophageal opening is so enlarged that it can pass 2-3 fingers - the "hernia gates" are formed.
Often the hernia of the esophagus goes "in the complex" with the ulcer of the stomach and duodenum (from 30 to 70% of all of cases), chronic gastroduodenitis (50%), pancreatitis and cholecystitis (15% and up to 50%, respectively).
The parasophageal hernia
This kind of hernia is extremely rare. There are no manifestations in the patient. Pathology is found by chance as a result of surveys on a different occasion. Exceptions are hernias that have reached a large size, which leads to the development of organic dysphagia, which is a constant, almost uncontrollable antispasmodic.
If such a hernia is infringed, the pain syndrome develops (in the epigastric region and behind the breastbone).
Symptoms of a hernia of the esophagus
In the case of a hernia of the esophagus, the symptoms can manifest themselves in different ways. When it has a small size, the patient can feel quite well, since the disease itself almost does not manifest itself.
Otherwise, the symptoms depend on the size of the hernia, its type, as well as the presence of complications and concomitant diseases:
- Heartburn. The most common symptom, from barely noticeable to painful, up to disability. Most often occurs after meals and at night.
- Painful sensationsOnly 50% of patients are concerned. The pain is most often localized in the retrosternal region (therefore it should be differentiated with an attack of angina), it has a burning, stitching and cutting character. Physical stress, accompanied by inclinations, is a provoking factor for the onset of pain. Painful sensations can intensify when the patient takes a horizontal position.
- Dysphagia- difficulty in passing food through the esophagus. It is observed when almost any type of food is passed, and is especially pronounced in hot, cold food or in large quantities.
- Belching- another very characteristic symptom of the disease. A peculiarity of belching in the hernia of the esophagus is that it is observed only in 35-70% of all patients and, as a rule, occurs either with the contents of the stomach or with air. This condition can occur absolutely suddenly during meals or during a conversation.
- Hiccups. It is observed rarely, but has a long (up to several weeks) character.
In the case of a sliding hernia, symptoms are observed only when the contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus. It can be heartburn, belching, nausea.
Diagnostics
Symptoms allow an experienced specialist to establish a diagnosis fairly accurately. Hernias of the esophagus are usually diagnosed on the basis of general symptoms and the results of some tests:
- X-ray examination based on barium contrast, in which the hernial protrusion is clearly visible in the image;
- Fibrogastroscopy, which helps to clarify the general condition of the stomach;
- pH-metry, which measures the acidity of the stomach, which is important in the appointment of treatment.
How to treat a hernia of the esophagus will depend on each specific case.
Diet
Nutrition with diaphragmatic hernia should be frequent small portions. Do not eat for 3 hours before bedtime. From the food should be excluded fried dishes, sweets, spicy seasonings, alcoholic, acidic juices, smoked products, strong tea, coffee - all these products increase the acidity of gastric juice and intensify the symptoms of a stomach hernia.
Diet in the hernia of the esophagus should limit the sour milk drinks, milk, cabbage, fresh bread, peas, grapes, carbonated drinks - these foods increase flatulence, which is also harmful to the patient. Before meals and after you can drink one tablespoon of unrefined oil.
But these are general recommendations, each organism is individual, therefore it is desirable for each patient to make a list of products for himself, after which he has heartburn, bloating, belching.
Treatment of hernia of esophagus
 First of all, conservative methods are used to treat hernias. If they do not give results, surgery is applied surgically.
First of all, conservative methods are used to treat hernias. If they do not give results, surgery is applied surgically.
The main requirement for treatment is to balance nutrition. As a rule, experts appoint a diet. The main task in the treatment is to eliminate the possibility of the transfer of the contents of the stomach into the esophagus and the occurrence of erosions and ulcers.
Conservative therapy begins with the administration of drugs that reduce the acidity of the stomach and the secretion of enzymes, as well as preparations to protect the esophageal mucosa. Some experts consider operation at a hernia of an esophagus as an extreme measure of treatment, however often it becomes a unique way of disposal of the patient from constant displays of a pathology.
Usually, surgical treatment is carried out if there are indications to it:
- severe esophagitis, not amenable to medication;
- Hernia of the esophagus of large size, especially if it is accompanied by difficulty in passing food and / or throwing food from
- stomach into the esophagus;
- a hiatal hernia with a high likelihood of infringement or has already caused the development of complications (anemia, narrowing of the esophagus and so on);
- anatomical insufficiency of the lower sphincter of the diaphragm;
- anterior hydrocephalic hernia;
- Barrett's esophagus.
Surgery can be performed in an open manner or with a laparoscope. There are several types of operations in hernia of the esophagus:
- fundoplication according to Nissen;
- Operation Belsi;
- gastrocardiopexia;
- Allison's method.
The choice of this or that method will depend on the patient himself and the presence of contraindications.
How to treat the hernia of the esophagus with folk remedies
If due to certain circumstances modern methods of treatment do not fit, then one can turn to folk medicine, using proven recipes.
The following methods are known:
- Grind and mix equal parts (one tablespoon) of leaves of mother-and-stepmother and flax seeds, peppermint grass, althea root. Three tablespoons of the collection pour a liter of cold water and insist one hour. Then put on a weak fire and simmer for five minutes in a water bath. Cool and strain, Drink 5-6 times a day for ½ cup decoction.
- Infusion of leaves of gooseberries. A half liter of boiling water will need a tablespoon of dry shredded shrub leaves. To insist it is necessary about 2 hours, then to drink up to meal on a glass half a glass, 4 times a day.
- Decoction on milk bought. Take 25 g of dried buns and poured milk (2 items). The mixture boils at minimum heat for a couple of minutes. Then it is cooled, filtered. Take the medicine several times a day for 2 tbsp. l .;
Use national recipes is after consultation with your doctor.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



