 Pulpit of the tooth - inflammation of soft tissue (pulp), which consists of nerves, blood vessels and connective tissue. Inflammatory process takes place in the pulp chamber and the root canal of the tooth.
Pulpit of the tooth - inflammation of soft tissue (pulp), which consists of nerves, blood vessels and connective tissue. Inflammatory process takes place in the pulp chamber and the root canal of the tooth.
Distinguish acute pulpitis, when the tooth reacts sharply to cold and heat or spontaneously hurts, and chronic pulpitis, in which inflammation passes without a pronounced clinical picture.
If the treatment of pulpitis is not timely and not qualitatively, then the disease develops - acute periodontitis. Such a disease is dangerous because a tooth loss can occur, inflammation of the bone tissue, bone marrow, soft tissues, lowering of immunity, penetration of blood into the blood can begin.
Causes
Why does pulpitis occur, what is it, and how to treat it? Causes of pulpitis can be:
- caries - due to the destruction of hard tooth tissues microorganisms get into the pulp chamber;
- tooth trauma- a bruise can lead to chronic inflammation of the tooth pulp;
- complication of other diseases- the infection penetrates the tooth through the root in the presence of a deep periodontal pocket or cyst.
- medical manipulation- incorrect actions of the dentist injure the pulp, which leads to its inflammation.
Infection is a primary factor in the development of pulpitis. If the pulp is exposed as a result of injury, the inflammation develops in the first hours after the injury. Pulpit tooth rarely occurs without caries, various microorganisms and their toxins. Sometimes pulpitis is diagnosed in healthy molars, which is most often explained by traumatizing the tooth.
Classification of pulpitis
Doctors distinguish 2 basic forms of pulpitis:
- Sharp- this form of pulpitis develops due to getting into the pulp of some infection. After penetration of the infection in the pulp, serous formation occurs, which after a short time becomes purulent.
- Chronic- this form of pulpitis, as a rule, develops due to untimely treatment of acute form.
For all types of acute pulpitis, spontaneous, paroxysmal pains are characteristic, which intensify at night.
- Focal acute pulpitis- it is characterized by short-term painful attacks and prolonged interobole intervals;
- Diffuse form of acute pulpitis, manifested by prolonged bouts of pain, a sharp reaction to temperature stimuli (mainly cold).
- Acute purulent. For this type of pulpitis is characterized by a purulent focus in the cavity of the tooth (abscess). The disease is accompanied by deterioration of the patient's well-being. The pain is pulsating, constant, there are no painful gaps (in contrast to focal and diffuse). Externally it looks like a deep carious lesion in a sick tooth. Below the cavity of the tooth appears a purulent discharge, the output of which can ease the pain.
Now consider the main types of chronic pulpitis:
- Fibrous pulpitis- there is a proliferation of fibrous connective tissue, can occur when the disease passes from the acute form in chronic, the pain is not always sharp, sharp, but always reminds of itself when external stimuli act on the tooth.
- Hypertrophic pulpitis- there is a hypertrophic proliferation of pulpal tissue through an open carious cavity, usually found in young age, and also in children, is characterized by bleeding gums around the affected tooth and pain when chewing.
- Gangrenous pulpitis- in the coronal pulp tissue disintegration is found, differs by strong attacks of pain, especially under the influence of hot food or hot tea, coffee.
Depending on the severity of the course and the severity of the symptoms of pulpitis, a treatment regimen is determined.
Symptoms of pulpitis
Recognize the pulpitis of the tooth is quite simple. With the development of this disease the patient, as a rule, feel the strongest toothache, which in most cases appears at night and brings a number of unpleasant sensations. At the very beginning of the disease, the patient complains of a minor aching pain, which eventually becomes stronger only.
Symptoms of acute pulpitis:
- Severe pain in the tooth, especially at night. Often the pain is paroxysmal.
- It happens that the whole jaw hurts, and without the help of a specialist it is difficult to determine which tooth causes pain.
- The appearance of a headache.
- Increased sensitivity of the tooth to touch, to hot or cold food.
- Lack of appetite.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Sometimes the body temperature rises.
Quite often there is chronic pulpitis. Symptoms of pulpitis in comparison with the acute form are much less pronounced. Predominantly chronic pulpitis manifests itself in a smell coming from the mouth, which is putrefactive, increased sensitivity to cold, hot.
In the hypertrophic form of the chronic form of this disease, a fibrous polyp appears in the carious cavity, because of which the tooth is much more susceptible to various infections. The main symptom of gangrenous pulpitis is intolerable pain that occurs when consuming hot drinks or food. Very interesting is the fact that the pain is significantly reduced when eating cold food or water.
Exacerbation of chronic pulpitis
Exacerbation of the chronic process - most often exacerbated fibrous and gangrenous pulpitis, with exacerbations of symptomatic chronic form combined with clinical manifestations of acute. The reasons may be - a prolonged stay in the cold, transferred infectious or viral diseases, mechanical or thermal injury to the tooth.
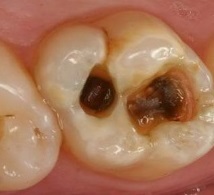
Pulpit tooth: photo
How pulpitis looks like, the photo shows the damage to the teeth in this disease:
Diagnostics
Pulpitis is diagnosed on the basis of subjective complaints and instrumental examination of the dentist. During the instrumental examination, a carious cavity with softened dentin is detected, the painful reaction of the affected tooth to a change in temperature. Percussion with pulpitis is almost always painless.
Sharp soreness is observed in a place where the carious cavity is in maximum contact with the pulp. Electroexcitability data (electroodontiagnosis) and X-ray studies make it possible to clarify the nature and depth of pulpitis.
Treatment of pulpitis
The meaning of pulpitis therapy is the limitation of inflammation and its gradual suppression. For this purpose, two main directions are used - organ-preserving treatment, in which the pulp remains and the surgical method, when the pulp is removed.
Methods of treatment of pulpitis:
- Conservative. The method allows to maintain the viability of the pulp. Apply it mainly for young people and if the disease is reversible pulp (with trauma). Treatment is the same as in caries. The main emphasis is placed on careful medication treatment of the tooth cavity. To this end, antiseptics, antibiotics, proteolytic enzymes are used. Do not use strong drugs, ether and alcohol.
- Surgical treatment of pulpitis. The way to cardinally solve the problem with inflammation of the pulp. In this case, the alveolar nerve along with the vessels is removed. The source of purulent tissue melting disappears, then pulpitis is suppressed by medications. Treatment is carried out for several visits, the intervals between which are from one day to a week, depending on the condition of the tooth.
It happens that the tooth hurts after treatment. To panic not to cost, as the pains arising after treatment of a teeth is a normal phenomenon and pass or take place for two three days. If pain does not pass during this period and affects the quality of life, you should contact a specialist.
Vital amputation
It helps to maintain the vitality of the nerves and blood vessels that feed the tooth, which ensures normal trophism of the tooth tissues and prevents the development of periapical complications. A number of authors have shown that after vital amputation, the root pulp retains its viability by producing secondary dentin.
Removal of the neurovascular bundle and its obstruction is performed under anesthesia in one visit in the absence of pronounced inflammatory phenomena passing into the periodontium. In the case of the spread of inflammation outside the root system, a medicinal substance is left in the canal (for antiseptics and for the removal of inflammation).
During treatment, it is necessary to make at least two pictures: the first - before the start of treatment, to evaluate the length and structure of the channels; second - after, to assess the quality of canal filling. The depulped tooth subsequently needs reinforcement (fixing the pin from fiberglass, titanium, silver, etc.) and (or) crowning, according to the indications.
Prevention
To prevent the development of pulpitis, the timely treatment of tooth decay on the tooth is important. This is the minimum program. As for the program maximum, it is necessary to begin prevention even from the pulpitis itself, but to implement recommendations aimed at strengthening the teeth and protecting them:
- Clean zones of gaps between teeth with flosses (threads).
- Carry out cleaning with toothbrushes and toothpastes of all accessible surfaces of the teeth every time after eating.
- Do not abuse sweet.
- To conduct professional hygiene 1 time in half a year (purification from a touch and a stone).
- To conduct remineralizing therapy and deep fluoridation of all teeth in agreement with the dentist.
The implementation of these tips will not only allow you to never feel the entire horror of pulpitis pains, but also protect your teeth from the development of caries.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



