 Aphthous stomatitis is one of many types of stomatitis, which differs from others in its characteristic feature - the presence on the mucosa of very painful ulcerative defects.
Aphthous stomatitis is one of many types of stomatitis, which differs from others in its characteristic feature - the presence on the mucosa of very painful ulcerative defects.
This form is the most unpleasant variety of stomatitis, and also gives a person a feeling of very strong discomfort.
What it is?
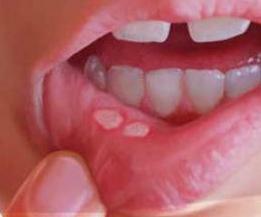
Aphthous stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa, in which erosions are formed on the mucous membrane - aphthae. Afts are painful ulceration of a round or oval shape 3-5 mm in size. But sometimes there are larger and larger irregularly shaped aphthae.
Usually, the sores are covered with a white and yellow coating and are framed by a thin red border. They can occur singly in the mouth or appear in large enough numbers. Afts can be in the sky, the tongue, the inside of the lips and cheeks. These ulcers cause burning and pain, especially worrisome when eating.
Based on the nature of lesions of the mucous tissue in medicinedistinguish four subspecies of the disease:
- necrotic;
- glandular;
- cicatrices;
- deforming.
Diagnosed aphthous stomatitis is relatively easy on admission to the dentist. To clarify the diagnosis and clarify the causative agent of infection from aft, a smear can be taken for analysis.
Causes
The reasons for the formation of aft in this disease are not exactly established. Most experts point out the relationship between the development of aphthous stomatitis and the reaction of the body's immune system. At some point, the human immune system is unable to recognize the molecules of matter that are present in the saliva. As a result, lymphocytes become active and aphthous ulcers are formed.
Causes of primary disease occurrencefoci of chronic infection can serve:
- chronic tonsillitis;
- angina;
- pharyngitis;
- diseases of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal tract).
As etiologic factors, unfavorable factors also appear:
- frequent change of belts with different climates;
- Occupations that adversely affect the mental and physical health of a person;
- stressful situations that occur regularly.
You can make a long list of typical infectious foci and adverse situations, but the principle of etiology Aphthous stomatitis remains one - the inability of the body to resist infection due to exhaustion.
Aphthous stomatitis in children
This insidious disease is often found in preschool children. In the first years of life, children actively explore the environment, pulling into their mouths are not always clean and safe items. This causes the appearance of wounds and infection, leading to the occurrence of aphthous stomatitis in children.
The first signs are similar to the common cold, but at the same time small red pimples appear in the mouth, which grow into pus-filled vesicles. Around this formation, you can see with a naked eye a red bezel.
The danger of aphthous stomatitis in children is not only the probability of the transition of the disease to a chronic form, but also the ingress of fungi and other infections into open wounds.
Symptoms
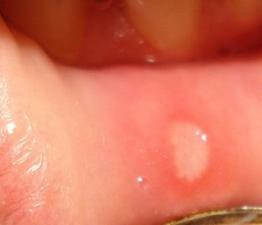 Symptoms of acute aphthous stomatitis in adults develop dramatically and unexpectedly. The patient is:
Symptoms of acute aphthous stomatitis in adults develop dramatically and unexpectedly. The patient is:
- On the mucous membrane of the lips, cheeks, gums appear small vesicles (vesicles), which burst and form small erosions, aphthae covered with a gray-white coating.
- General malaise and fever to 38-39 ° C;
- Soreness in the mouth when talking, eating.
- As the size and number of aphthas increases, soreness appears when chewing food, the ability to eat solid foods is minimized.
- The entire mucosa becomes loose, swollen, inflamed (signs of catarrhal gingivitis), a white coating appears on the tongue.
With aphthous stomatitis, it is advisable to consult a doctor who will give the patient the right treatment. Effective therapy will avoid the transition of the disease into a chronic form.
Aphthous stomatitis: photo
How does this ailment in adults and children look like, we offer detailed photos to view.
Stages of the disease
Aphthous inflammation of the oral cavity proceeds in several stages:
- In the initial stageThere are such symptoms: fever, general malaise, an increase in the cervical lymph nodes, a decrease in appetite;
- The second stage- there are reddening with the subsequent appearance in their place of ulcerative defects;
- Single small sores up to 5 mm in diameter gray with a white or yellow coating are observed in the 3 stages of the disease. Of the general symptoms, malaise and fever remain;
- The final stageaccompanied by a gradual disappearance of discomfort, burning and itching in the mouth.
From the time of detection of the first aphtha to the time of their complete healing, approximately 1.5-2.5 weeks pass. The condition of the oral cavity returns to normal: usually after ulcers there is no scarring or any other markings.
But if a person suffered from a deforming form of aphthous stomatitis, then after healing the soft tissues of the lips and palate will remain with a slightly altered structure.
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis
This form is characterized by the periodic appearance of aphthous elements throughout the long years, with periods of remission and exacerbation.
The most likely causes of the disease are: mechanical trauma mucosa, decreased immunological reactivity, chronic diseases. This type of stomatitis differs from acute by the absence of acute reaction of the body, the appearance of single aphids and recurrent course.
When examining the oral cavity, one can find aphthae at various stages of development. The exacerbation lasts 7-10 days, after which a remission occurs.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
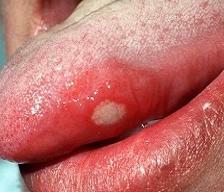 In the case of aphthous stomatitis, treatment in adults is aimed at either complete elimination of the symptoms of the disease or its stable remission. Both are achieved with the help of both general and local therapy, depending on the clinical situation.
In the case of aphthous stomatitis, treatment in adults is aimed at either complete elimination of the symptoms of the disease or its stable remission. Both are achieved with the help of both general and local therapy, depending on the clinical situation.
First of all, it is necessary to ensure the disinfection of the oral cavity. Disinfectants are a number of antiseptic solutions, which should be treated with a surface affected by ulcers. To do this, use solutions:
- hydrogen peroxide;
- furacilin;
- chlorhexidine.
In passing, the patient can take as necessary antipyretic, antiallergic and other drugs (containing novocaine, lidocaine, heparin, hydrocortisone, etc.), which can improve the general condition of the patient. The use of solutions of citral, vitamin C and P, preparations containing propolis, etc. help to speed up the healing process.
If it is determined that the cause of aphthous stomatitis is a viral infection, the doctor may prescribe antiviral drugs.
To conduct treatment for aphthous stomatitis at home should only be under the supervision of a specialist, strictly observing all of his prescriptions. Taking non-prescription potent medicines, a person should give himself a report on what such frivolous behavior is can lead not only to the severe form of recurrent chronic aphthous stomatitis, but also to even more dangerous complications.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



