 Acute purulent otitis media (otitis media purulenta acuta) - is an acute purulent inflammation of the mucosa a tympanic cavity in which all parts of the middle ear are involved in one way or another in catarrhal inflammation.
Acute purulent otitis media (otitis media purulenta acuta) - is an acute purulent inflammation of the mucosa a tympanic cavity in which all parts of the middle ear are involved in one way or another in catarrhal inflammation.
This disease with certain symptoms is similar to an ordinary cold. So when otitis is also characterized by fever and headache.
In addition, otitis often occurs simultaneously with catarrhal diseases. But there are other symptoms characteristic of otitis, which indicate the development of the inflammatory process in the ear.
Cold can be "experienced" without resorting to the help of doctors, but when signs of otitis appear, you should seek help from an otolaryngologist. Because if you do not start timely treatment of purulent otitis media in adults, this disease can lead to a noticeable decrease in hearing and even cause a development of meningitis.
Causes
The cause of the disease is a combination of factors such as lowering local and general resistance and getting the infection into the tympanum. Purulent otitis occurs as a result of inflammation of the auricle, affecting the middle ear cavity, mucous membrane and tympanic membrane.
The causes of the middle purulent otitis media:
- getting into the auricle of bacteria, viruses, fungi;
- complications of diseases of the nose, nasal sinuses, nasopharynx;
- severe ear contusion;
- sepsis;
- consequences of meningitis, measles, tuberculosis;
- supercooling.
The most frequent way of penetrating the infection is tubogenic - through the auditory tube. Less often the infection enters the middle ear through the damaged eardrum when it is injured or through the wound of the mastoid process. In this case, they speak of a traumatic average otitis.
Symptoms of purulent otitis
There are several signs that help determine if you have acute purulent otitis, and not another hearing disorder. But the main symptoms in various diseases of the field of otolaryngology usually coincide.
Traditional symptoms of otitis media:
- pulsating pain in the ear;
- pain behind the ear;
- heat;
- chills;
- extraneous noise in the ear;
- decreased hearing.
These signs are characteristic for the initial stage of the disease, when the inflammation becomes the cause of extensive suppuration. Usually this process lasts 2-3 days. Further, acute purulent otitis media of the middle ear passes into the phase of perforated damage to the tympanic membrane, as a result of which pus through the formed the opening in the membrane flows out of the ear cavity outwards, and the patient achieves a significant relief, pains decrease.
The third stage is final, the body fights the infection, the inflammation gradually decreases, pus ceases to stand out, the tympanic membrane restores integrity.
Signs of otitis in the child
Each stage of the development of the disease is characterized by certain symptoms.
Symptomatics of purulent otitis in a child of the 1st stage:
- earache;
- heat;
- hearing loss.
Symptoms of the 2nd stage:
- the temperature decreases;
- the pain subsides;
- hearing loss continues;
- the purulent discharge begins to go from the ear.
Symptoms of the third stage:
- the temperature decreases;
- the pain disappears;
- hearing is restored;
- the allocation ceases;
- Perforation of the tympanic membrane is cicatrized.
This disease requires early diagnosis and administration of antibiotic therapy.
Chronic purulent otitis
This inflammation of the middle ear, which is characterized by a recurring course of pus from the ear, resistant Perforation of the tympanic membrane and progressive hearing loss (hearing loss can reach 10-50%).
This otitis manifests itself in the following clinical picture:
- Persistent purulent discharge from the ear, having putrefactive odor;
- Noise in the affected ear;
- Deterioration of hearing.
It develops with untimely begun or inadequate treatment of acute otitis media. It can be a complication of chronic rhinitis, sinusitis, etc. or a consequence of a traumatic rupture of the tympanic membrane. Chronic otitis media affects 0.8-1% of the population. In more than 50% of cases, the disease begins to develop in childhood.
Chronic suppurative otitis media without bone destruction and complications can be treated by medicinal methods under out-patient supervision of an otolaryngologist.
Complications
The lack of appropriate treatment leads to irreparable damage to health. The consequences of otitis in adults are the result of a structural transition of further inflammation to the temporal bone or inside the skull.
Complications may include:
- violation of the integrity of the tympanic membrane;
- mastoiditis - inflammation of cells in the bone;
- paralysis of the facial nerve.
- meningitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain;
- encephalitis - an inflammation of the brain;
- hydrocephalus - accumulation of fluid in the cerebral cortex.
To avoid these unpleasant diseases, you need to know how to treat purulent otitis in adults.
Treatment scheme for acute purulent otitis media of the middle ear
In adults treatment of purulent otitis media of the middle ear includes the appointment of such procedures and drugs:
- antibiotics;
- anesthetics, antipyretic drugs;
- vasoconstrictor ear drops;
- heat compresses (before the appearance of pus);
- Physiotherapy (UHF, electrophoresis);
- antihistamines;
- surgical cleaning of the ear passage from the pus.
It should be borne in mind that after the appearance of purulent discharge, in no case can warming procedures be done. In the chronic course of the disease, a puncture or dissection of the tympanic membrane may be required.
How to treat purulent otitis in adults
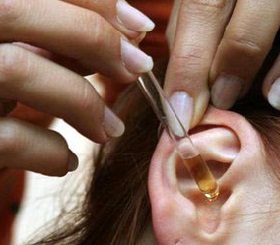 Diagnosis usually presents no difficulties. The diagnosis is based on complaints and the results of otoscopy (visual inspection of the ear canal with a special instrument). If a destructive process is suspected in bone tissue, a radiography of the temporal bone is performed.
Diagnosis usually presents no difficulties. The diagnosis is based on complaints and the results of otoscopy (visual inspection of the ear canal with a special instrument). If a destructive process is suspected in bone tissue, a radiography of the temporal bone is performed.
Purulent otitis in adults requires treatment as an outpatient, at high temperatures in combination with a fever it is recommended that bed rest is observed. Hospitalization is required if a mastoid process is suspected.
To reduce pain in the initial stages of the disease apply:
- paracetamol (4 times a day for one tablet);
- ear drops otypax (twice a day for 4 drops);
- a tampon on Цитовичу (gauze tampon, пропиптаный a solution of boric acid and glycerin for three hours is inserted in an aural passage).
For the removal of puffiness in the tissues of the auditory tube is appointed:
- nazivin;
- tizine;
- santorine;
- naphthyzine.
Antibiotics used for purulent otitis:
- amoxicillin;
- augmentin;
- cefuroxime.
If after several days of treatment no improvement occurs or the phenomena increase, surgical treatment, it is immediately indicated when signs of irritation of the inner ear or meninges appear. After paracentesis or self-perforation, it is necessary to provide an outflow of pus from the middle ear: drain the auditory pass sterile gauze swabs 2-3 times a day, or wash the ear with a warm solution of boric acid.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



