 A sinusitis is an inflammation that affects one or more of the paranasal sinuses. It can develop as an independent disease, and as a complication against the background of various infectious diseases.Acute sinusitis refers to one of the most common pathologies that the ENT doctor encounters in his work.
A sinusitis is an inflammation that affects one or more of the paranasal sinuses. It can develop as an independent disease, and as a complication against the background of various infectious diseases.Acute sinusitis refers to one of the most common pathologies that the ENT doctor encounters in his work.
Sinusitis is divided into chronic and acute, this division is caused by different duration of attacks on the body. Acute sinusitis - treatment takes up to 2 months, and after receding, but chronic - can be cured for a long time, but with the slightest cold come back again. Chronic form - the problem of people with weakened immunity, immunodeficiency, and therefore the question of how to cure sinusitis is very, very acute.
In this article, we will look at the manifestations of sinusitis in adults, especially the first symptoms and effective ways of treating at home.
What it is?
Why does sinusitis occur, and what is it? Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane, which is localized in one or several paranasal sinuses simultaneously. One of the main reasons that causes the development of sinusitis is poorly cured or neglected rhinitis. In addition, the trigger for the development of sinusitis can be acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI). The disease, the development of which occurs against the background of respiratory infections of the upper respiratory tract, is usually called community-acquired forms.
Depending on its location,Sinusitis can be of several kinds:
- sinusitis - inflammation of the maxillary sinus sinus, which is a complication in the flu, acute cold, scarlet fever, measles and many other infectious diseases.
- frontal - inflammation of the frontal sinus, which proceeds much heavier than other types of sinusitis.
- etmoiditis - manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the cells of the latticed maze and is the most common form of sinusitis.
- sphenoiditis - an inflammation of the sphenoid sinus, which is rare enough.
The first sign of exacerbation of sinusitis is a prolonged runny nose. Thus it is necessary to pay attention to allocation from a nose. If they turn yellowish greenish, this indicates the bacterial nature of the inflammation. In such a situation, bacteria can enter the maxillary sinuses at any time and the sinusitis begins.
Also, sinusitis is unilateral or bilateral, with the defeat of all the paranasal sinuses from one or both sides. Acute antritis often occurs during an acute cold, flu, measles, scarlet fever and other infectious diseases, as well as due to root disease of the four posterior upper teeth.

Symptoms of sinusitis
The signs of sinusitis in adults depend on which sinus is inflamed. In general, the clinical picture of all sinusitis consists of several permanent and variable symptoms:
- difficulty nasal breathing, nasal in the voice;
- abundant discharge from the nose (mucous or purulent);
- unpleasant sensations in the nose, near-nasal area or above the eye;
- fever subfebrile or febrile;
- decreased sense of smell;
- headache.
Depending on the type of sinusitis, the symptoms in adults will differ:
- Sinusitis. The disease begins acutely. The patient's body temperature rises to 38-39C, signs of general intoxication are expressed, chills are possible. In some cases, the patient's body temperature may be normal or subfebrile. Patients with sinusitis are concerned about pain in the area of the affected maxillary sinus, zygomatic bone, forehead and root of the nose. Pain is worse on palpation. Possible irradiation in the temple or the corresponding half of the face. Some patients develop diffuse headaches of varying intensity. Nasal breathing on the side of the lesion is disrupted. In bilateral sinusitis, nasal congestion forces the patient to breathe through the mouth. Sometimes, due to blockage of the lacrimal canal, lacrimation develops. Discharge from the nose first serous, liquid, then become viscous, cloudy, greenish.
- Frontite. With an acute front, the patient is disturbed by sharp pains in the forehead area, which are aggravated by pressing or tapping on the brow, a headache of another localization, difficulty in nasal breathing, abundant discharge from the corresponding half of the nose (initially serous, then serous-purulent), pain in the eye, lacrimation, photophobia. The body temperature rises to the level of fibril (up to 39 ° C), but can be subfebrile. The clinical picture of the chronic frontitis is less pronounced than that of the acute one. Headache is usually aching or oppressive, more often localized in the area of the affected frontal sinus. Discharge from the nose is especially plentiful in the mornings, have a purulent character, often with an unpleasant odor.
- Etmoiditis. As a rule, the inflammatory process in the anterior parts of the latticed labyrinth develops simultaneously with the frontitis or sinusitis. Inflammation of the posterior sections of the trellis labyrinth is often accompanied by sphenoiditis. A patient with ethmoiditis complains of headaches, pressing pain in the nose and nose. In children, pain is often accompanied by conjunctival hyperemia, edema of the inner parts of the lower and upper eyelid. Some patients develop neurological pain. Body temperature usually rises. Separated in the first days of the disease serous, then becomes purulent. The sense of smell is sharply reduced, nasal breathing is difficult. With a violent flow of sinusitis, inflammation can spread to the orbit, causing protrusion of the eyeball and pronounced edema of the eyelids.
- Sphenoiditis. The main symptoms of chronic sphenoiditis are pain in the parietal (sometimes occipital) area, a sense of unpleasant odor. An important clinical sign of chronic sphenoiditis is the swelling of the wedge-shaped sinus along the anterior wall of the nasopharynx and the posterior pharyngeal wall. The process can spread into the cavity of the skull, other paranasal sinuses, into the orbit. A sphenoiditis can give a complication from the organs of vision (retrobulbar neuritis).
With acute sinusitis in adults, the temperature rises, the head begins to ache, it becomes difficult to breathe, since the nose is clogged mucus (periodically zalozhennost passes from one nostril to another), allocation from a nose thus go purulent, sometimes with blood. In the place where the inflamed sinus is located, there is pain, and also there may be swelling of the soft tissues of the face. At night, there are bouts of dry cough. The sense of sinusitis is reduced or absent altogether.
Symptoms of sinusitis in a chronic stage may include all signs of the disease or only some of them. Signs of the disease do not pass even after two weeks. What is sinusitis with chronic inflammation is best known to patients with asthma, seasonal or food allergies. Treatment in this case should be accompanied by the exclusion of allergens and products that cause the manifestation of rhinitis.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of sinusitis is based on patient complaints, clinical symptoms, laboratory and instrumental studies. To confirm the final diagnosis, a general blood test is used (indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body), radiography or computed tomography.
How to treat sinusitis?
If symptoms of sinusitis occur, treatment in adults involves the use of special drugs, they effectively suppress the pathogen and eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
- To reduce the temperature prescribed antipyretic drugs: paracetamol, nurofen.
- In the presence of allergies, prescribe the administration of antihistamines: tavegil, claritin.
- To eliminate edema of the nasal mucosa, vasoconstrictive drugs or aerosols are prescribed.
- If you suspect a sinusitis, antibiotics are prescribed.
- In rhinitis in children, nasal sprays are prescribed: triamcinolone, mometasone furoate, fluticasone, beclomethasone.
The main goals of sinusitis treatment:
- Eradication (complete destruction) of the causative agent in the event that the inflammation is caused by an infectious agent;
- Elimination of other provoking factors, for example, deformations of the structures of the nose;
- Cessation of symptoms of sinusitis;
- Restoring normal sinus drainage;
- Prevention of complications;
- Prevention of the transition of acute sinusitis to chronic form.
In chronic sinusitis, physiotherapy (magnetotherapy, heating) and sanatorium treatment are additionally used. Surgical treatment consists in the puncture (puncture) of the sinus, if there is pus in it. Also, in chronic sinusitis, plasty of the maxillary sinus is performed to improve the outflow (drainage) of its contents.
Antibiotics for sinusitis in adults
At home, antibiotic treatment for acute and chronic sinusitis in adults is effective. The decision to prescribe antibacterial drugs is taken only by a doctor. The course of treatment is usually 10-14 days.
Antibiotics for sinusitis is indicated in those cases when the bacterial nature of the disease is proved. A doctor may suspect purulent sinusitis if the purulent purulent discharge from the nasal passages, headache and pain in the projection of the sinuses does not decrease after a week on the background of the therapy. Antibiotic therapy can be started earlier in the course of the disease, regardless of its duration.
In the mild form of sinusitis, antibiotics from the group of macrolides and cephalosporins give priority. In case of severe disease, penicillins of the second and third generation or cephalosporins are prescribed. In the case of chronic sinusitis, the use of protected penicillins is preferred.
For treatment of acute and chronic sinusitis in recent years, a three-day course of azithromycin is often recommended, which is especially effective in mycoplasma sinusitis. This type of disease of the paranasal sinuses is often observed in children, while it does not respond to treatment with other antibiotics.
In acute sinusitis, in some cases, local effective antibiotics (bioparox) are used.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures include:
- Washing of the sinuses by the "cuckoo" method;
- Puncture and further drainage of cavities with antiseptic agents;
- Electrophoresis;
- Phonophoresis with ointments with antiseptic effect;
- Inhalation with solutions of antibiotics, herbal decoctions;
- UHF sinus;
- Laser treatment by the endonasal method;
- The use of quantum rays.
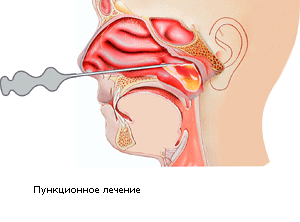
Sinus puncture
In the later stages of sinusitis, classical nasal rinses in domestic or stationary conditions (the so-called "cuckoo") do not help to withdraw from cavities of sinuses stagnant pus: in this case, appoints a very unpleasant, painful, but effective procedure, called a puncture and puncture.
Here the doctor punches through the nose soft cartilaginous tissue with a special surgical spatula? Then he enters the catheter, connects a syringe with the disinfectant solution to the system and injects the liquid under pressure, thus, through the nose, washing out the pus that accumulates in the cavity. If necessary, the catheter is left in the cavity and the washout procedure is repeated several times.
Prevention
The first thing you should pay attention to in the prevention of sinusitis is the timely treatment of colds, colds and flu. Often it is these diseases that become the triggers of sinusitis. To treat a runny nose or cough is necessary at home. Preliminary consultation with a doctor on the choice of effective funds.
Besides,adhere to the following recommendations:
- On a mandatory basis, take preventive dental checkup: infections with pulpitis, stomatitis, etc. can very quickly overcome the bone barrier and cause inflammation of the paranasal sinuses;
- Do not self-medicate: with a cold, fever and general malaise, which does not go away within 2-3 days, consult a doctor;
- Systematic hardening procedures will significantly increase immunity, which will reduce the frequency of viral diseases and, accordingly, eliminate the risk of sinusitis.
If you suspect of this disease, do not test fate and engage in self-medication at home. You should immediately seek qualified help. Efficient and rapid recovery is possible with proper treatment.

How to choose probiotics for the intestine: a list of drugs.

Effective and inexpensive cough syrups for children and adults.

Modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Review of tablets from the increased pressure of the new generation.
 Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.
Antiviral drugs are inexpensive and effective.



